Home /
AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT)
AV nodal reentry tachycardia, Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Re-entry and Supraventricular Tachycardia
- In supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), impulses originate in the atria or in the AV junction
- Re-entry is one of the mechanisms of tachycardia
- where the impulse circulates in a loop, most commonly around an anatomical obstacle (scar)
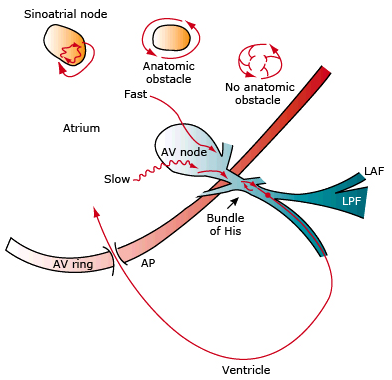
- Sinoatrial Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia
- Re-entry occurs in the SA node
- or the re-entry passes through the SA node
- Intra-atrial Re-entry Tachycardia
- Re-entry occurs somewhere in the atrium
- or re-entry occurs without an obstacle
- AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia
- Re-entry occurs in the AV node
- AV Re-entry Tachycardia
- It is macro re-entry, where the impulse circulates between:
- the atria and ventricles through the AV node and an accessory pathway
- There are 3 accessory pathways:
- Atrial Flutter
- It is macro re-entry, where the impulse circulates
- through the entire right atrium most commonly
AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia (AVNRT)
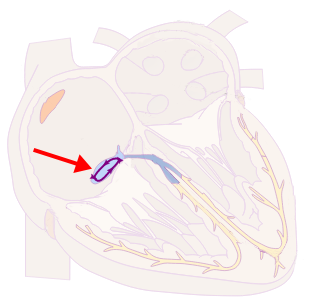
- In the AV node, there are 2 pathways where the impulse starts to circulate (micro re-entry)
- with a frequency of: 120-250/min.
- Heart rhythm is thus regulated by the AV node (overdrive suppression)
- It is the most common cause of palpitations (heart pounding)
- Especially in young healthy women
- It is paroxysmal (sudden onset and termination)
- Most common triggering factors:
- Alcohol, stress, fatigue, coffee, energy drinks
- It is often incorrectly labeled as
- Paroxysmal Supraventricular (SVT) Tachycardia
- Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia
2 Pathways and the AV Node
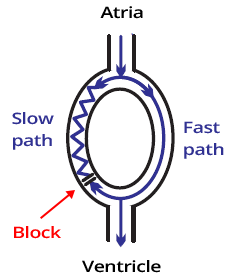
- There are 2 pathways in the AV node
- Fast Pathway (Has a long refractory period)
- Slow Pathway (Has a short refractory period)
- The impulse can travel through the pathways in both directions
- Anterograde (from top to bottom)
- Retrograde (from bottom to top)
- With sinus rhythm
- The impulse reaches the ventricles only through the fast pathway (anterograde)
- Retrograde impulse from the fast pathway
- blocks the anterograde impulse in the slow pathway
How Does AVNRT Occur?
atria (P)
Sinus Rhythm:
Anterograde impulse of the slow pathway is blocked by the retrograde impulse from the fast pathway. The impulse activates the ventricles
only through the fast pathway.
AES
Impulse from Atrial Extrasystole (
PES) travels
anterograde through the slow pathway, as the fast pathway is still in the
refractory period (from the previous sinus beat). The fast pathway has a longer refractory period.
P´
AVNRT: The impulse
circulates in re-entry within the AV node. Anterograde through the slow pathway (creating a
QRS complex), retrograde through the fast pathway (creating a
retrograde P wave).
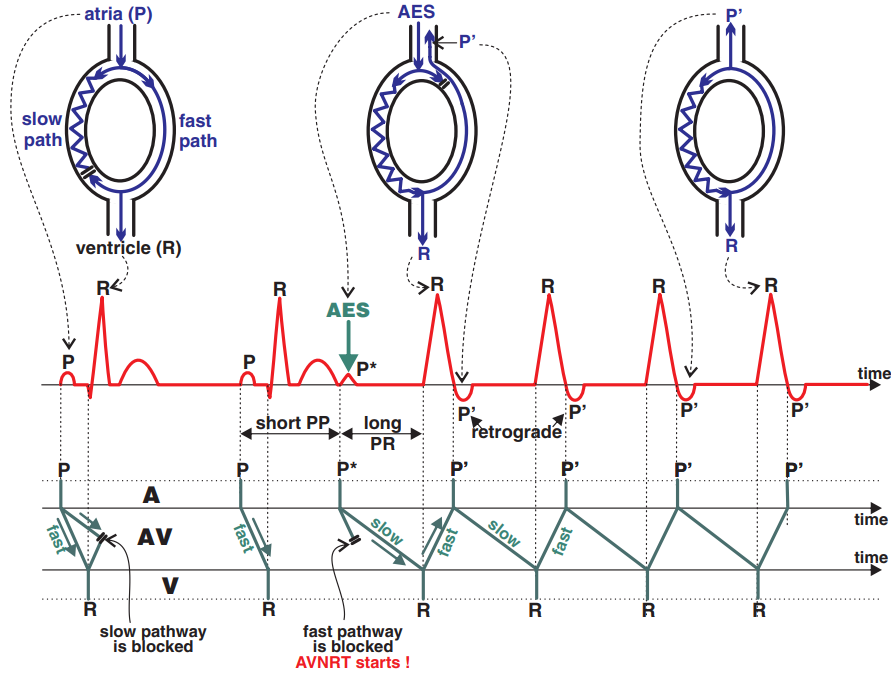
AV Nodal Re-entry Tachycardia
- Laddergram illustrates the spread of the impulse through the conduction system
- A - Atria, AV - AV junction, V - Ventricles
- P wave (P)
- Originates from the SA node (Sinus Rhythm)
- Atrial Extrasystole (P*)
- Occurs earlier than the expected P wave (Sinus Rhythm)
- PP* interval is shorter than the previous PP interval
- P*Q interval is prolonged because the ventricles (R) are activated by the atrial extrasystole through the slow pathway
- AVNRT
- Anterograde activation of the ventricles (R) through the slow pathway
- and then retrograde activation of the atria (P´) through the fast pathway
- Retrograde P waves are negative because the atrial vector is directed from the AV node towards the SA node
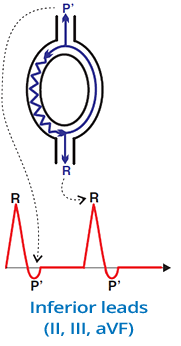
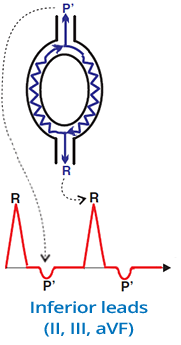
Pseudo S and Pseudo R Waves
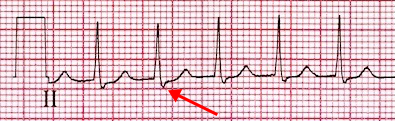
Pseudo S Wave (II, III, aVF)
- In the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- There is a pseudo S wave (after the QRS complex)
- It is a retrograde P wave
- whose vector is directed away from the inferior leads
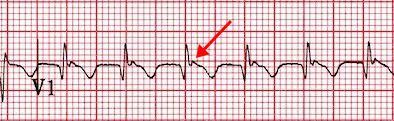
Pseudo R Wave (V1)
- Lead V1 is a mirror lead to the inferior leads
- In V1, there is a pseudo R wave (after the QRS complex)
- It is a retrograde P wave
- whose vector is directed toward V1
ECG and AVNRT

