Home /
Third Degree AV Block
AV block 3rd degree, Complete heart block
Atrioventricular (AV) Node
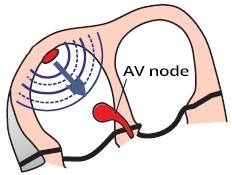
- In sinus rhythm, impulses are generated regularly (approx. 60/min) in the SA node
- Each impulse spreads through the atria (P wave) to the AV node
- In the AV node, the impulse is delayed by approximately 0.1s
- During this time, the atria pump blood into the ventricles
- Then the impulse continues to the ventricles (QRS complex)
PQ Interval
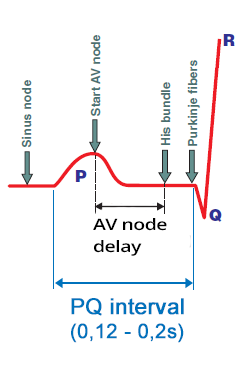
- Impulse originates in SA node
- When it travels to the atrial myocardium, it starts generating P wave
- Simultaneously, it spreads through the conduction system towards the AV node
- The impulse in the conduction system does not create a curve
- The impulse enters the AV node
- The impulse spreads from the SA node
- At the time of atrial activation (peak of the P wave)
- It arrives through the conduction system to the AV node
- Delayed (decremental) conduction in the AV node
- The impulse “lingers” in the AV node for about 0.1s (no curve is formed)
- Then it passes to the His bundle (no curve is formed)
- Activation of the ventricular septum
- From the His bundle, the impulse through Purkinje fibers
- Begins to activate the ventricular septal myocardium
- Begins to form a Q wave
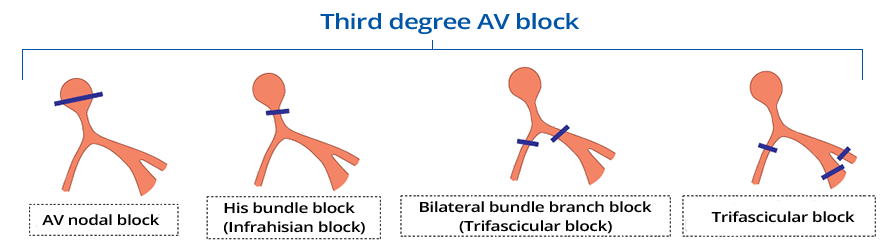
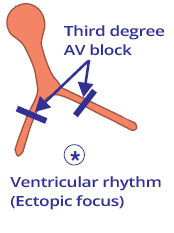
AV Block III (Complete AV Block)
- Conduction system is blocked "cut" at the level of the AV junction
- Atria and ventricles are electrically isolated from each other
- No impulse from the atria (P wave) reaches the ventricles
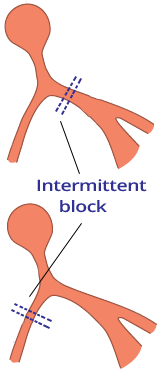
- The conduction system can be blocked in 4 locations:
- Sometimes AV Block III is classified as:
- Suprahisian (block is above the His bundle)
- Infrahisian (block is below the His bundle)
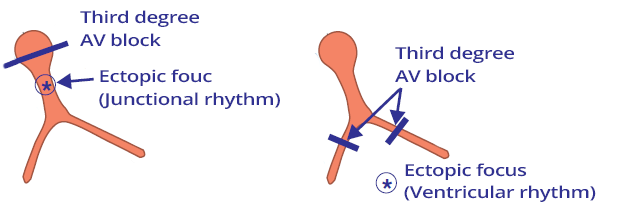
Backup Rhythm
- In AV block III, the ventricles should stop (absence of QRS complexes)
- Because impulses from the atria (P waves) are blocked at the AV junction
- On the ECG, we would see only P waves without QRS complexes (asystole)
- Protective mechanism is the activation of an ectopic focus below the block
- The ectopic focus starts generating impulses and results in:
ECG and AV Block III Degree
- P waves are independent of QRS complexes (AV dissociation)
- PQ interval changes
- SA node generates impulses (P waves) at its own rate, but all P waves are blocked at the AV junction
- Ectopic focus below the AV block generates impulses (QRS complexes) at its own rate
- Below the AV block, a backup rhythm is activated:
- Differential Diagnosis:
- High-grade AV block
- It is an intermittent block of P waves (the AV junction "occasionally" allows impulses to pass to the ventricles)
- PQ interval is constant
AV Block III Degree (QRS < 0.12s)

AV Block III Degree and Junctional Rhythm
- Laddergram shows the spread of impulses through the conduction system
- A - Atria, AV - AV junction, V - Ventricles
- SA node generates impulses regularly
- Heart rate of P waves (SA node) is 75/min
- All impulses from the SA node (P waves) are blocked suprahisally
- Below the AV block in the AV junction, an ectopic focus has been activated, leading to a junctional rhythm
- Frequency: 55/min
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s), as impulses spread to the ventricles through the conduction system
- AV dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- PQ interval changes
AV Block III Degree (QRS > 0.12s)
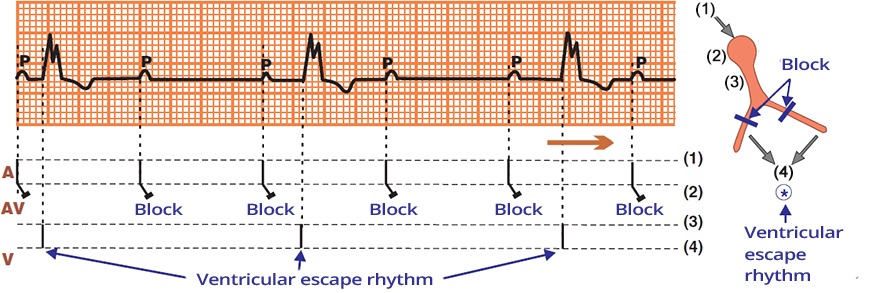
AV Block III Degree and Ventricular Rhythm
- SA node generates impulses regularly
- Heart rate of P waves (SA node) is 75/min
- All impulses from the SA node (P waves) are blocked infrahisally
- Below the AV block in the ventricles, an ectopic focus has been activated, leading to a ventricular rhythm
- Frequency: 35/min
- Broad QRS complexes (> 0.12s), as impulses activate the ventricles through the myocardium, not through the conduction system
- AV dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- PQ interval changes
AV Block II Degree
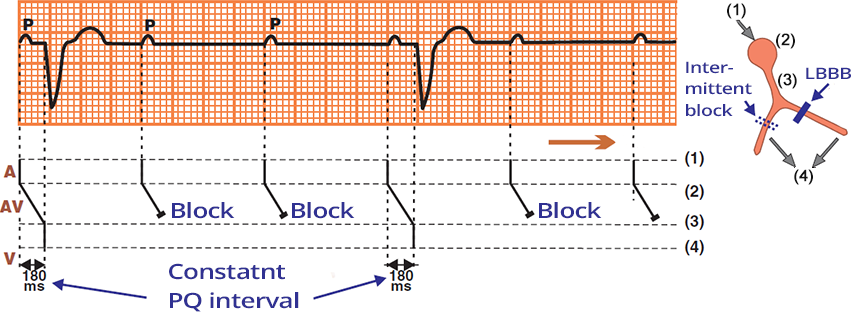
AV Block II Degree - Mobitz II (High Degree)
- Mobitz II means that the AV junction area intermittently conducts impulses to the ventricles
- The patient has a pre-existing left bundle branch block
- There is intermittent block of the right bundle branch
- Every 3rd impulse from the SA node passes through the right bundle branch and activates the ventricles
- Ventricular conduction is 3:1
- No AV dissociation, as there is a certain relationship between the P waves and QRS complexes
- PQ interval is the same at 0.18s, indicating that the atria and ventricles are electrically connected
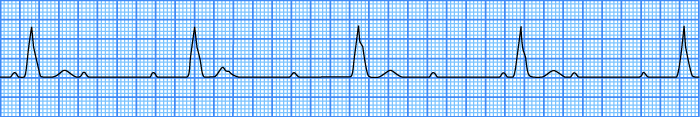
3rd Degree AV Block


