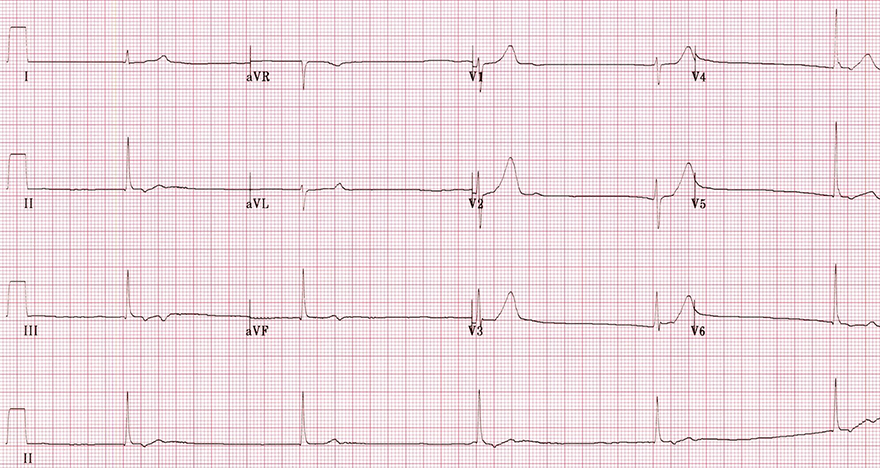
- Main signs of intoxication
- Secondary signs of intoxication

Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)
Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)

Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

Home /
Calcium Channel Blockers (Intoxication)
Calcium channel blockers overdose, toxicity
Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB)
- Inhibit the entry of calcium into the cells of blood vessels and the heart, resulting in:
- Used to treat high blood pressure
- CCBs are classified based on chemical structure into:
- Dihydropyridine CCBs
- Mainly act on blood vessels
- resulting in vasodilation
- Minimal ECG changes occur in overdose
- Examples: Amlodipine, Nitrendipine, Felodipine, Lacidipine...
- Non-dihydropyridine CCBs
- Mainly act on cardiomyocytes, resulting in:
- Negative inotropy (reduced contractility)
- Negative chronotropy (reduced rate of impulses)
- Negative dromotropy (reduced conduction of impulses)
- ECG changes occur in overdose
- There are only 2: Verapamil, Diltiazem
|
|
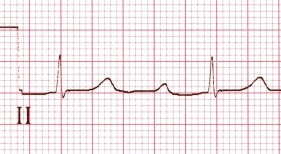
ECG and Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)
- Non-dihydropyridine CCBs and Beta-blockers produce the same ECG changes in intoxication
|
- Main signs of intoxication
- Secondary signs of intoxication
|
|

Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)

Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)

Non-dihydropyridine CCBs (Intoxication)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
|











