
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Retrograde invasion of bundle branch, Retrograde concealed conduction


Block in Phase 3
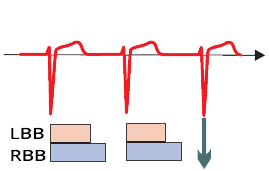
Physiological Conduction
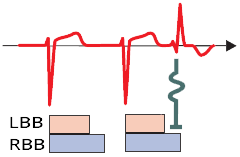
Aberrant Conduction
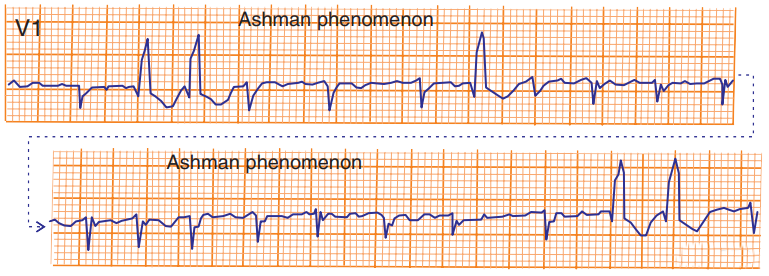
Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation

Mechanism of Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block
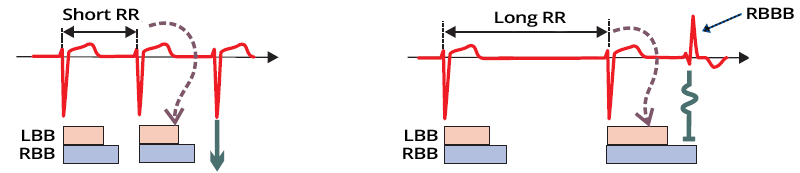
Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block and Ashman's Phenomenon
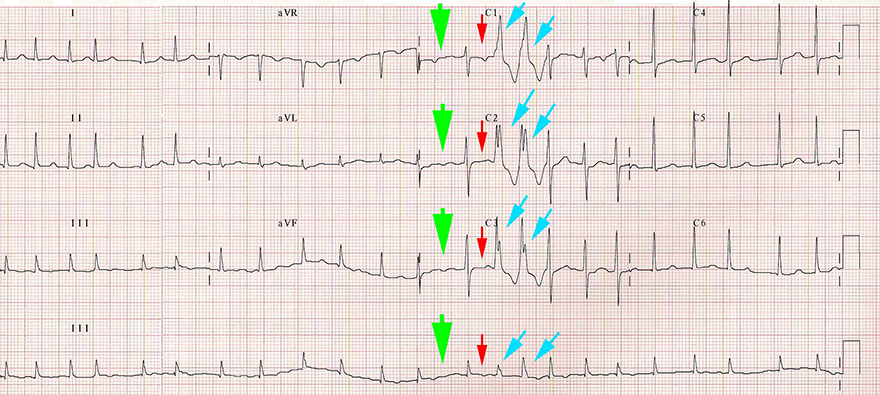
Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block and Ashman Phenomenon
Sources
Home /
Retrograde invasion of bundle branch, Retrograde concealed conduction

|

|
Block in Phase 3

Physiological Conduction
|

Aberrant Conduction
|

Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation

Mechanism of Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block

Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block and Ashman's Phenomenon

Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block and Ashman Phenomenon
Sources