

First-Degree AV Block
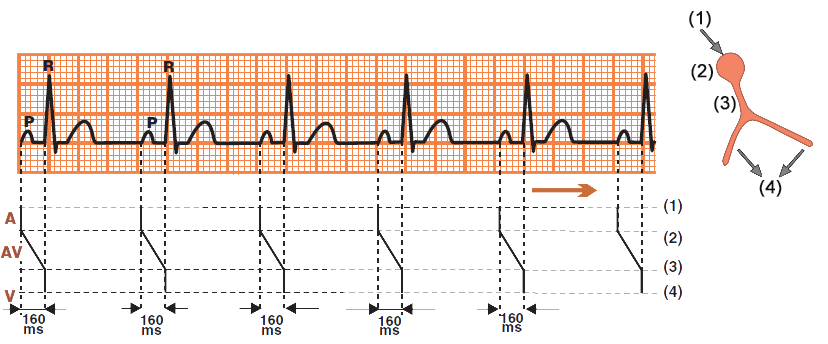
Sinus Rhythm

First-Degree AV Block

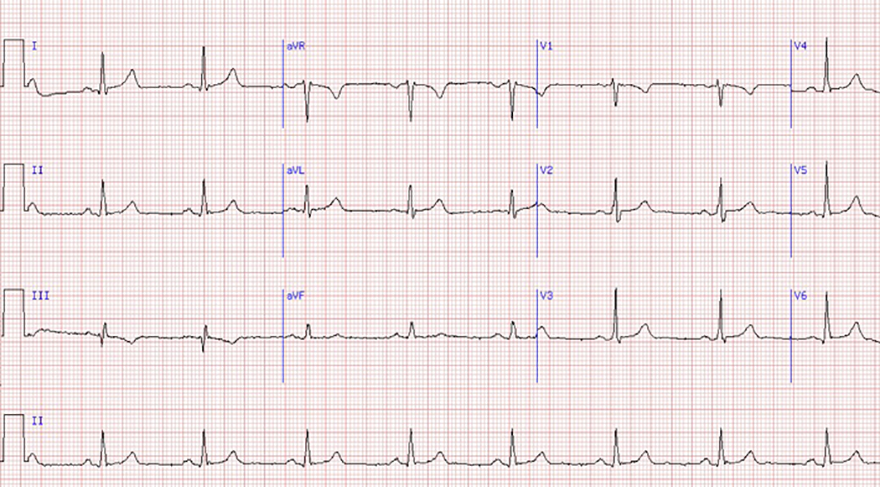
Sinus Rhythm

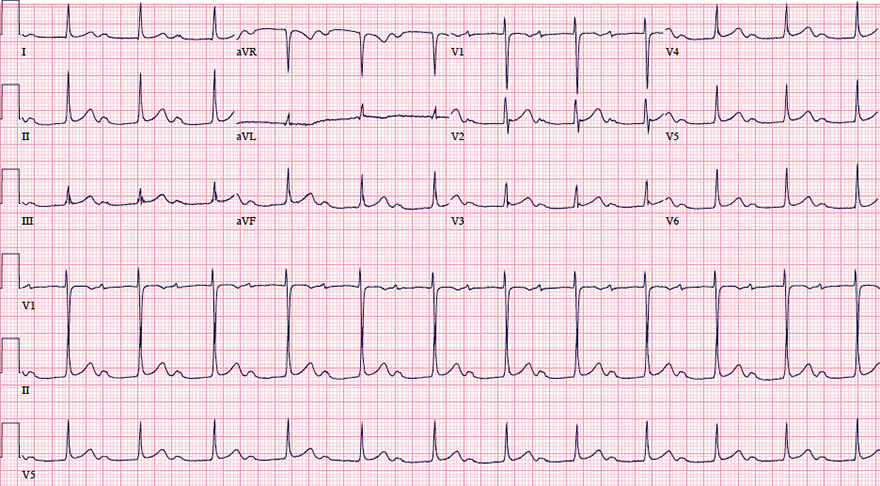
First-Degree AV Block

First-Degree AV Block

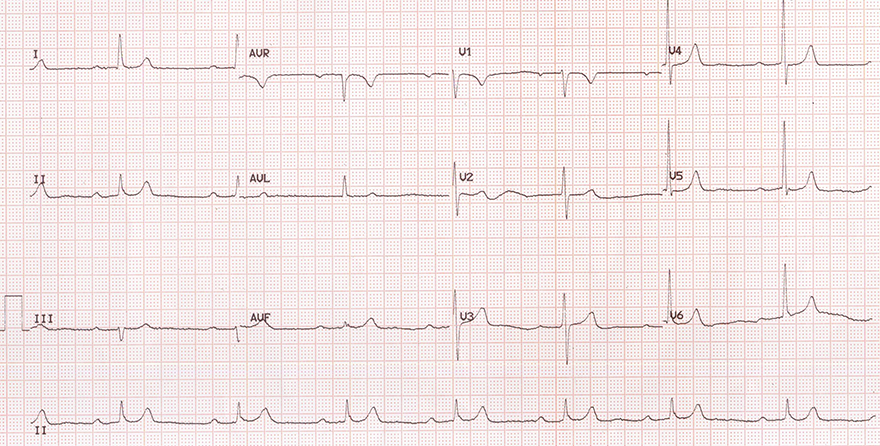
First-Degree AV Block and Sinus Bradycardia


First-Degree AV Block and Sinus Bradycardia
Sources
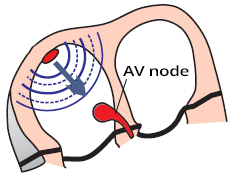
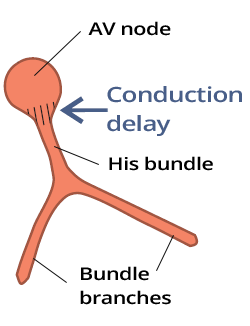
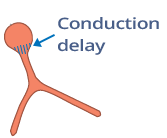
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
|

|
PQ Interval
|

|
First-Degree AV Block
|

|

First-Degree AV Block

Sinus Rhythm

First-Degree AV Block

|
Sinus Rhythm
|

|

|
First-Degree AV Block
|

|

|
First-Degree AV Block
|

|

|
First-Degree AV Block and Sinus Bradycardia
|

|

|
First-Degree AV Block and Sinus Bradycardia
|

|
Sources