Home /
Ashman Phenomenon
Ashman phenomenon, Ashman beats, Gouaux-Ashman phenomenon, Phase 3 long-short cycle sequence aberrancy
Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- Action potential (impulse) is a rapid change in the electrical voltage of cardiomyocytes
- It arises due to changes in the concentration of intracellular and extracellular ions
- The action potential propagates

Phase 3 of the action potential
- On the ECG, it is seen as the T wave (ventricular repolarization)
- It is the relative refractory period (RRP)
Action Potential and Refractory Period
- ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- During ARP, cardiomyocytes do not respond to another impulse
- RRP (Relative Refractory Period)
- During RRP, cardiomyocytes only respond to a suprathreshold impulse
- For example, if the right bundle branch is in ARP
- And a supraventricular impulse arrives at the bundle branch during ARP
- Then this impulse will be blocked in the bundle branch
- The next impulse will pass through the bundle branch only outside of ARP


- The left bundle branch
- has a short ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- The right bundle branch
- has a long ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
ECG and Phase 3 Block
- The right bundle branch (RBB) has a longer absolute refractory period (ARP)
- than the left bundle branch (LBB)
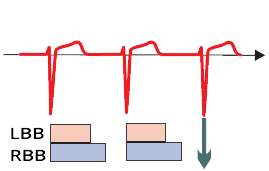
Physiological Conduction
- Supraventricular impulse
- Passes through the bundle branches
- outside of RRP
- The impulse is not blocked
- QRS complexes are narrow and have a uniform shape
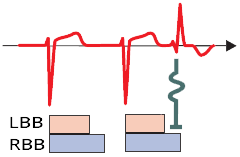
Aberrant Conduction
- Supraventricular extrasystole
- Occurred during the RRP of the right bundle branch
- The extrasystole is blocked only in the right bundle branch
- QRS complex is wide and has the shape of a right bundle branch block
- The impulse is conducted only through the left bundle branch
Ashman's Phenomenon

- First described by American doctors Ashman and Gouaux in 1947
- They observed that during atrial fibrillation
- if a long RR interval is followed by a short RR interval
- Then the short RR interval ends with a wide QRS complex resembling a RBBB
- This is a type of aberrant conduction caused by a block of the supraventricular impulse
- It occurs due to a prolongation of the refractory period of the ventricular conduction system
- On ECG, it is seen as a long RR - short RR interval ending with aberrant conduction
Refractory Period and RR Interval
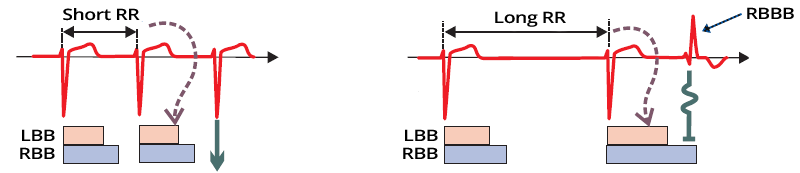
Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Left shows atrial fibrillation
- The RR interval is nearly constant
- Ashman's phenomenon is not present
- The supraventricular impulse is not blocked in the ventricular conduction system
- Right shows atrial fibrillation with Ashman's phenomenon
- After a prolonged RR interval, a short RR interval follows
- The prolonged RR interval prolongs the subsequent refractory period of the conduction system
- The supraventricular impulse of the short RR interval
- Reaches the conduction system during the refractory period and gets blocked
- On the ECG, a QRS complex appears with the pattern of a right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- Because the right bundle has a longer refractory period than the left

