
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, Orthodromic and Antidromic AVRT, Orthodromic Reciprocating Tachycardia (ORT)
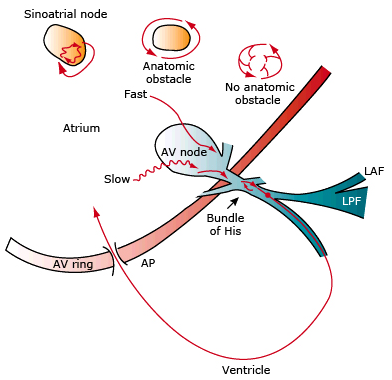
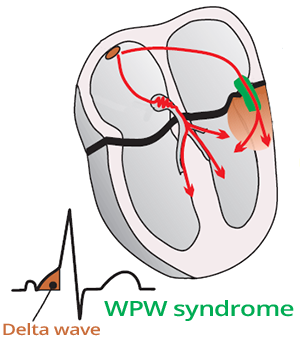

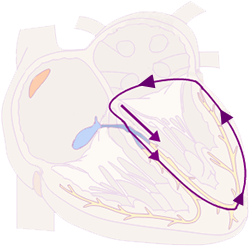
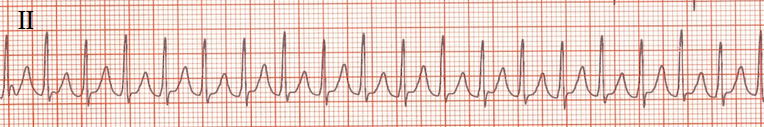
Orthodromic AVRT
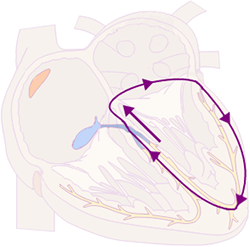

Antidromic AVRT

Orthodromic AVRT


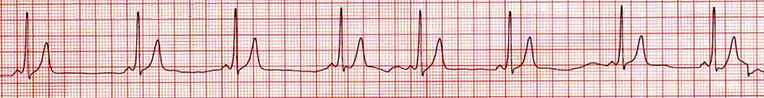
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
WPW Syndrome

Orthodromic AVRT
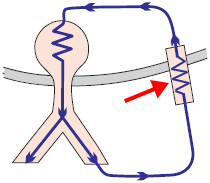
PJRT

PJRT


Wide-Complex Tachycardia

WPW Syndrome

Orthodromic AVRT
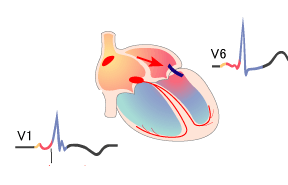

WPW Syndrome (Type A)

Orthodromic AVRT


WPW Syndrome (Type A)
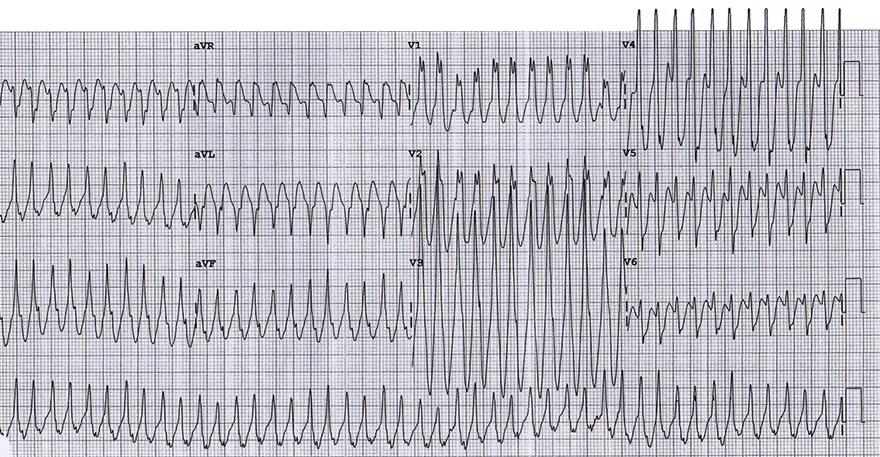
Antidromic AVRT

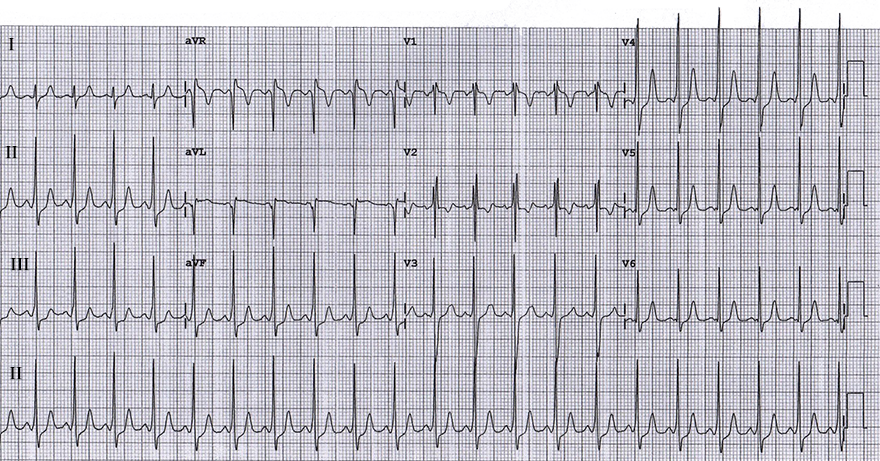
WPW Syndrome (Type B)

Antidromic AVRT

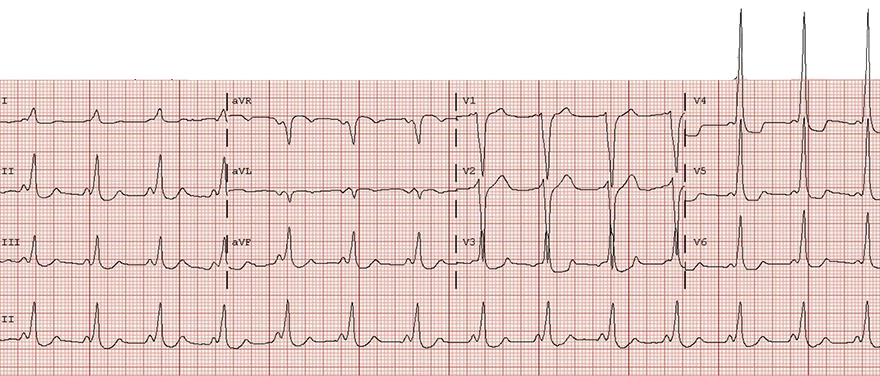
WPW Syndrome (Type B)

Antidromic AVRT

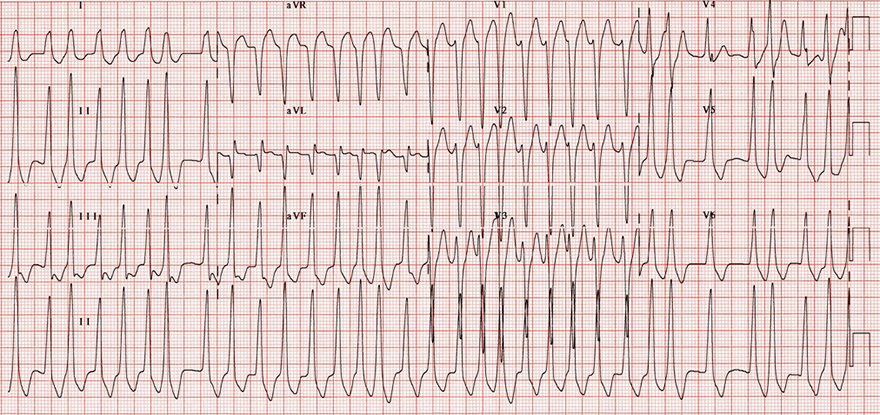
Antidromic AVRT and Atrial Fibrillation


Antidromic AVRT and Atrial Fibrillation
Sources
Home /
Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia (AVRT), Atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia, Orthodromic and Antidromic AVRT, Orthodromic Reciprocating Tachycardia (ORT)
|

|
WPW Syndrome
|

|
|

|

 |
Orthodromic AVRT
|


|
Antidromic AVRT
|

Orthodromic AVRT
Differential Diagnosis of AVRT
|

|
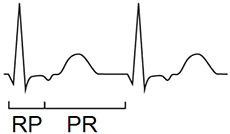
ECG and Orthodromic AVRT
|

|

Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)

WPW Syndrome
 |
 |
 |
|
Orthodromic AVRT
|
PJRT
|
PJRT
|
ECG and Antidromic AVRT
|

|

Wide-Complex Tachycardia

WPW Syndrome

Orthodromic AVRT

|
WPW Syndrome (Type A)
|

|

Orthodromic AVRT

|
WPW Syndrome (Type A)
|

|

Antidromic AVRT

|
WPW Syndrome (Type B)
|

|

Antidromic AVRT

|
WPW Syndrome (Type B)
|

|

Antidromic AVRT

|
Antidromic AVRT and Atrial Fibrillation
|

|

|
Antidromic AVRT and Atrial Fibrillation
|

|
Sources