
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |


Junctional Rhythm


Accelerated Junctional Rhythm

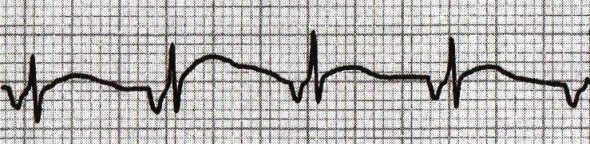
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm

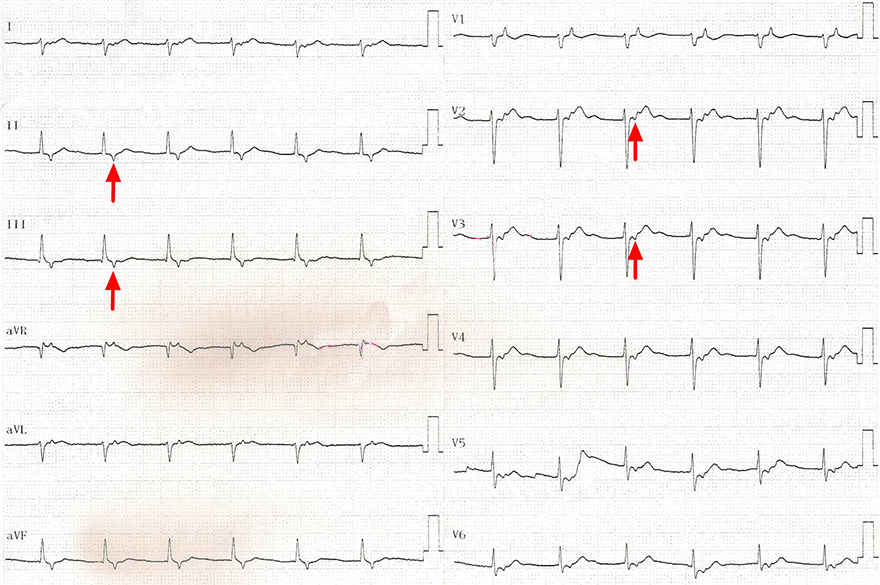
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm


Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
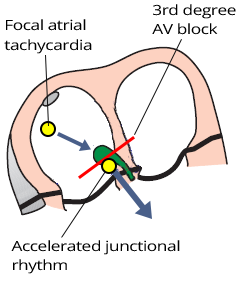
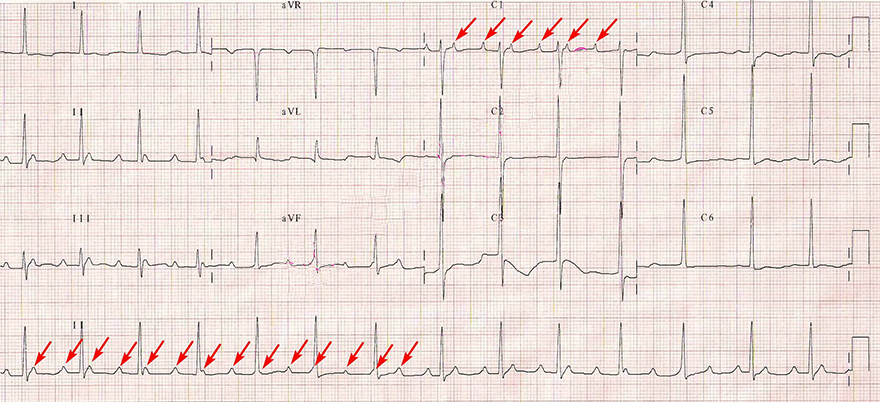
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm and 3rd Degree AV Block
Sources
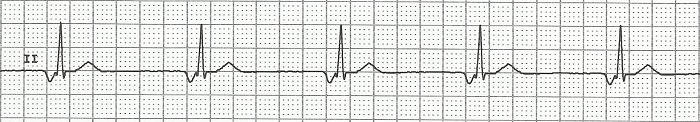
Junctional Rhythm
|

|
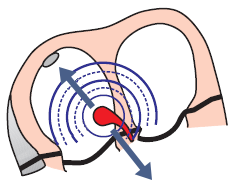
ECG and Junctional Rhythm
|

|
 Upper Junctional Rhythm
|
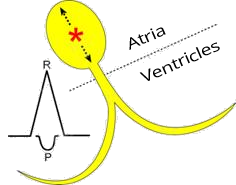
 Middle Junctional Rhythm
|
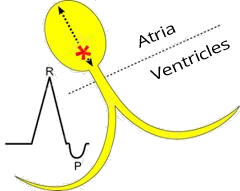
 Lower Junctional Rhythm
|

Junctional Rhythm

|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm |

|

|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
|

|

|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
|

|

|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm
|

|

|
Accelerated Junctional Rhythm and 3rd Degree AV Block
|

|
Sources