3rd Degree AV Block
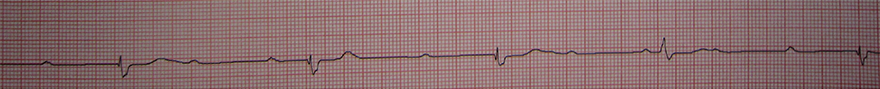
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial frequency (P waves): 60/min.
- Ventricular frequency (QRS complexes): 27/min.
- PQ interval varies
- This is an infra-Hisian 3rd Degree AV Block

3rd Degree AV Block
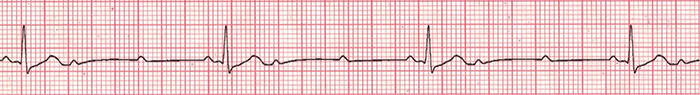
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial frequency (P waves): 100/min.
- Ventricular frequency (QRS complexes): 27/min.
- PQ interval varies
- This is a supra-Hisian 3rd Degree AV Block

3rd Degree AV Block
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial frequency (P waves): 75/min.
- Ventricular frequency (QRS complexes): 27/min.
- PQ interval varies
- This is an infra-Hisian 3rd Degree AV Block
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s), as a ventricular ectopic focus is activated

2nd Degree AV Block - Mobitz II (3:1)
- AV Dissociation is not present because there is a consistent relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
- PQ interval is constant at 0.18s, indicating that the atria and ventricles are electrically connected
- Conduction to the ventricles is 3:1
- Every 3rd P wave is conducted to the ventricles, resulting in a QRS complex
- Impulses (P waves) are intermittently blocked in the His bundle
- This is an 2nd Degree AV Block (High-Grade) - Mobitz II (3:1)


2nd Degree AV Block - Mobitz II (4:1)
- AV Dissociation is not present because there is a consistent relationship between P waves and QRS complexes
- PQ interval is constant at 0.2s, indicating that the atria and ventricles are electrically connected
- Conduction to the ventricles is 4:1
- Every 4th P wave is conducted to the ventricles, resulting in a QRS complex
- Impulses (P waves) are intermittently blocked in the His bundle
- This is an 2nd Degree AV Block (High-Grade) - Mobitz II (4:1)

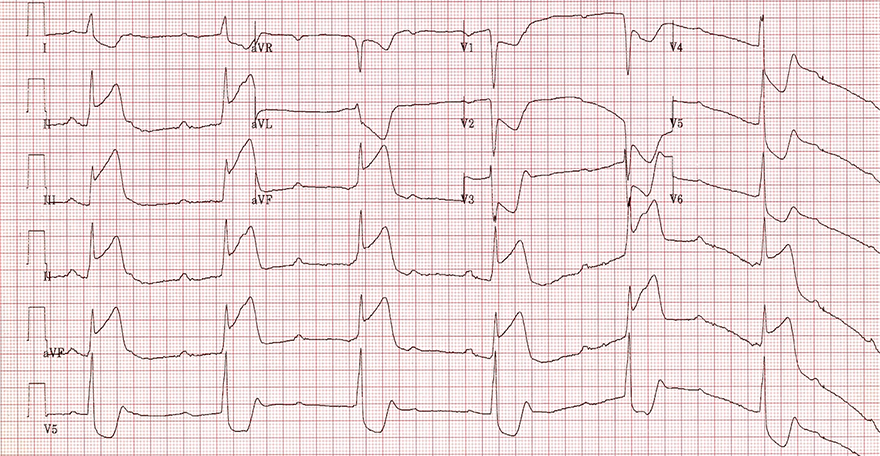
AV Block III Degree and Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction
- STEMI Inferior Wall
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial Frequency (P waves): 85/min.
- Ventricular Frequency (QRS complexes): 38/min.
- PQ Interval is changing
- This is a suprahisian AV Block III Degree

