
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Bundle branch reentry (reentrant) ventricular tachycardia (BBRVT)
 |
 |
 |
BBRT |
BBRT |
Interfascicular Tachycardia |
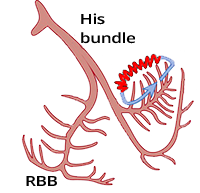
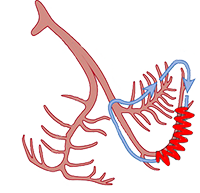
| Anterograde: Right bundle branch |
Anterograde: Left bundle branch |
Anterograde: Left or right fascicle |
| Retrograde: Left bundle branch |
Retrograde: Right bundle branch |
Retrograde: Contralateral fascicle |
 |
 |
 |
BBRT |
BBRT |
Interfascicular Tachycardia |
| ECG Appearance: LBBB |
ECG Appearance: RBBB |
ECG Appearance: RBBB |
| QRS Complexes >0.12s |
QRS Complexes >0.12s |
QRS Complexes about 0.12s |
| Anterograde: Right Bundle Branch |
Anterograde: Left Bundle Branch |
Anterograde: Left or Right Fascicle |
| Retrograde: Left Bundle Branch |
Retrograde: Right Bundle Branch |
Retrograde: Contralateral Fascicle |


Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type A)


Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type A)


Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type B)
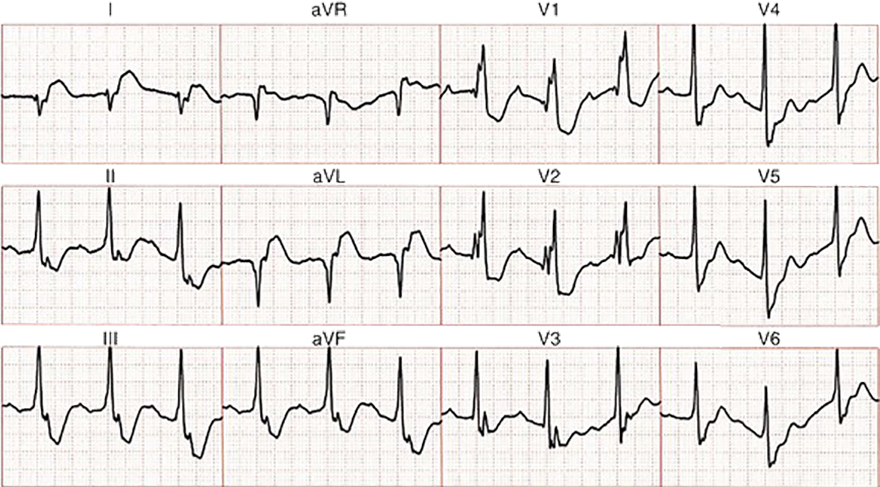
Sinus Rhythm (RBBB + AV Block I + Left Posterior Hemiblock)

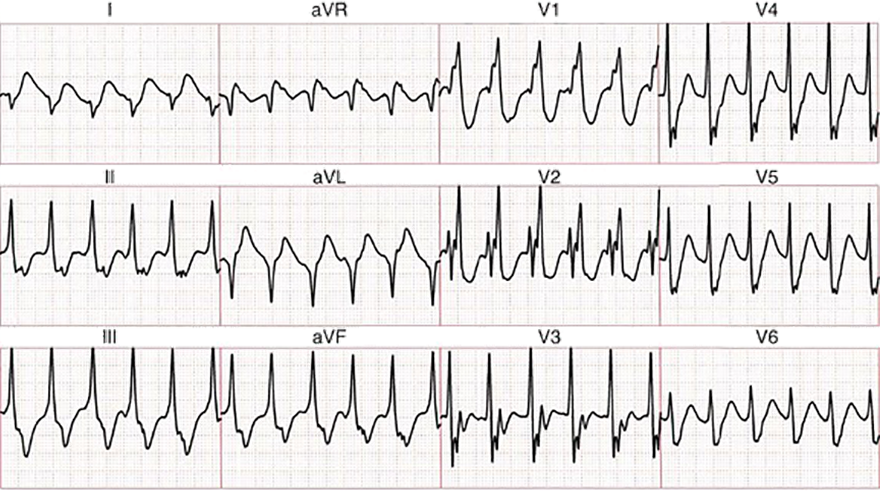
Interfascicular Ventricular Tachycardia
Sources
Home /
Bundle branch reentry (reentrant) ventricular tachycardia (BBRVT)
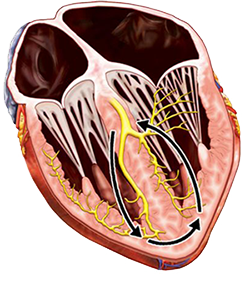
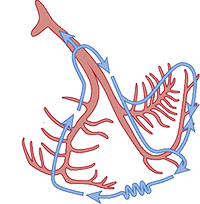
Bundle Branch Re-entrant Tachycardia
|

|
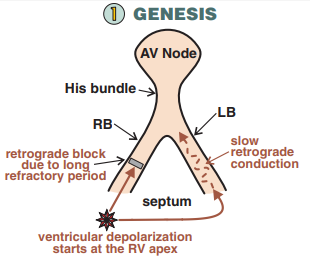
Genesis of Bundle Branch Re-entrant Tachycardia
|

|
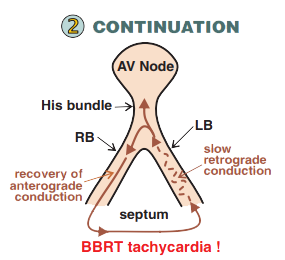
Mechanism of Re-entry
|

|
 |
 |
 |
|
BBRT (Type A) |
BBRT (Type B) |
Interfascicular Tachycardia |
|
| Anterograde: | Right bundle branch | Left bundle branch | Left or right fascicle |
| Retrograde: | Left bundle branch | Right bundle branch | Contralateral fascicle |

|
|

|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
BBRT (Type A) |
BBRT (Type B) |
Interfascicular Tachycardia |
|
| ECG Appearance: | LBBB | RBBB | RBBB |
| QRS Complexes | >0.12s | >0.12s | about 0.12s |
| Anterograde: | Right Bundle Branch | Left Bundle Branch | Left or Right Fascicle |
| Retrograde: | Left Bundle Branch | Right Bundle Branch | Contralateral Fascicle |

|
Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type A)
|

|

|
Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type A)
|

|

|
Bundle Branch Reentry Ventricular Tachycardia (Type B)
|

|

Sinus Rhythm (RBBB + AV Block I + Left Posterior Hemiblock)

|
Interfascicular Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
Sources