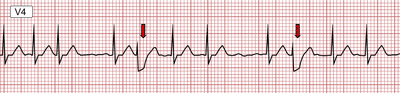
Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- On the ECG, there is atrial fibrillation in lead V1 with calibration of 10mm
- Initially, the RR intervals are relatively constant
- Then follows a long-short RR interval
- The long RR prolongs the refractory period
- The short RR ends with aberrant conduction showing the pattern of a right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- The impulse of the short RR passes through the right bundle during the refractory period and gets blocked
- Ashman's phenomenon most commonly occurs with atrial fibrillation
- When RR intervals change irregularly
Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
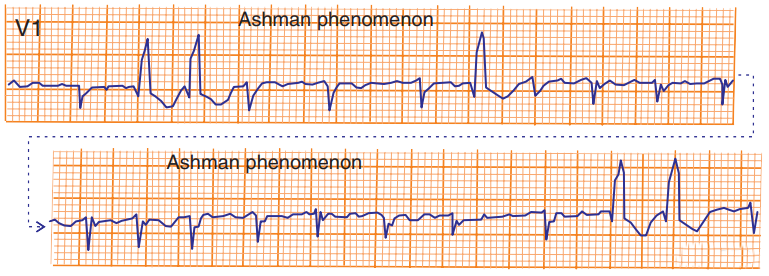
Ashman's Phenomenon and Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block
Ventricular Extrasystole and Ashman's Phenomenon
- Ventricular Extrasystole is sometimes mistaken for Ashman's Phenomenon
- Because both conditions produce a wide QRS complex
|
Ventricular Extrasystole |
Ashman's Phenomenon |
| QRS Width |
0.15-0.2s |
0.12s-0.15s |
| QRS Shape |
Bizarre |
RBBB or LBBB |
| Coupling Interval |
Same |
Variable |
| Compensatory Pause |
Yes |
No |
- QRS Width
- Ventricular Extrasystole (VES) has a wider QRS
- Because the ventricles are slowly activated from an ectopic focus through the myocardium
- In Ashman's Phenomenon, part of the ventricles are activated faster through the conduction system
- Therefore, the QRS is narrower
- QRS Shape
- VES has a bizarre QRS
- Because it originates in an ectopic focus somewhere in the ventricle
- In Ashman's Phenomenon, part of the ventricles are activated through the bundle branch (most often the left)
- Coupling Interval (the interval between the extrasystole and the preceding QRS)
- In VES, it is the same
- Because each VES is from the same focus
- (rarely, VES can originate from 2 foci, resulting in 2 different coupling intervals)
- Ashman's Phenomenon has a variable coupling interval
- Because the supraventricular impulse is blocked randomly in the refractory period
- Compensatory Pause
- VES has a complete compensatory pause
- Because the impulse from the VES retrogradely blocks the supraventricular impulse in the conduction system
- However, the compensatory pause is assessed during a regular sinus rhythm, not during atrial fibrillation
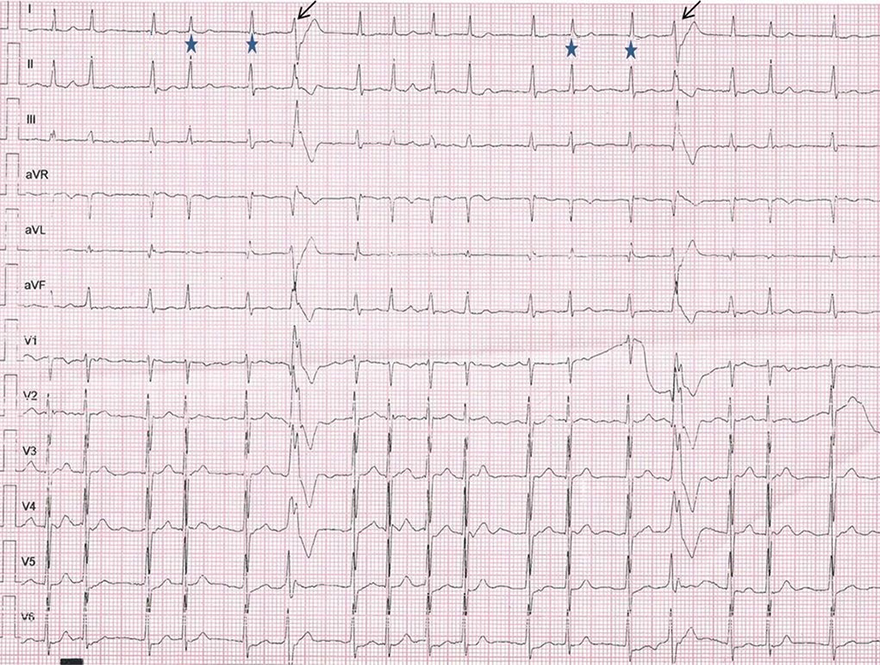
Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation

Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation on a 12-lead ECG
- After a long RR interval (green arrow), a short RR interval (red arrow) follows
- The short RR interval is terminated by aberrant conduction (blue arrow)
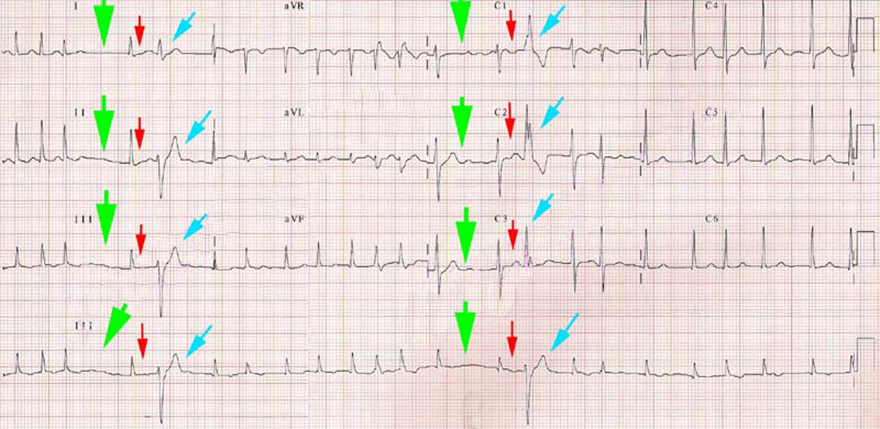
Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation on a 12-lead ECG
- After a long RR interval (green arrow), a short RR interval (red arrow) follows
- The short RR interval is terminated by aberrant conduction (blue arrow)
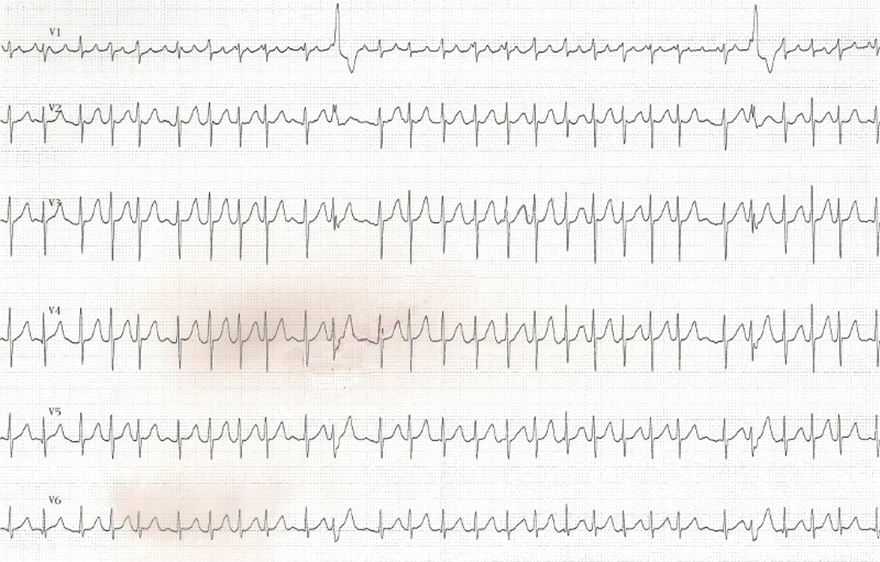
Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

Home /
Ashman Phenomenon
Ashman phenomenon, Ashman beats, Gouaux-Ashman phenomenon, Phase 3 long-short cycle sequence aberrancy
Phase 3 of the Action Potential
- Action potential (impulse) is a rapid change in the electrical voltage of cardiomyocytes
- It arises due to changes in the concentration of intracellular and extracellular ions
- The action potential propagates

Phase 3 of the action potential
- On the ECG, it is seen as the T wave (ventricular repolarization)
- It is the relative refractory period (RRP)
Action Potential and Refractory Period
- ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- During ARP, cardiomyocytes do not respond to another impulse
- RRP (Relative Refractory Period)
- During RRP, cardiomyocytes only respond to a suprathreshold impulse
- For example, if the right bundle branch is in ARP
- And a supraventricular impulse arrives at the bundle branch during ARP
- Then this impulse will be blocked in the bundle branch
- The next impulse will pass through the bundle branch only outside of ARP
- The left bundle branch
- has a short ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
- The right bundle branch
- has a long ARP (Absolute Refractory Period)
|


|
ECG and Phase 3 Block
- The right bundle branch (RBB) has a longer absolute refractory period (ARP)
- than the left bundle branch (LBB)

