
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Atrial myocardial infarction (ischemia), Ta wave elevation and depression, Atrial Ischemia, Atrial Injury

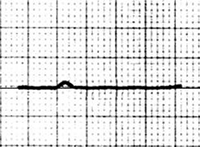
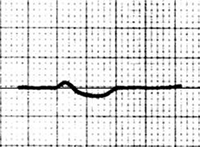


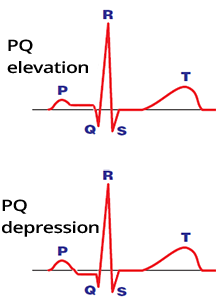
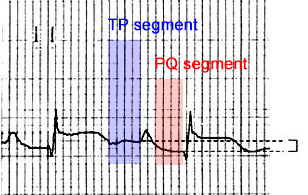
PQ Depression (1mm)
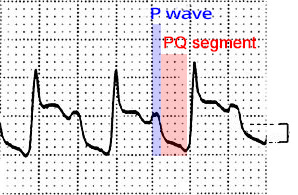
PQ Depression (2mm)

Atrial Infarction
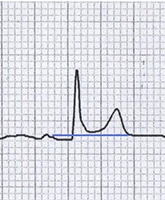
Pericarditis

Right Atrial Infarction and Inferior Wall STEMI
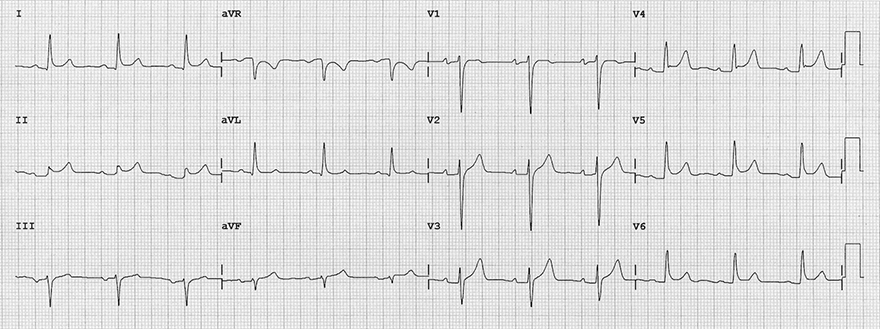
Acute Pericarditis

Right Atrial Infarction and STEMI of the Inferior Wall

Right Atrial Infarction and STEMI of the Inferior Wall
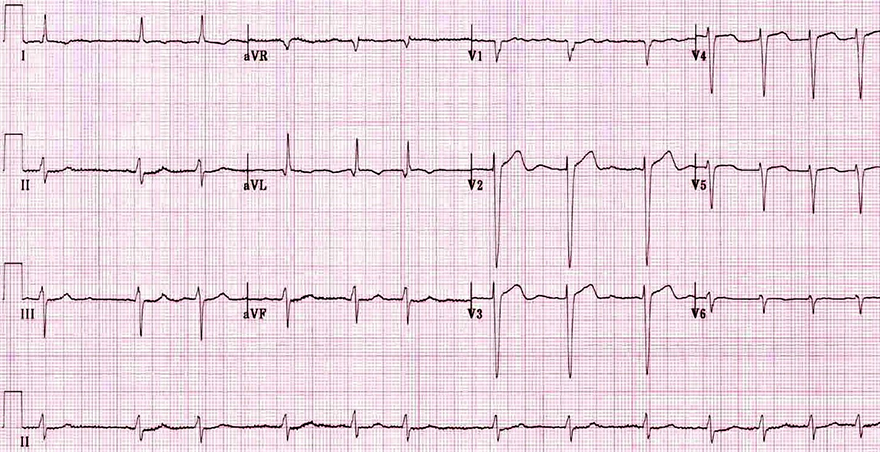
Atrial Infarction and Atrial Fibrillation
Sources
Home /
Atrial myocardial infarction (ischemia), Ta wave elevation and depression, Atrial Ischemia, Atrial Injury

|
|
Ta Wave
|
 
|
Atrial Infarction
|

|
PQ (PTa) Segment
|
 |
ECG and Atrial Infarction
|

|

PQ Depression (1mm)
|

PQ Depression (2mm)
|

Atrial Infarction
|

Pericarditis
|

Right Atrial Infarction and Inferior Wall STEMI

Acute Pericarditis

Right Atrial Infarction and STEMI of the Inferior Wall

Right Atrial Infarction and STEMI of the Inferior Wall

Atrial Infarction and Atrial Fibrillation
Sources