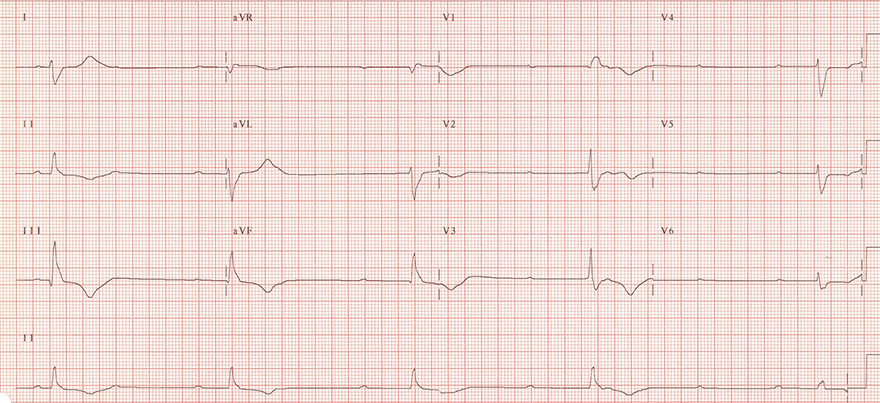
AV Block III Degree
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial Frequency (P waves): 60/min.
- Ventricular Frequency (QRS complexes): 27/min.
- PQ Interval is changing
- This is an Infranodal AV Block III Degree

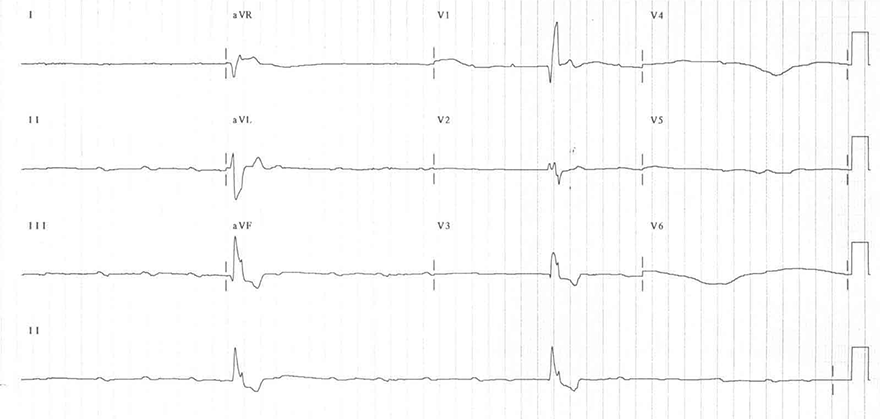
AV Block III Degree
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial Frequency (P waves): 100/min.
- Ventricular Frequency (QRS complexes): 15/min.
- PQ Interval is changing
- This is an Infranodal AV Block III Degree
- With a ventricular frequency of 15/min., the ventricles are unable to ensure adequate circulation
- Patient experiences syncope - loss of consciousness
- Patient requires urgent pacing

