
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

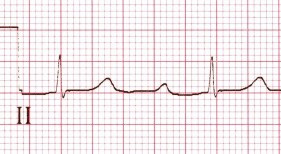

Propranolol (Intoxication)
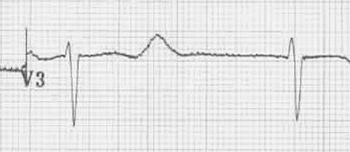
Sotalol (Intoxication)
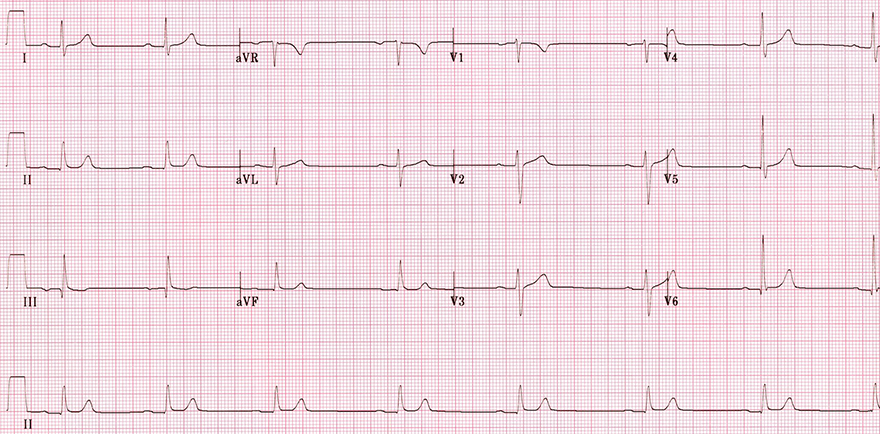
Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Sotalol (Intoxication)
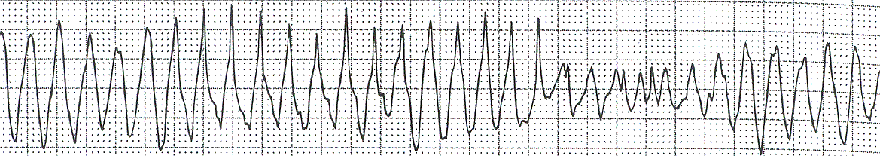
Torsades de Pointes

Flecainide (Intoxication)
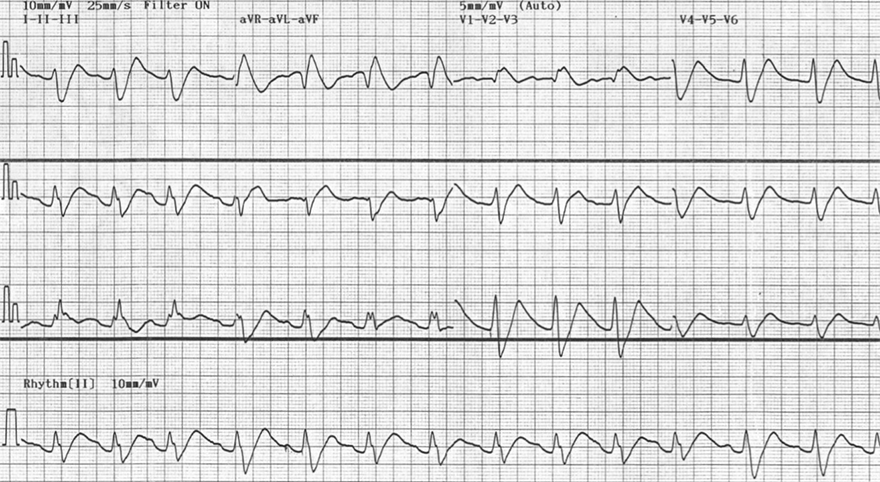
Flecainide (Intoxication)
Sources
Sympathetic Nervous System
|

|
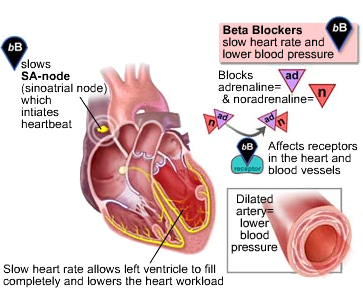
Beta-Blockers (BB)
|

|
|
|
|

|

|

|
|
Propranolol (Intoxication)
|
Sotalol (Intoxication)
|

Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Beta Blockers (Intoxication)

Sotalol (Intoxication)

Torsades de Pointes

Flecainide (Intoxication)

Flecainide (Intoxication)
Sources