- Heart Rate: 120-250/min.
- 90% of all AVNRT cases are Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT, which shows:
- Pseudo S wave (II, III, aVF)
- Pseudo R wave (V1)
- Atypical and Rare AVNRT do not show pseudo waves
- AVNRT is paroxysmal
- It starts suddenly (after an extrasystole) and ends suddenly
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart Rate is regular
- QRS alternans (changing amplitude of QRS complexes) may be present
Classification of AVNRT
- AVNRT is classified according to the direction of impulse circulation in the AV node
- Typical AVNRT (Slow-Fast) (90% of all AVNRT cases). The impulse propagates:
- Anterogradely through the slow pathway
- Retrogradely through the fast pathway
- Atypical AVNRT (Fast-Slow) (8%)
- Anterogradely through the fast pathway
- Retrogradely through the slow pathway
- Rare AVNRT (Slow-Slow) (2%)
- Anterogradely through the slow pathway
- Retrogradely through the slow pathway
Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
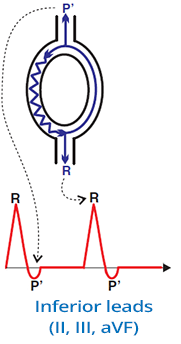
- Most common AVNRT, accounts for 90% of all AVNRT cases
- The impulse circulates:
- Anterogradely through the Slow pathway to the ventricles
- Retrogradely through the Fast pathway to the atria
- Retrograde P' wave
- Appears just after the QRS
- Atria are activated through the Fast pathway (just after the ventricles)
- Sometimes it is hidden in the QRS and not visible
- When the ventricles and atria are activated "simultaneously"
- ECG and Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Pseudo S wave (II, III, aVF)
- Pseudo R wave (V1, V2)

Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Pseudo S wave (II, III, aVF)
- In the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- It is a pseudo S wave (following the QRS)
- It is a retrograde P wave
- Whose vector points away from the inferior leads

Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Pseudo R wave (V1)
- Lead V1 is a mirror image lead to the inferior leads
- In V1, there is a pseudo R wave (following the QRS)
- It is a retrograde P wave
- Whose vector points toward V1
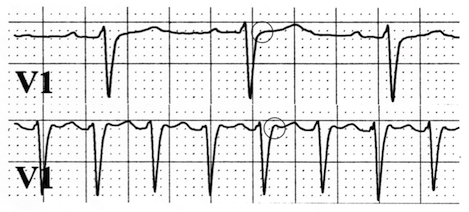
Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- The image shows an ECG from a single patient
- Upper V1 lead
- Sinus rhythm, Frequency 90/min.
- There is no pseudo R wave (circle) at the end of the QRS
- Lower V1 lead
- The patient experienced sudden palpitations (heartbeats)
- Between the QRS complexes are T waves, not P waves
- A pseudo R wave (circle) appeared at the end of the QRS
- In the inferior leads (II, III, aVF) there is certainly a pseudo S wave
- It is Typical Fast-Slow AVNRT

Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- At the beginning of the ECG, there is a sinus rhythm with a frequency of 60/min.
- Followed by a atrial extrasystole (red arrow)
- The extrasystole triggered AVNRT with a frequency of 150/min.
- Pseudo R wave in V1 (red dashed arrow)
Atypical (Fast-Slow) AVNRT
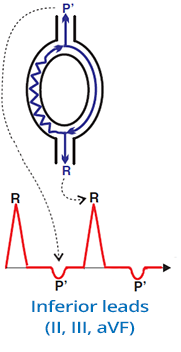
- Accounts for 8% of all AVNRT cases
- The impulse circulates:
- Anterogradely through the Fast (rapid) pathway to the ventricles
- Retrogradely through the Slow (slow) pathway to the atria
- Retrograde P' wave:
- Occurs after the QRS complex (it is further behind the QRS compared to typical AVNRT)
- ECG and Atypical (Fast-Slow) AVNRT
- Retrograde P' wave after QRS (II, III, aVF)
- P wave after QRS (V1, V2, aVR)
- Represents a typical retrograde P wave (not adjacent to QRS as seen in typical AVNRT)
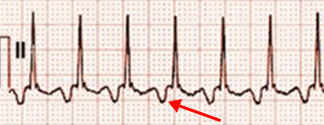
Atypical (Fast-Slow) AVNRT
- In the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- There is a Retrograde P' wave (after QRS)
- Vector points away from the inferior leads
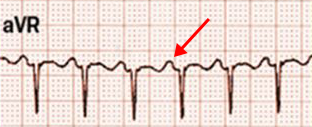
Atypical (Fast-Slow) AVNRT
- Leads V1, V2, aVR
- In aVR, there is a P wave (after QRS)
- The vector points towards aVR
Rare (Slow-Slow) AVNRT

- Accounts for 2% of all AVNRT cases
- Impulse circulates:
- Anterogradely through the Slow (slow) pathway to the ventricles
- Retrogradely through the Slow (slow) pathway to the atria
- ECG and Rare (Slow-Slow) AVNRT
Differential Diagnosis of AVNRT

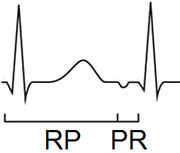
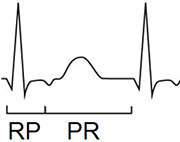
- In differential diagnosis of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) and AVNRT
- Evaluate the RP and PR intervals
- RP interval (Beginning of QRS - Beginning of P wave)
- PR interval (Beginning of P wave - Beginning of QRS)
- Based on the ratio of RP to PR interval, SVT is classified into:
- SVT with a short RP interval (RP < PR)
- SVT with a long RP interval (RP > PR)
- In ECG diagnosis of AVNRT, also evaluate:
- Length of the RP interval, with a threshold of 90ms


