Home /
Coronary Circulation
Coronary circulation, Coronary arteries and vessels
Conduction System of the Heart
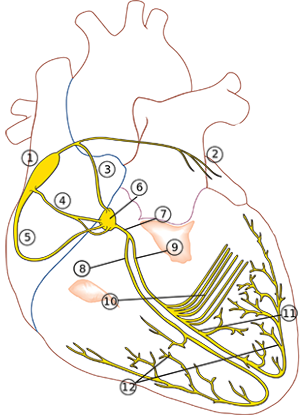
- The conduction system is responsible for
- the generation and propagation of impulses throughout the working myocardium
- Certain parts are essential for heart function
- Especially the heart's pacemakers (SA node, AV node)
- This is why they have duplicate blood supply
- The conduction system includes:
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node (1)
- Bachmann's Bundle (2)
- Internodal Pathways (3,4,5)
- Anterior Internodal Pathway (James' Tract) (3)
- Middle Internodal Pathway (Wenckebach's Tract) (4)
- Posterior Internodal Pathway (Thorel's Tract) (5)
- Atrioventricular (AV) Junction (6,7)
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node (6)
- Bundle of His (7)
- Right Bundle Branch (8)
- Left Bundle Branch (9)
- Left Posterior Fascicle (10)
- Left Anterior Fascicle (11)
- Purkinje Fibers (12)
Right and Left Coronary Arteries
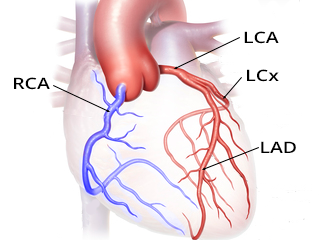
- The heart is supplied by 2 coronary arteries
- which originate just above the aortic valve from the aortic root
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- The right coronary artery
- Has larger primary branches because it supplies the right ventricle
- through which deoxygenated blood flows
- Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
- The left coronary artery
- After a short course, it divides into:
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- also known as the RIA, or
- Anterior interventricular branch.
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- LCx can be referred to by multiple terms:
- Circumflex artery (Cx or CX)
- Ramus circumflex artery (RCx or RCX)
- Left circumflex artery (LCx or LCX)
- The course and branching pattern of coronary arteries are variable
- The left and right coronary arteries have minimal anastomoses (connections)
- In case of occlusion of the main stem or branch of one artery
- It leads to ischemia up to myocardial infarction beyond the occlusion (occlusion = 100% stenosis)
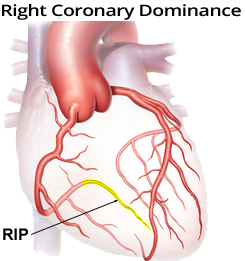
Ramus Interventricularis Posterior and Anterior

- Ramus Interventricularis Posterior (RIP) supplies
- The inferior part of the heart
- The posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum, where the AV node is located
- RIP is responsible for the function of the AV node
- RIP can be a branch of the left or right coronary artery
- Ramus Interventricularis Anterior (RIA) supplies
- The anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum
- RIA is a branch of the left coronary artery
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
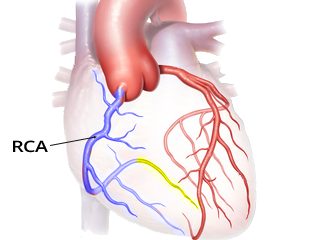
- In 70% of people, it is dominant because RIP originates from it
- Proximal occlusion of the dominant right coronary artery (RCA)
Right Coronary Artery Supplies

- Right ventricle except the apex
- Apex of the heart is supplied by RIA
- Right atrium
- Conus arteriosus (part of the right ventricular outflow tract)
- along with branches from the left coronary artery
- SA node in 60% of people
- 40% of people have SA node supplied by RCx
- 30% of the left ventricle in the posterior part near the ventricular septum
- If dominant, it gives rise to RIP which supplies
- Inferior wall of the heart
- Posterior 1/3 of the ventricular septum
- AV node
- His bundle
Right Coronary Artery (Branching)

Ramus coni arteriosi
- It is the first branch of the right coronary artery
- Supplies the conus arteriosus
- The conus arteriosus is part of the ventricular septum in the outflow tract of the right ventricle
- The conus arteriosus is also supplied by branches of the left coronary artery
Ramus nodi sinuatrialis
- Encircles the superior vena cava
- Supplies the SA node
- 70% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis from the right coronary artery
- 30% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis from the LCx (left coronary artery)
Rami atriales
- Supplies the right atrium
Rami ventriculares dextri
- Group of branches that supply the right ventricle
- Ramus ventricularis dextri anterior
- Ramus ventricularis dextri posterior
- Ramus marginalis dextri runs along the right border of the heart to the apex
- Their course is variable
- Sometimes they run forward, sometimes backward
- Most commonly there are 2 anterior and 2 posterior branches
- Sometimes the terminal branch may also supply the right atrium
Ramus interventricularis posterior (RIP)
- 70% of people have dominant right coronary artery, because RIP arises from it
- The dominant right artery through RIP supplies
- Inferior wall of the heart
- Posterior third of the ventricular septum
- AV node
- Bundle of His
Left Coronary Artery (LCA)

- 10% of people have dominant left coronary artery because RIP originates from it
- Left Coronary Artery branches into
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- Sometimes referred to as RIA
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- The heart is supplied by 3 arteries:
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- Proximal occlusion of the left coronary artery
Ramus Interventricularis Anterior (RIA) Supply
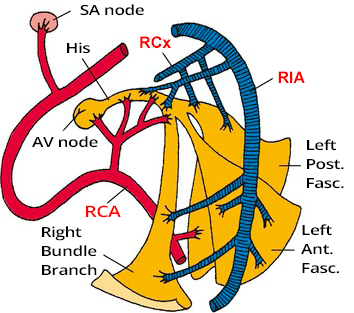
- Significant part of the conduction system
- Proximal branch supplies:
- RIA further has septal and diagonal branches which supply:
- Right bundle branch
- Anterior fascicle
- Sometimes the distal part of RIA also supplies the posterior fascicle
- Proximal occlusion of RIA has a very poor prognosis and can cause:
- Distal occlusion of RIA has a better prognosis and can cause:
Ramus circumflexus (RCx)
- Is the second major branch of the left coronary artery
- With left coronary artery dominance (10% of people)
- RIA arises directly from RCx
- Regardless of dominance, RCx always supplies
- lateral part of the left ventricle
- posterior part of the left ventricle
- Sometimes from RCx emerges ramus nodi sinuatrialis for SA node
- Posterior fascicle is supplied by
- RIP (with right coronary artery dominance)
- RCx
- Ischemic damage to the posterior fascicle is very rare
- Posterior fascicle has dual vascular supply and is thicker than the anterior fascicle
Left Coronary Artery (Branching)
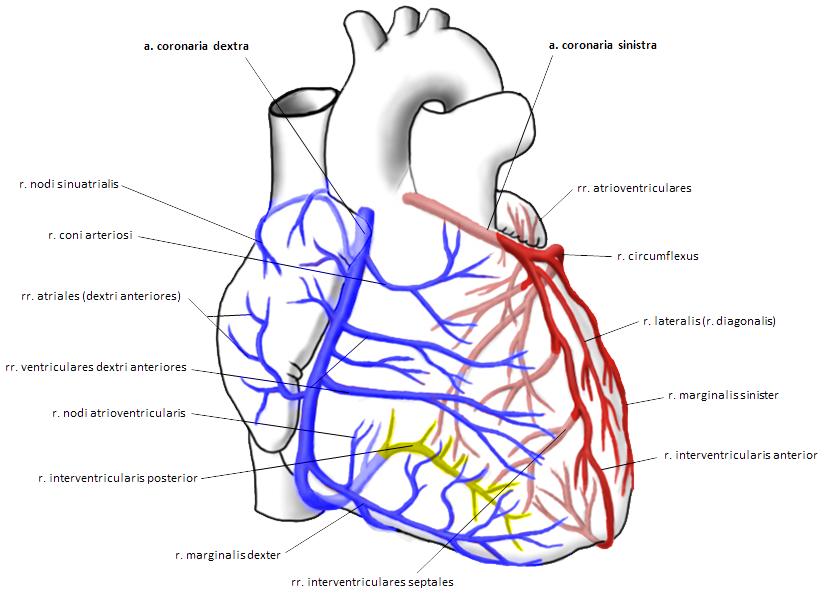
Ramus nodi sinuatrialis
- Supplies the SA node
- 30% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis originating from the left coronary artery
- 70% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis originating from the right coronary artery
Rami atrioventriculares
- Branches at the junction of the left atrium and ventricle
- Supply part of the left atrium and ventricle
Ramus lateralis (diagonalis)
- Is the first branch of RIA
- Supplies the marginal area of the left ventricle
- First branches of RIA are sometimes referred to as
- Rami ventriculares anteriores sinistri, with ramus lateralis (diagonalis) being the largest branch
Rami interventriculares septales anteriores
- Are distal branches of RIA
- Supply the anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum
- The posterior 1/3 is supplied by RIP
Ramus marginalis sinister
- Is a branch of RCx
- Runs along the left border of the heart, extending towards the apex of the heart
- Supplies the left border of the heart
- The right border of the heart is supplied by ramus marginalis dexter (branch of the right coronary artery)
Ramus interventricularis posterior (RIP)
- 10% of people have a dominant left coronary artery (because RIP originates from RIA)
- RCx via RIP supplies
- The inferior wall of the heart
- The posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum
- The AV node
- The His bundle
Arterial Supply of the Heart
- The heart is supplied by 3 main arteries:
- ACD (Arteria coronaria dextra)
- RIA (Ramus interventricularis anterior)
- RCx (Ramus circumflexus)
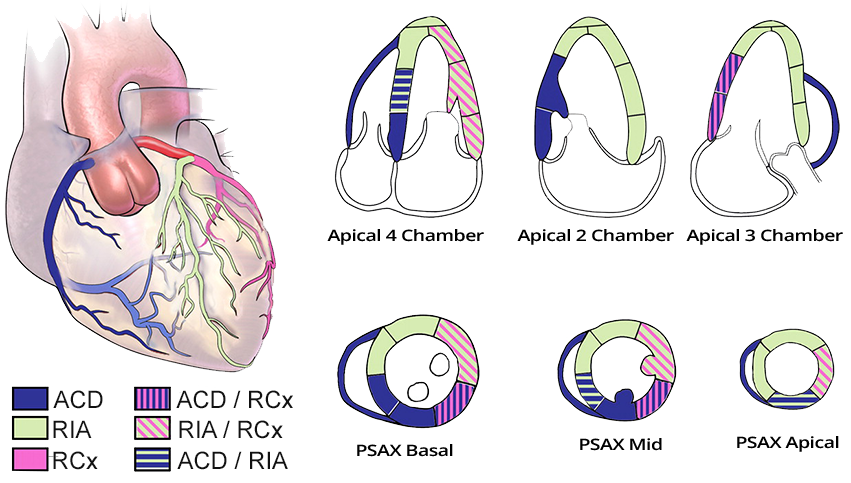
Arterial Supply of the Heart
- On transverse and longitudinal sections, you can see
- which parts of the heart are supplied by each artery
Veins of the Heart and Coronary Sinus
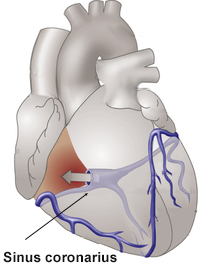
- Coronary Sinus
- Is the main collecting vessel for venous drainage of the heart
- Drains into the right atrium
- Into the coronary sinus drain
- Vena cordis magna (Drains blood from the left coronary artery)
- Vena cordis media (Drains blood from ramus interventricularis posterior)
- Vena cordis parva (Drains blood from the right coronary artery)
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers

Home /
Coronary Circulation
Coronary circulation, Coronary arteries and vessels
Conduction System of the Heart
- The conduction system is responsible for
- the generation and propagation of impulses throughout the working myocardium
- Certain parts are essential for heart function
- Especially the heart's pacemakers (SA node, AV node)
- This is why they have duplicate blood supply
- The conduction system includes:
- Sinoatrial (SA) Node (1)
- Bachmann's Bundle (2)
- Internodal Pathways (3,4,5)
- Anterior Internodal Pathway (James' Tract) (3)
- Middle Internodal Pathway (Wenckebach's Tract) (4)
- Posterior Internodal Pathway (Thorel's Tract) (5)
- Atrioventricular (AV) Junction (6,7)
- Atrioventricular (AV) Node (6)
- Bundle of His (7)
- Right Bundle Branch (8)
- Left Bundle Branch (9)
- Left Posterior Fascicle (10)
- Left Anterior Fascicle (11)
- Purkinje Fibers (12)
|

|
Right and Left Coronary Arteries
- The heart is supplied by 2 coronary arteries
- which originate just above the aortic valve from the aortic root
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- The right coronary artery
- Has larger primary branches because it supplies the right ventricle
- through which deoxygenated blood flows
- Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
- The left coronary artery
- After a short course, it divides into:
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- also known as the RIA, or
- Anterior interventricular branch.
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- LCx can be referred to by multiple terms:
- Circumflex artery (Cx or CX)
- Ramus circumflex artery (RCx or RCX)
- Left circumflex artery (LCx or LCX)
- The course and branching pattern of coronary arteries are variable
- The left and right coronary arteries have minimal anastomoses (connections)
- In case of occlusion of the main stem or branch of one artery
- It leads to ischemia up to myocardial infarction beyond the occlusion (occlusion = 100% stenosis)
|

|
Ramus Interventricularis Posterior and Anterior
- Ramus Interventricularis Posterior (RIP) supplies
- The inferior part of the heart
- The posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum, where the AV node is located
- RIP is responsible for the function of the AV node
- RIP can be a branch of the left or right coronary artery
- Ramus Interventricularis Anterior (RIA) supplies
- The anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum
- RIA is a branch of the left coronary artery
|

|
Coronary Artery Dominance
- Coronary artery dominance is determined by the ramus interventricularis posterior (RIP)
Coronary Artery Dominance
- Right coronary artery dominance
- 70% of people have a dominant right coronary artery
- RIP originates from the right coronary artery
- Left coronary artery dominance
- 10% of people have a dominant left coronary artery
- RIP originates from the left coronary artery
- Codominance of coronary arteries
- 20% of people exhibit codominance
- RIP receives dual supply from both left and right coronary arteries
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- In 70% of people, it is dominant because RIP originates from it
- Proximal occlusion of the dominant right coronary artery (RCA)
|

|
Right Coronary Artery Supplies
- Right ventricle except the apex
- Apex of the heart is supplied by RIA
- Right atrium
- Conus arteriosus (part of the right ventricular outflow tract)
- along with branches from the left coronary artery
- SA node in 60% of people
- 40% of people have SA node supplied by RCx
- 30% of the left ventricle in the posterior part near the ventricular septum
- If dominant, it gives rise to RIP which supplies
- Inferior wall of the heart
- Posterior 1/3 of the ventricular septum
- AV node
- His bundle
|

|
Right Coronary Artery (Branching)

Ramus coni arteriosi
- It is the first branch of the right coronary artery
- Supplies the conus arteriosus
- The conus arteriosus is part of the ventricular septum in the outflow tract of the right ventricle
- The conus arteriosus is also supplied by branches of the left coronary artery
Ramus nodi sinuatrialis
- Encircles the superior vena cava
- Supplies the SA node
- 70% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis from the right coronary artery
- 30% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis from the LCx (left coronary artery)
Rami atriales
- Supplies the right atrium
Rami ventriculares dextri
- Group of branches that supply the right ventricle
- Ramus ventricularis dextri anterior
- Ramus ventricularis dextri posterior
- Ramus marginalis dextri runs along the right border of the heart to the apex
- Their course is variable
- Sometimes they run forward, sometimes backward
- Most commonly there are 2 anterior and 2 posterior branches
- Sometimes the terminal branch may also supply the right atrium
Ramus interventricularis posterior (RIP)
- 70% of people have dominant right coronary artery, because RIP arises from it
- The dominant right artery through RIP supplies
- Inferior wall of the heart
- Posterior third of the ventricular septum
- AV node
- Bundle of His
Left Coronary Artery (LCA)
- 10% of people have dominant left coronary artery because RIP originates from it
- Left Coronary Artery branches into
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- Sometimes referred to as RIA
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- The heart is supplied by 3 arteries:
- Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
- Left Anterior Descending Artery (LAD)
- Left Circumflex Artery (LCx)
- Proximal occlusion of the left coronary artery
|

|
Ramus Interventricularis Anterior (RIA) Supply
- Significant part of the conduction system
- Proximal branch supplies:
- RIA further has septal and diagonal branches which supply:
- Right bundle branch
- Anterior fascicle
- Sometimes the distal part of RIA also supplies the posterior fascicle
- Proximal occlusion of RIA has a very poor prognosis and can cause:
- Distal occlusion of RIA has a better prognosis and can cause:
|

|
Ramus circumflexus (RCx)
- Is the second major branch of the left coronary artery
- With left coronary artery dominance (10% of people)
- RIA arises directly from RCx
- Regardless of dominance, RCx always supplies
- lateral part of the left ventricle
- posterior part of the left ventricle
- Sometimes from RCx emerges ramus nodi sinuatrialis for SA node
- Posterior fascicle is supplied by
- RIP (with right coronary artery dominance)
- RCx
- Ischemic damage to the posterior fascicle is very rare
- Posterior fascicle has dual vascular supply and is thicker than the anterior fascicle
Left Coronary Artery (Branching)

Ramus nodi sinuatrialis
- Supplies the SA node
- 30% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis originating from the left coronary artery
- 70% of people have ramus nodi sinuatrialis originating from the right coronary artery
Rami atrioventriculares
- Branches at the junction of the left atrium and ventricle
- Supply part of the left atrium and ventricle
Ramus lateralis (diagonalis)
- Is the first branch of RIA
- Supplies the marginal area of the left ventricle
- First branches of RIA are sometimes referred to as
- Rami ventriculares anteriores sinistri, with ramus lateralis (diagonalis) being the largest branch
Rami interventriculares septales anteriores
- Are distal branches of RIA
- Supply the anterior 2/3 of the interventricular septum
- The posterior 1/3 is supplied by RIP
Ramus marginalis sinister
- Is a branch of RCx
- Runs along the left border of the heart, extending towards the apex of the heart
- Supplies the left border of the heart
- The right border of the heart is supplied by ramus marginalis dexter (branch of the right coronary artery)
Ramus interventricularis posterior (RIP)
- 10% of people have a dominant left coronary artery (because RIP originates from RIA)
- RCx via RIP supplies
- The inferior wall of the heart
- The posterior 1/3 of the interventricular septum
- The AV node
- The His bundle
Arterial Supply of the Heart
- The heart is supplied by 3 main arteries:
- ACD (Arteria coronaria dextra)
- RIA (Ramus interventricularis anterior)
- RCx (Ramus circumflexus)

Arterial Supply of the Heart
- On transverse and longitudinal sections, you can see
- which parts of the heart are supplied by each artery
Veins of the Heart and Coronary Sinus
- Coronary Sinus
- Is the main collecting vessel for venous drainage of the heart
- Drains into the right atrium
- Into the coronary sinus drain
- Vena cordis magna (Drains blood from the left coronary artery)
- Vena cordis media (Drains blood from ramus interventricularis posterior)
- Vena cordis parva (Drains blood from the right coronary artery)
|

|
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers