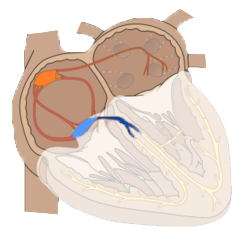

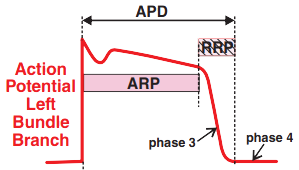
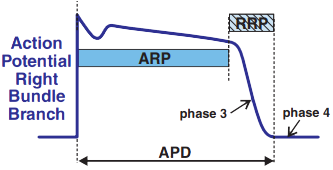
ECG (lead V6) and Action Potential
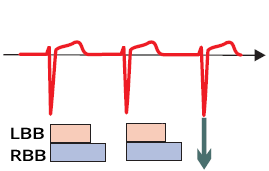
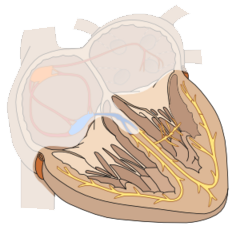
Physiological Conduction
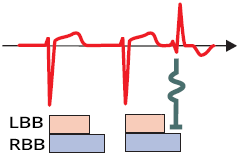
Aberrant Conduction

Aberrant Conduction and Sinus Rhythm
Sources
Supraventricular Impulse
|

|
Ventricular Conduction and QRS Complex
|

|

ECG (lead V6) and Action Potential
|


|

Physiological Conduction
|

Aberrant Conduction
|

Aberrant Conduction and Sinus Rhythm
Sources