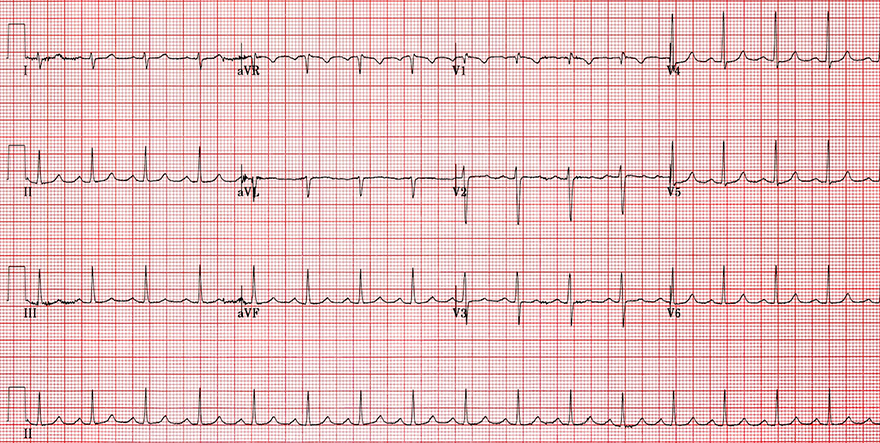
Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Frequency: 150/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms)
- At the end of QRS complexes:
- Pseudo r wave (V1, V2)
- Pseudo s wave (II, III, aVF)
- It is a Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
Sinus Rhythm
- This ECG is from the previous patient
- On this ECG, there is a sinus rhythm with a frequency of 100/min.
- No pseudo waves (r, s) are present
- The re-entry circuit in the AV node was interrupted (after carotid sinus massage)

Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT

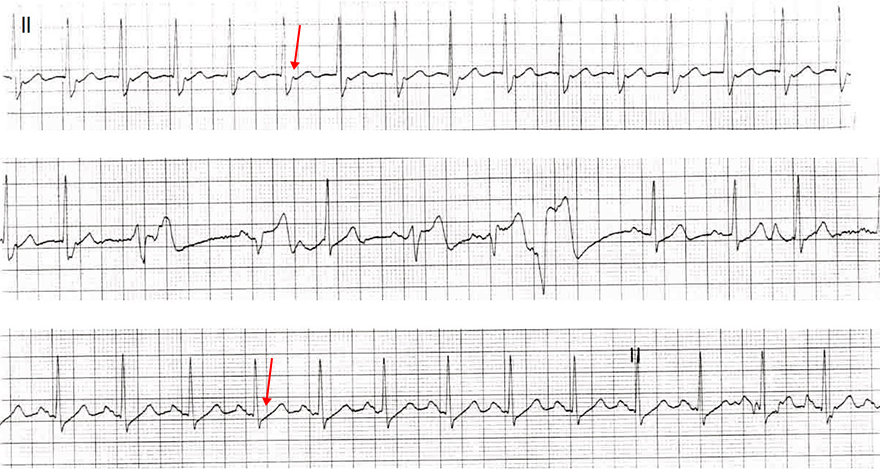
Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Continuous ECG recording from lead II
- Upper ECG
- Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Pseudo s wave (at the end of QRS)
- Middle ECG
- The patient received intravenous 6mg Adenosine
- Adenosine slows conduction through the AV node (interrupts re-entry)
- Ventricular extrasystoles occurred, followed by sinus rhythm
- Lower ECG
- Sinus rhythm
- Pseudo s wave at the end of QRS has disappeared
- There is a P wave before each QRS


Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Frequency: 120/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms)
- Retrograde P waves after the QRS complex
- (not "stuck" to the end of the QRS complex)
- Negative in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- Positive in the leads (aVR, V1-V3)
- This is a Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- RP interval < 90ms (even if P waves are further after the QRS complex)

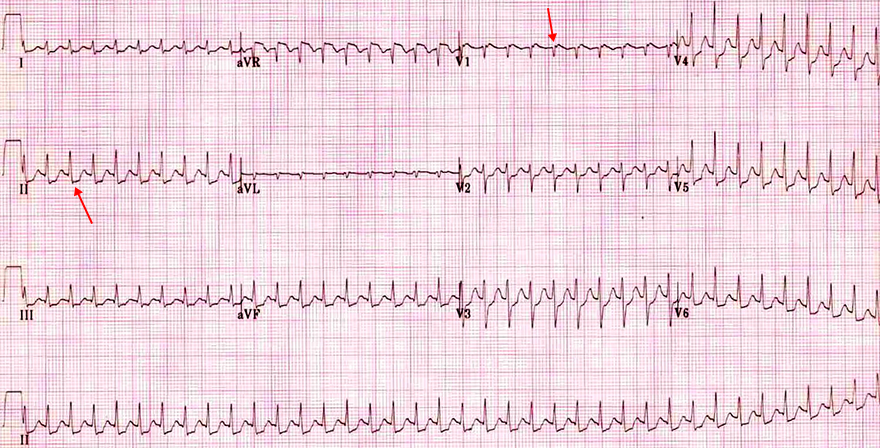
Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Frequency: 135/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms)
- Retrograde P waves after the QRS complex
- (not "stuck" to the end of the QRS complex)
- Negative in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- Positive in the leads (aVR, V1-V3)
- This is a Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- RP interval < 90ms (even if P waves are further after the QRS complex)
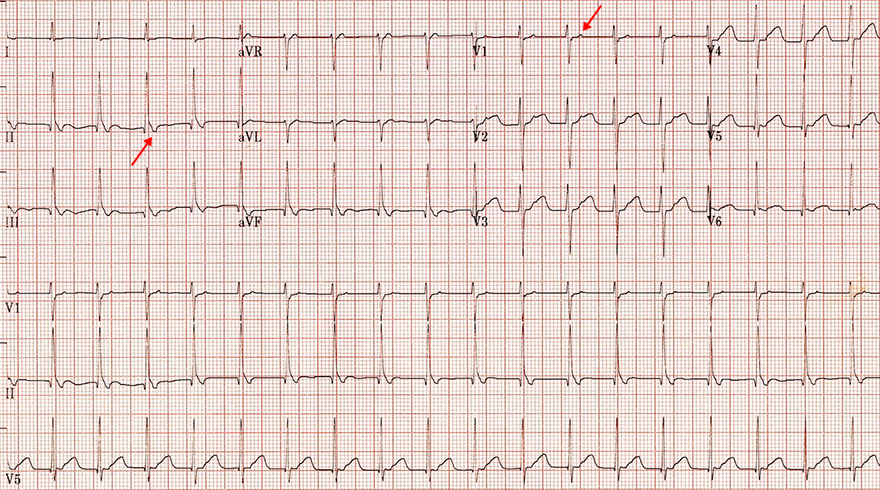
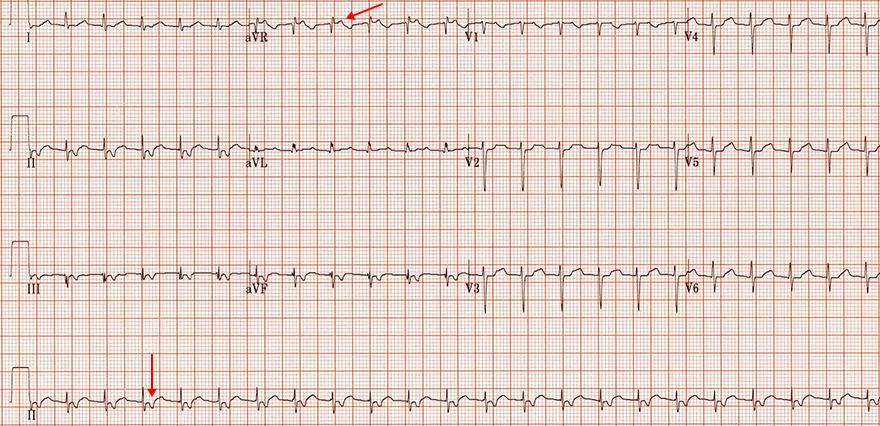
Rare (Slow-Slow) AVNRT
- Frequency: 125/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms)
- Retrograde P waves after the QRS complex
- Negative in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- Positive in the leads (V1-V3)
- This is a rare (slow-slow) AVNRT
- RP < PR
- RP > 90ms (RP interval is 4 squares: 120ms)


Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT and Sinus Rhythm
- Typical (Slow-Fast) AVNRT
- Frequency: 136/min.
- Pseudo r wave (V1)
- It is not functional incomplete right bundle branch block
- Because there is no deep S wave in V6
- Sinus Rhythm
- Frequency: 107/min.
- Pseudo r wave (disappeared)


Atypical (Fast-Slow) AVNRT
- Frequency: 150/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms)
- Retrograde P waves after the QRS complex
- Negative in the inferior leads (II, III, aVF)
- Positive in the lead (aVR)
- This is atypical (fast-slow) AVNRT
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers