
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
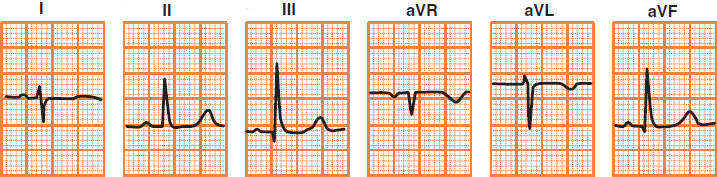
Right Axis Deviation
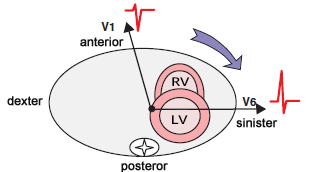

Clockwise Heart Rotation
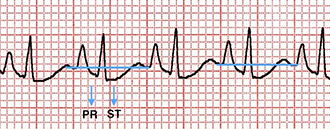
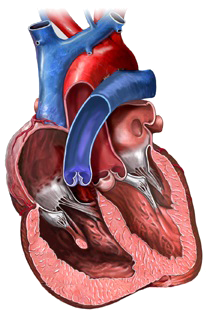
Right Heart Strain
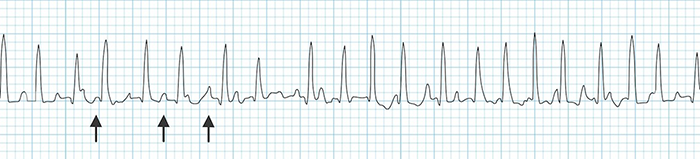
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
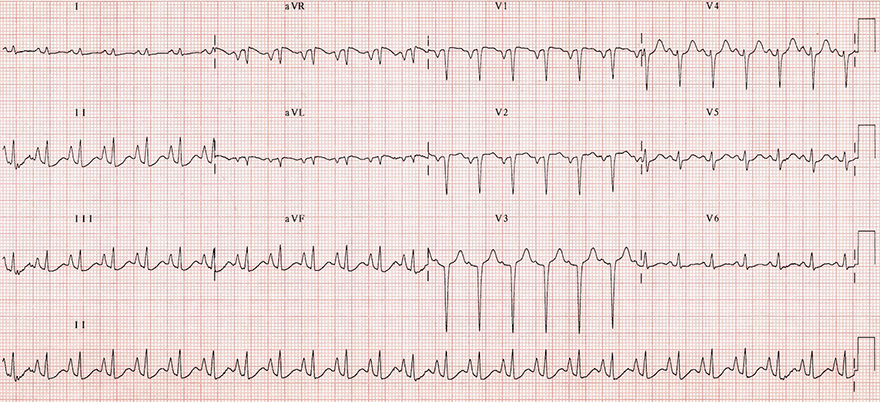
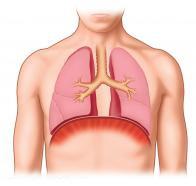
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
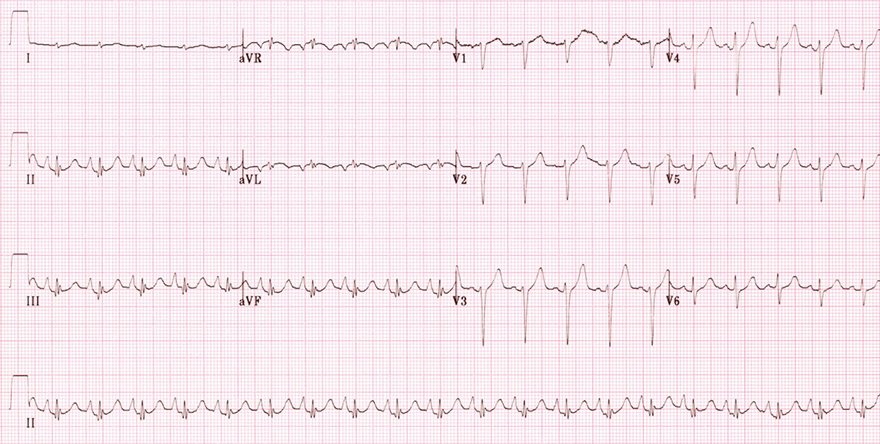
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
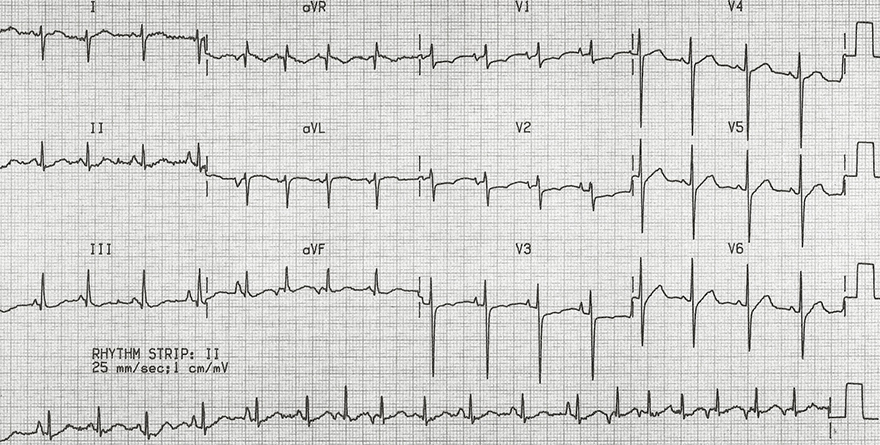
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Sources
Cor Pulmonale
|
 |
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
|
 
|

|
|
|
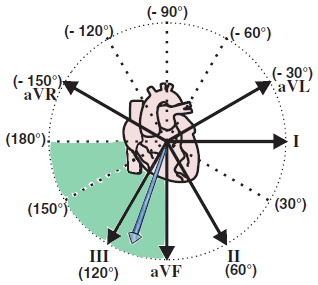
Right Axis Deviation
|

|
 |
 |
Clockwise Heart Rotation

Right Heart Strain

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease

Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Sources