Home /
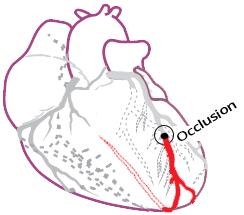
Anterior STEMI myocardial infarction and localisation occlusion (culprit artery) of the left anterior descending artery (LAD)




Classification of STEMI by Stage


| STEMI | ST elevations | Reciprocal ST depressions |
| Septal | V1-V2 | None |
| Anterior | V2-V5 | None |
| Anteroseptal | V1-V4 | None |
| Anterolateral | V3-V6, I, aVL | III, aVF |
| Extensive Anterior | V1-V6, I, aVL | III, aVF |
| Anteroinferior (Wraparound LAD) |
(V2-V4) + (II, III, aVF) | None |



Acute Anterior STEMI


Old Anterior Myocardial Infarction

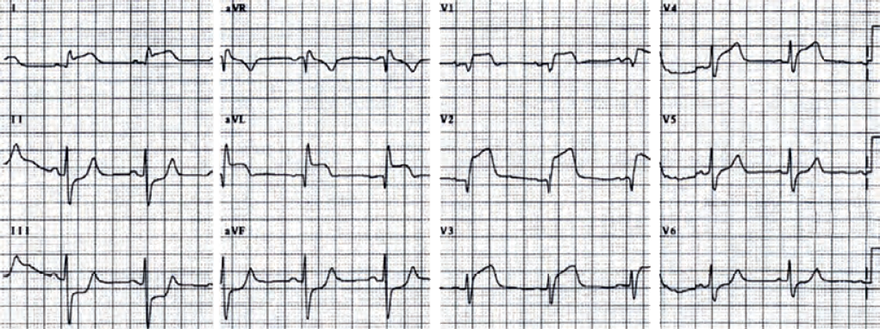
Acute Anterior STEMI
Acute Anterior STEMI

Acute Anterior STEMI


Acute Anterior STEMI
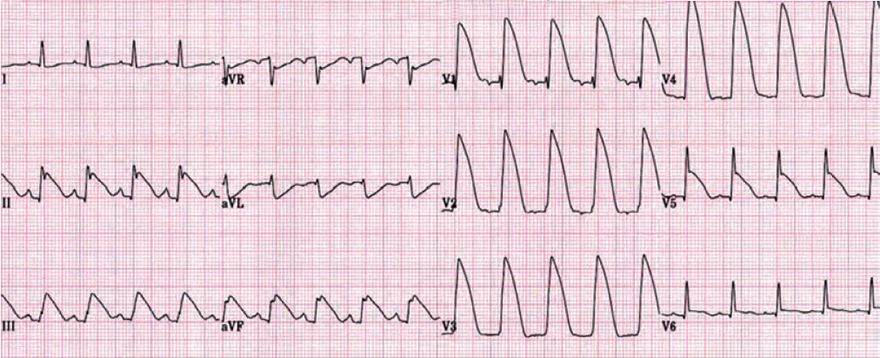
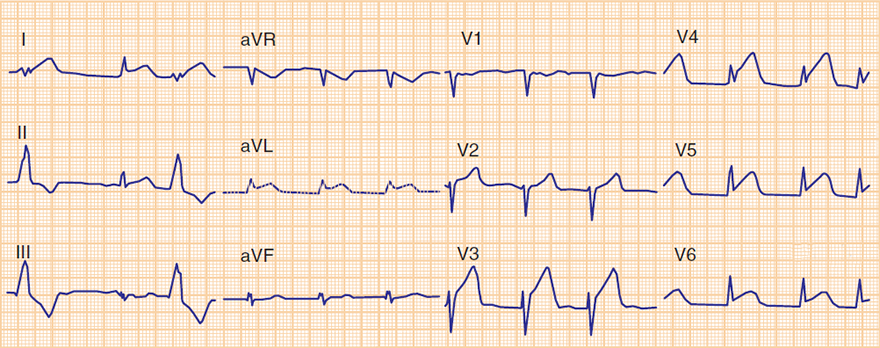
Acute Anterior and Inferior STEMI

