Home /
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (Cardiomyopathy)
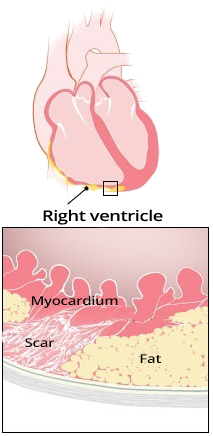

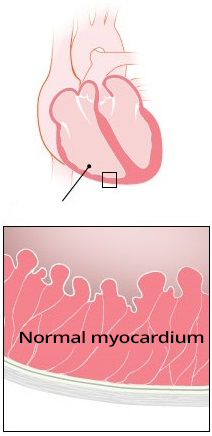
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
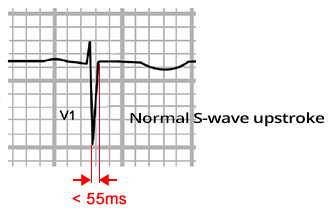
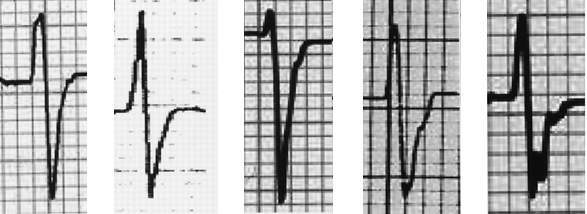
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia


Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
Sources
Home /
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia (Cardiomyopathy)
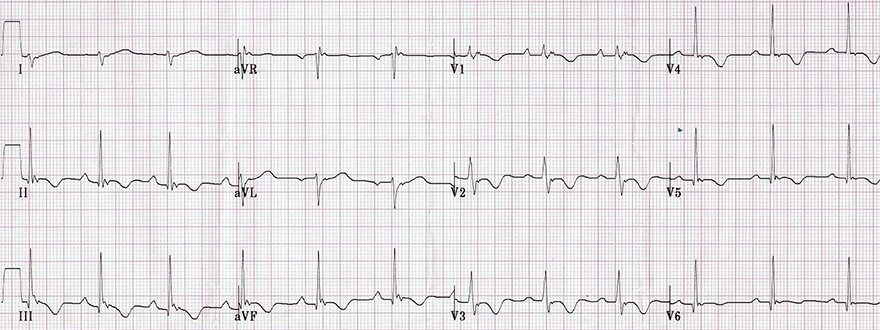
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
|

|
|

|
|

|
|

|
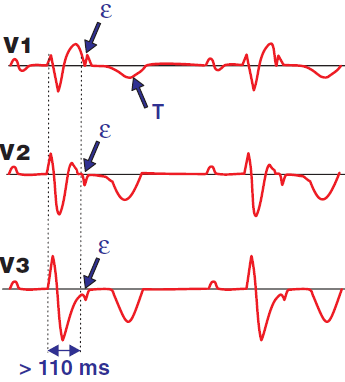
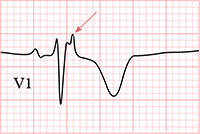
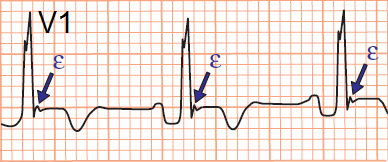
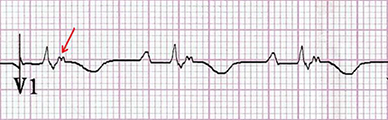
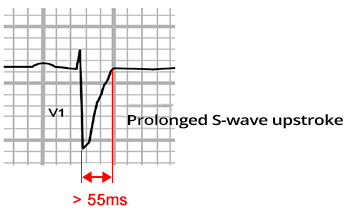
ECG and Epsilon Wave (ε)
|

|

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
|

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
|

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

|

|

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

|
|

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
Sources