Home /
Digoxin Toxicity - ECG
Digoxin toxicity, Digitalis toxicity
Therapeutic Window of Digoxin

- Digoxin is used for:
- Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic window
- The therapeutic plasma level is 0.5 - 1.5ng/ml
- A level of < 0.5ng/ml is ineffective
- A level of > 2ng/ml is toxic and poses a risk of cardiac arrhythmias
ECG and Digoxin
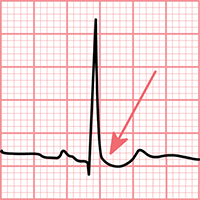
- ECG changes can occur even at therapeutic levels of digoxin
- The patient is not digoxin-intoxicated
- Changes are mainly in leads with high R waves (I, V5, V6)
- Digoxin affects repolarization (ST segment and T wave)
- Main ECG signs
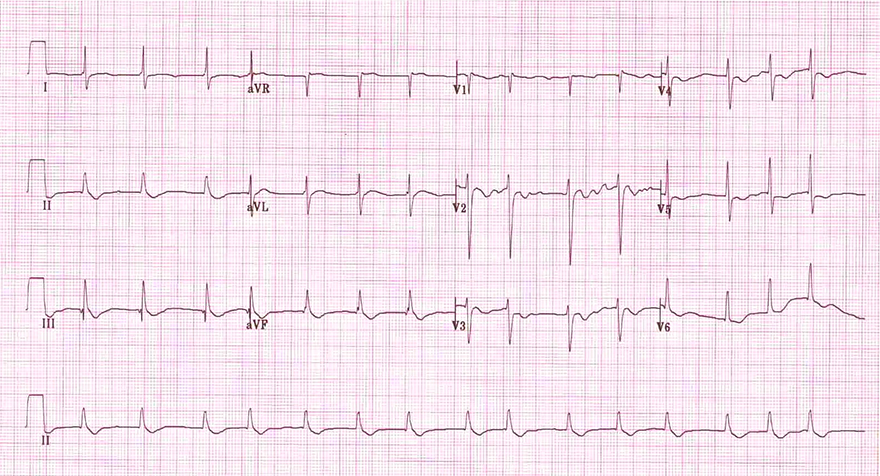
Digoxin and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Fibrillation
- The heart rate is irregularly irregular
- No P waves are visible
- Downsloping ST depression (II, III, aVF, V5, V6)
- The patient is not digoxin-intoxicated
- Flat to negative T waves (in all leads)
Digoxin Toxicity
- In digoxin toxicity (> 2ng/ml), changes occur in the conduction system:
- Most commonly,
- Digoxin toxicity is worsened by:
ECG and Digoxin Toxicity
- Digoxin toxicity does not have a single characteristic ECG pattern
- Most common arrhythmias in digoxin toxicity:
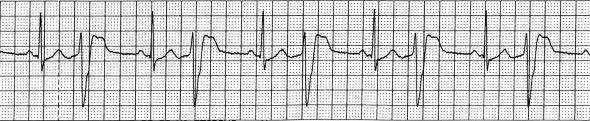
Digoxin Toxicity and Ventricular Bigeminy
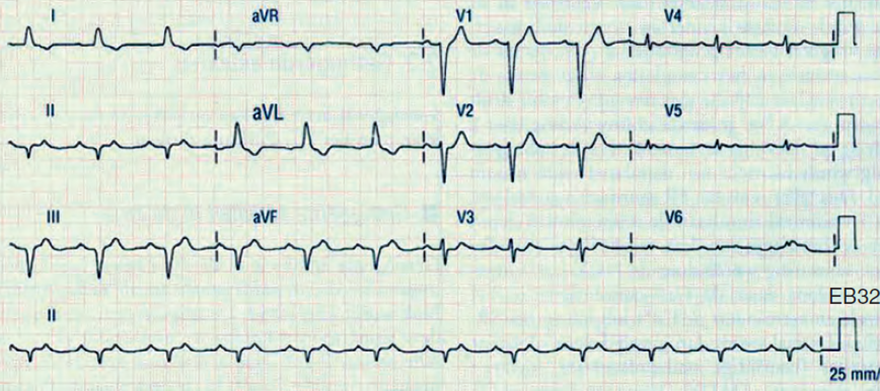
Digoxin Toxicity, Focal Atrial Tachycardia, and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)
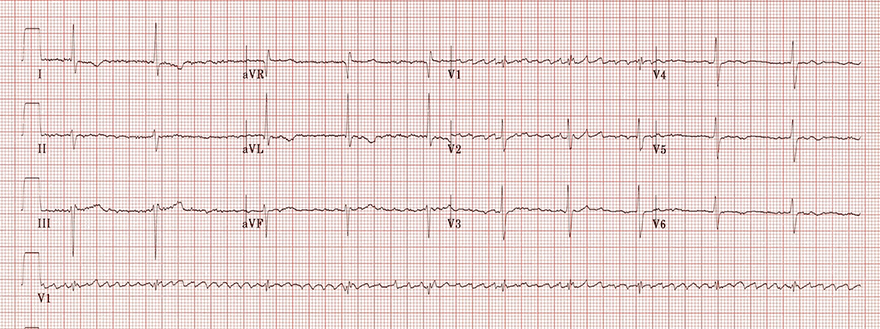
Digoxin Toxicity and Controlled Atrial Fibrillation
- Frequency of atria approximately 400/min.
- Regular QRS complex frequency 60/min.
- Atrial fibrillation almost always has an irregular ventricular response
- Third-degree AV block
- Atria and ventricles are electrically isolated from each other
- An escape junctional rhythm with a frequency of 60/min. is activated
- The patient was digoxin toxic
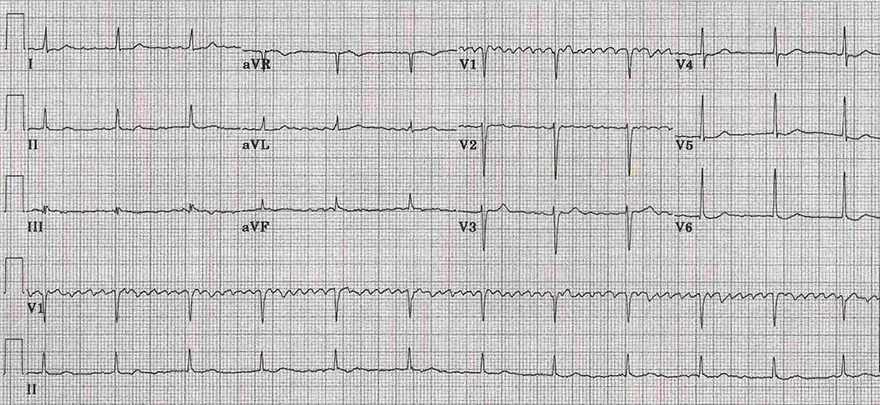
Digoxin Toxicity and Controlled Atrial Fibrillation
- Frequency of atria approximately 400/min.
- Regular QRS complex frequency 75/min.
- Atrial fibrillation almost always has an irregular ventricular response
- Third-degree AV block
- Atria and ventricles are electrically isolated from each other
- An escape junctional rhythm with a frequency of 75/min. is activated
- The patient was digoxin toxic
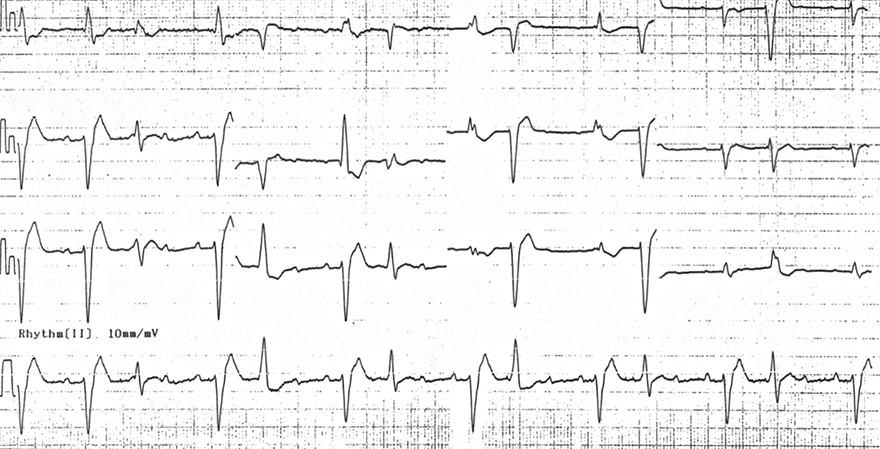
Digoxin Toxicity, Focal Atrial Tachycardia, AV Block, Bigeminy
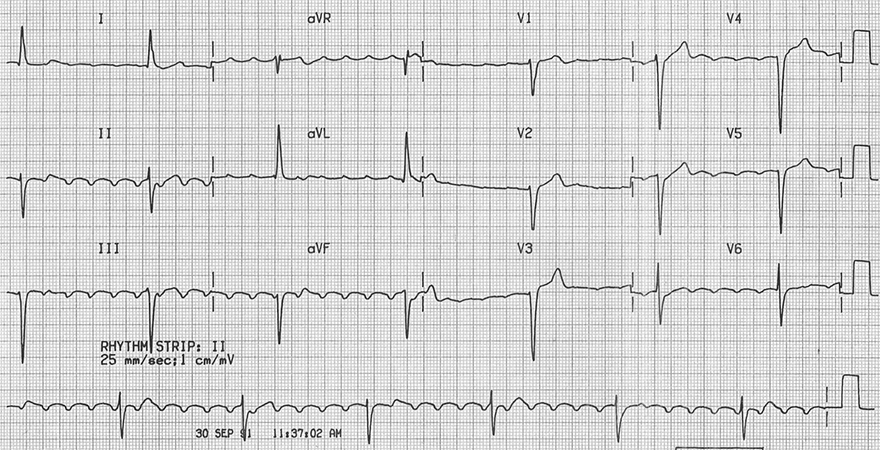
Digoxin Toxicity and Atrial Flutter
- Frequency of F waves: 300/min.