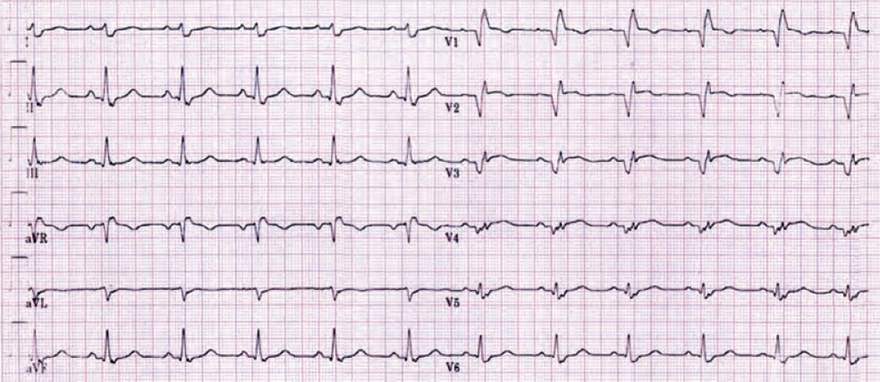
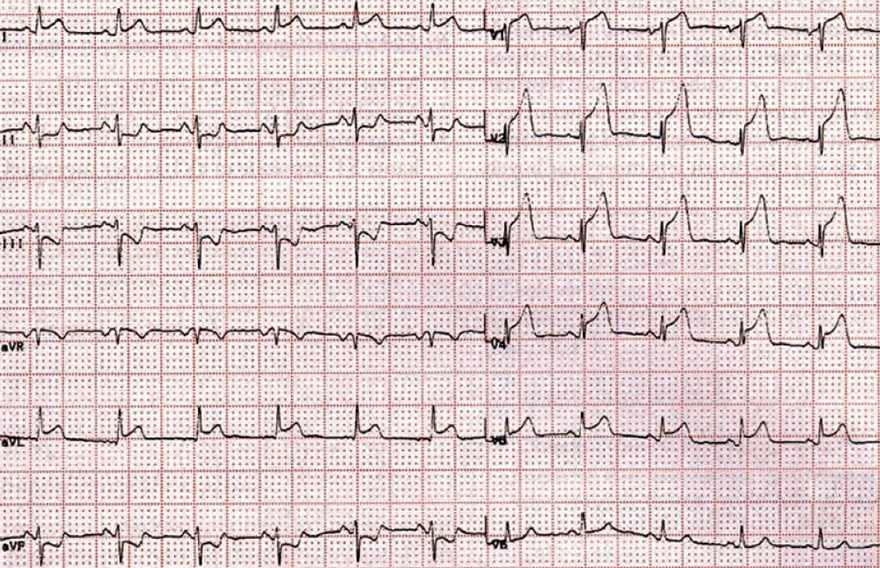
Acute Anterior STEMI
Sources
Home /
Anterior STEMI myocardial infarction and localisation occlusion (culprit artery) of the left anterior descending artery (LAD)
|

|
Anterior Wall STEMI
|

|
|

|

Classification of STEMI by Stage
ECG and Anterior STEMI
|

|
LAD Occlusion with "Wraparound"
|

|
| STEMI | ST elevations | Reciprocal ST depressions |
| Septal | V1-V2 | None |
| Anterior | V2-V5 | None |
| Anteroseptal | V1-V4 | None |
| Anterolateral | V3-V6, I, aVL | III, aVF |
| Extensive Anterior | V1-V6, I, aVL | III, aVF |
| Anteroinferior (Wraparound LAD) |
(V2-V4) + (II, III, aVF) | None |
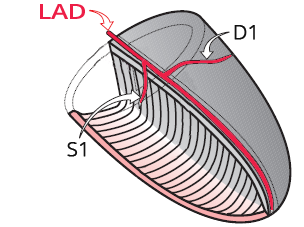
Localization of Occlusion in the LAD
|

|
|

|
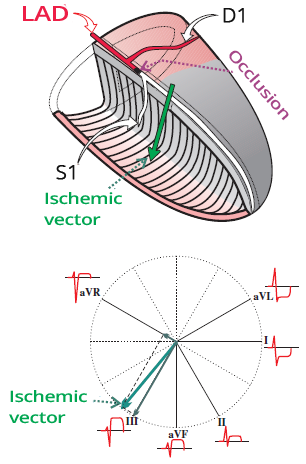
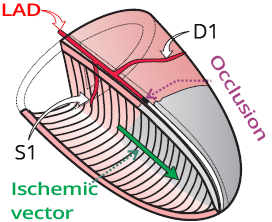
ECG and Occlusion of the LAD Between S1 and D1
|

|
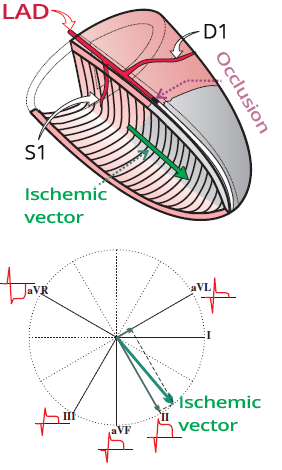
ECG and Occlusion of the LAD Between D1 and S1
|

|
ECG and Occlusion of the LAD Distal to S1, D1
|

|

|
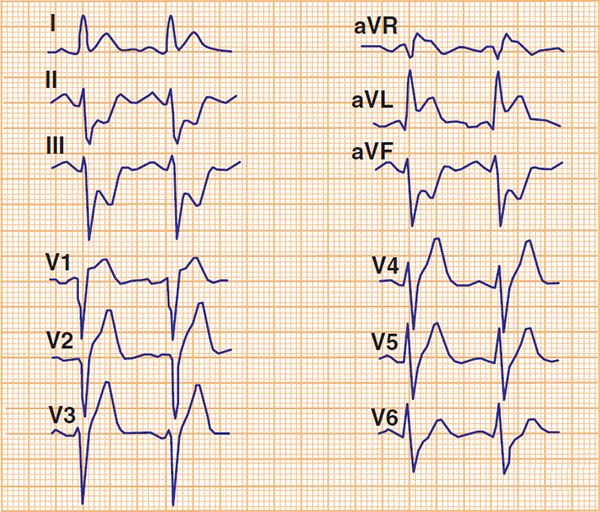
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Old Anterior Myocardial Infarction
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior and Inferior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|
Sources