
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |


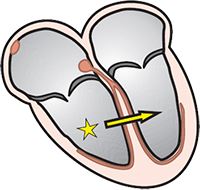
Sinus Rhythm
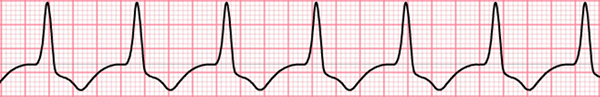
Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm

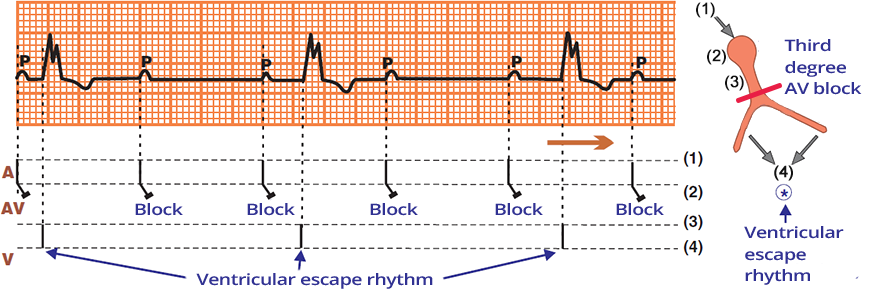
AV Dissociation in Third-Degree AV Block (Complete AV Block)

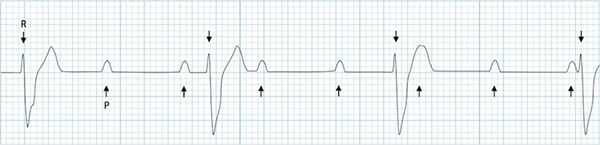
Complete AV Dissociation

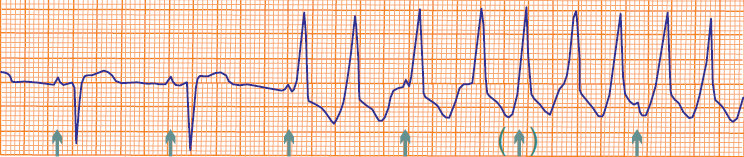
Incomplete AV Dissociation


Incomplete AV Dissociation

Isorhythmic AV Dissociation

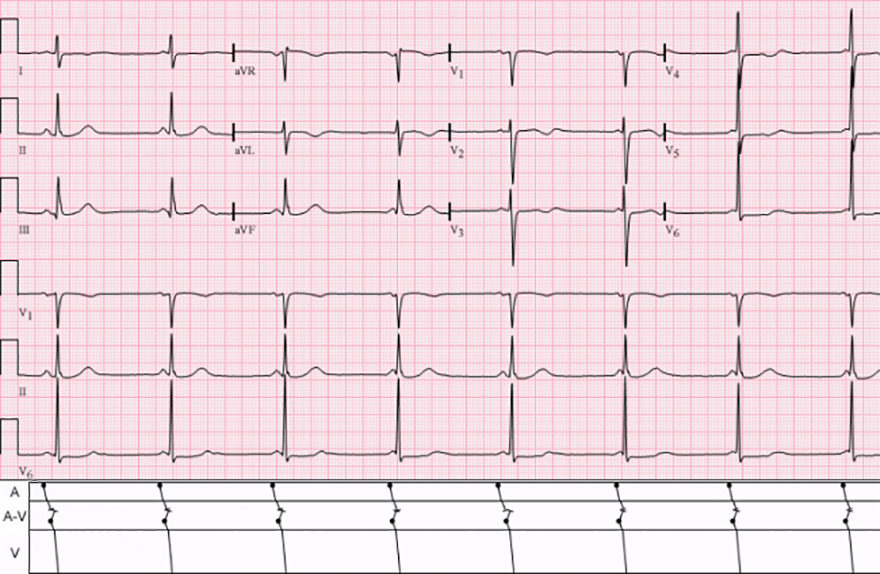
Isorhythmic AV Dissociation
Sources
Sinus Rhythm
|

|

Sinus Rhythm
Ventricular Rhythm
|

|

Accelerated Ventricular Rhythm
|

|

AV Dissociation in Third-Degree AV Block (Complete AV Block)

Complete AV Dissociation
|

|

|
Incomplete AV Dissociation
|

|

|
Incomplete AV Dissociation
|

|

|

|
Isorhythmic AV Dissociation

|
Isorhythmic AV Dissociation
|

|
Sources