Physiological Conduction
- Supraventricular impulse
- Passes through the bundle branches
- outside of RRP
- The impulse is not blocked
- QRS complexes are narrow and have a uniform shape
|

Aberrant Conduction
- Supraventricular extrasystole
- Occurred during the RRP of the right bundle branch
- The extrasystole is blocked only in the right bundle branch
- QRS complex is wide and has the shape of a right bundle branch block
- The impulse is conducted only through the left bundle branch
|
Ashman's Phenomenon
- First described by American doctors Ashman and Gouaux in 1947
- They observed that during atrial fibrillation
- if a long RR interval is followed by a short RR interval
- Then the short RR interval ends with a wide QRS complex resembling a RBBB
- This is a type of aberrant conduction caused by a block of the supraventricular impulse
- It occurs due to a prolongation of the refractory period of the ventricular conduction system
- On ECG, it is seen as a long RR - short RR interval ending with aberrant conduction
|

|
Refractory Period and RR Interval

Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Left shows atrial fibrillation
- The RR interval is nearly constant
- Ashman's phenomenon is not present
- The supraventricular impulse is not blocked in the ventricular conduction system
- Right shows atrial fibrillation with Ashman's phenomenon
- After a prolonged RR interval, a short RR interval follows
- The prolonged RR interval prolongs the subsequent refractory period of the conduction system
- The supraventricular impulse of the short RR interval
- Reaches the conduction system during the refractory period and gets blocked
- On the ECG, a QRS complex appears with the pattern of a right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- Because the right bundle has a longer refractory period than the left

Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- On the ECG, there is atrial fibrillation in lead V1 with calibration of 10mm
- Initially, the RR intervals are relatively constant
- Then follows a long-short RR interval
- The long RR prolongs the refractory period
- The short RR ends with aberrant conduction showing the pattern of a right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- The impulse of the short RR passes through the right bundle during the refractory period and gets blocked
- Ashman's phenomenon most commonly occurs with atrial fibrillation
- When RR intervals change irregularly

Ashman's Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation

Ashman's Phenomenon and Aberrant Retrograde Bundle Branch Block
Ventricular Extrasystole and Ashman's Phenomenon
- Ventricular Extrasystole is sometimes mistaken for Ashman's Phenomenon
- Because both conditions produce a wide QRS complex
|
Ventricular Extrasystole |
Ashman's Phenomenon |
| QRS Width |
0.15-0.2s |
0.12s-0.15s |
| QRS Shape |
Bizarre |
RBBB or LBBB |
| Coupling Interval |
Same |
Variable |
| Compensatory Pause |
Yes |
No |
- QRS Width
- Ventricular Extrasystole (VES) has a wider QRS
- Because the ventricles are slowly activated from an ectopic focus through the myocardium
- In Ashman's Phenomenon, part of the ventricles are activated faster through the conduction system
- Therefore, the QRS is narrower
- QRS Shape
- VES has a bizarre QRS
- Because it originates in an ectopic focus somewhere in the ventricle
- In Ashman's Phenomenon, part of the ventricles are activated through the bundle branch (most often the left)
- Coupling Interval (the interval between the extrasystole and the preceding QRS)
- In VES, it is the same
- Because each VES is from the same focus
- (rarely, VES can originate from 2 foci, resulting in 2 different coupling intervals)
- Ashman's Phenomenon has a variable coupling interval
- Because the supraventricular impulse is blocked randomly in the refractory period
- Compensatory Pause
- VES has a complete compensatory pause
- Because the impulse from the VES retrogradely blocks the supraventricular impulse in the conduction system
- However, the compensatory pause is assessed during a regular sinus rhythm, not during atrial fibrillation

Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation

Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation on a 12-lead ECG
- After a long RR interval (green arrow), a short RR interval (red arrow) follows
- The short RR interval is terminated by aberrant conduction (blue arrow)

Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial fibrillation on a 12-lead ECG
- After a long RR interval (green arrow), a short RR interval (red arrow) follows
- The short RR interval is terminated by aberrant conduction (blue arrow)

Ashman Phenomenon and Atrial Fibrillation
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers





























