
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
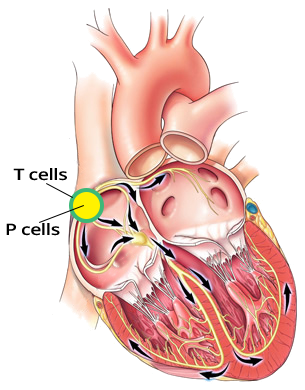
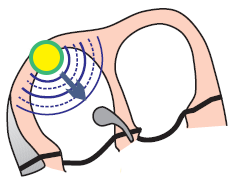

Sinus Rhythm (1st Degree SA Block?)
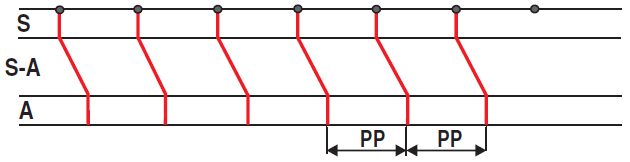
Sinus Rhythm
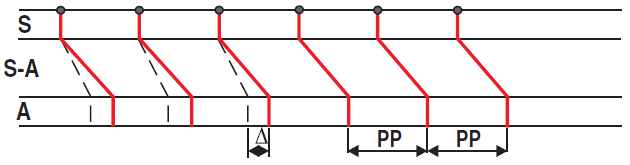
First-Degree SA Block

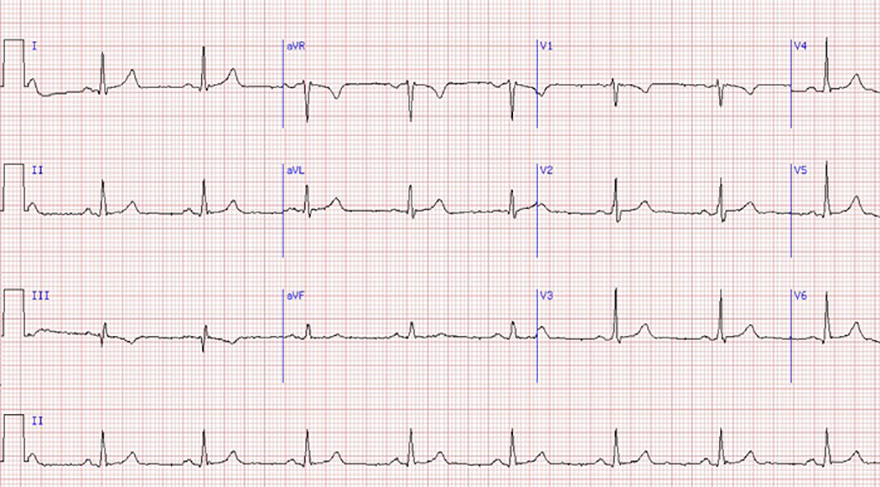
Sinus Rhythm
Sources
Sinoatrial Node (P and T Cells)
|

|
1st Degree SA Block
|

|

Sinus Rhythm (1st Degree SA Block?)

Sinus Rhythm

First-Degree SA Block

|
Sinus Rhythm
|

|
Sources