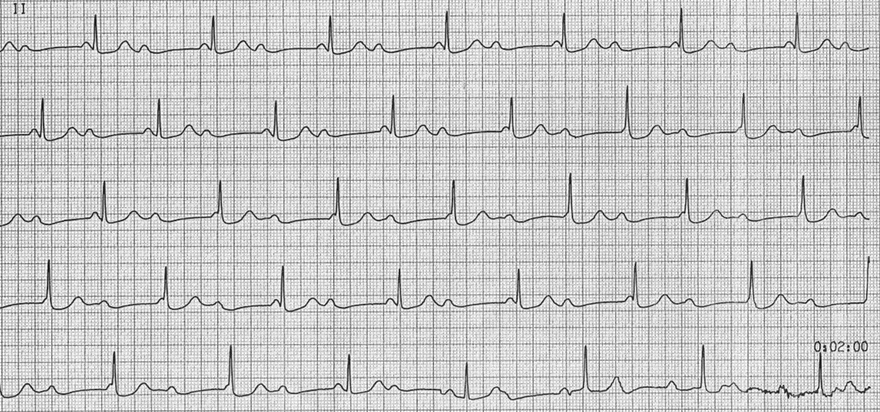
AV Block III Degree
- On the ECG, we only see a continuous lead II
- Atrial Frequency (P waves): 85/min.
- Ventricular Frequency (QRS complexes): 42/min.
- Atrial frequency is approximately 2x higher than the ventricular frequency
- Consider AV Block II Degree with 2:1 Conduction
- Shortened PQ interval (<0.12s) could indicate:
- However, the P wave gradually merges into the QRS complex
- This is a Suprahisian AV Block III Degree
- This represents Isorhythmic AV Dissociation
- Atria (P waves) and ventricles (QRS complexes) are electrically isolated
- However, their frequencies are such that they mimic mutual electrical connection (1st line)
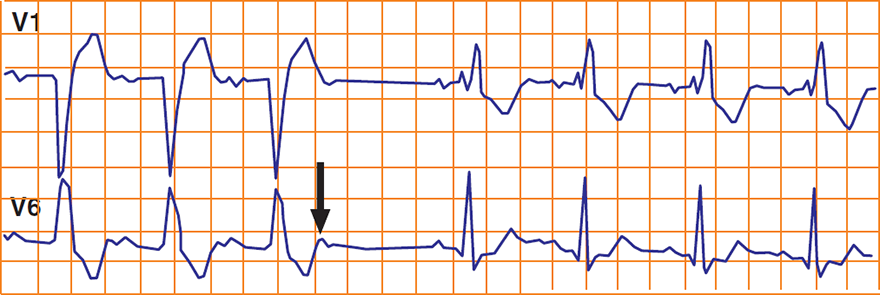
Alternating Tawara's Bundle Block
- At the beginning of the ECG there is a left Tawara's bundle block (LBBB)
- After a atrial extrasystole
- This indicates severe damage to the conduction system
- Both Tawara's bundles are damaged
- PQ interval in LBBB is longer than PQ interval in RBBB
- This indicates that the right Tawara's bundle is more damaged
- Because it takes longer to activate the ventricles
- Such a patient may develop
- AV Block II Degree - Mobitz II
- AV Block III Degree
- A patient with such an ECG is indicated for pacemaker insertion

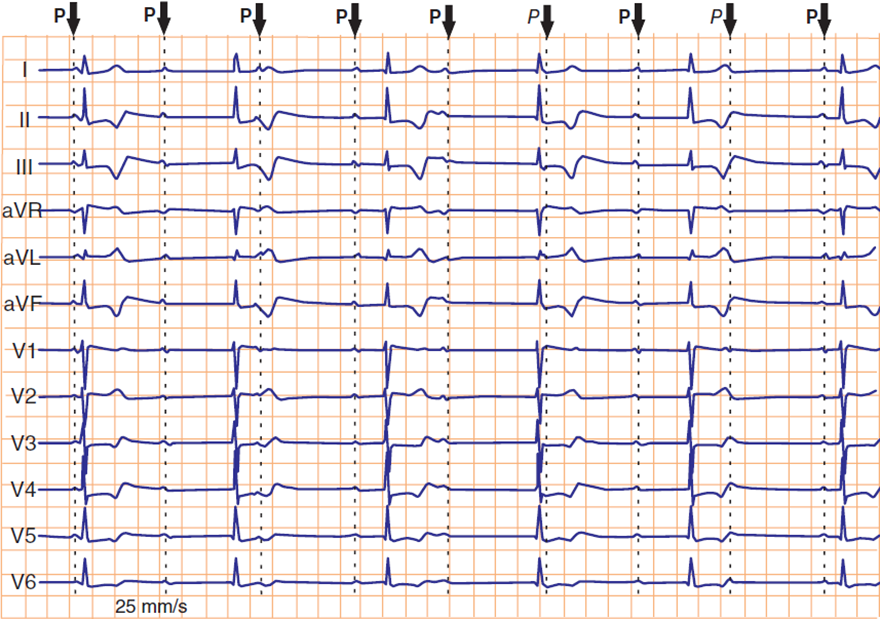
AV Block of the Third Degree
- AV Dissociation - P waves are independent of QRS complexes
- Atrial frequency (P waves): 70/min.
- Ventricular frequency (QRS complexes): 45/min.
- PQ interval is variable
- It is a supraventricular AV block of the third degree
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers































