- F waves have the characteristic "sawtooth" appearance
- Atrial flutter always has an F wave frequency of approximately 300/min.
- Conduction to the ventricles: 5:1, indicating slow conduction to the ventricles
- Every 5th F wave is followed by a QRS complex
- The patient was digoxin toxic
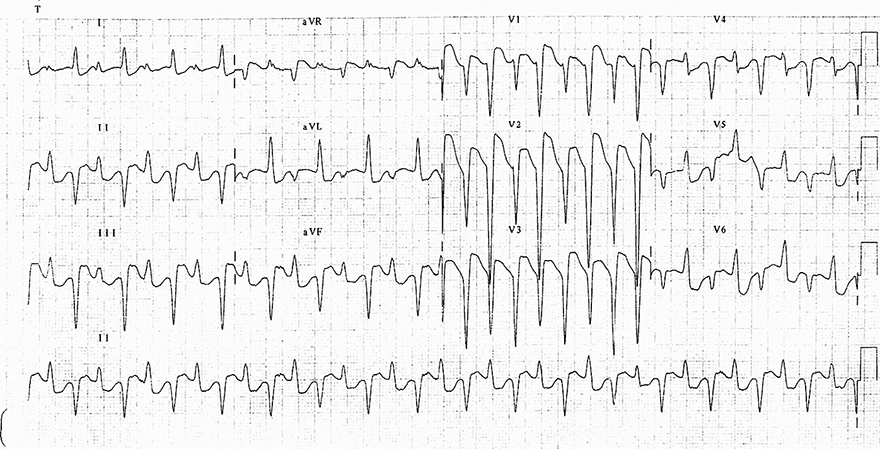
Digoxin Toxicity and Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia
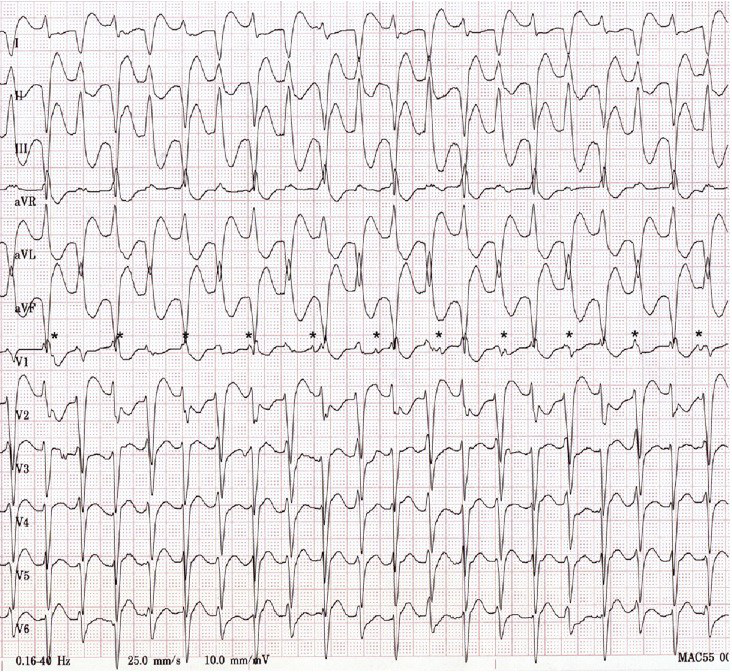
Digoxin Toxicity and Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia
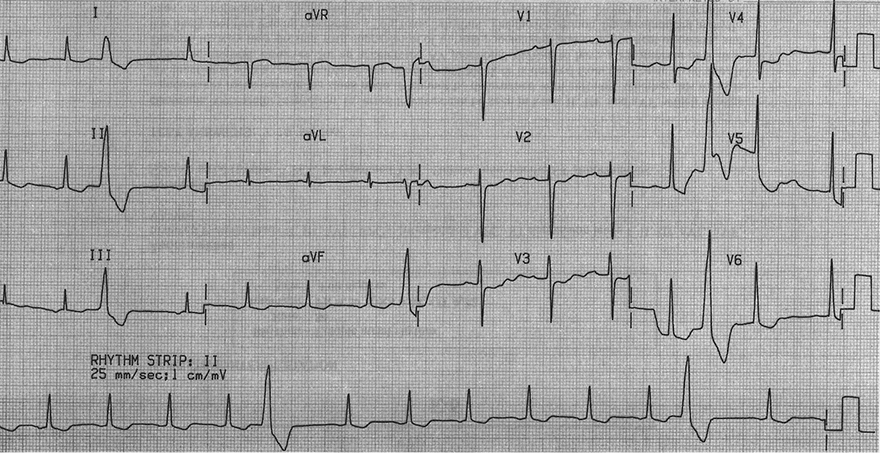
Digoxin and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus Rhythm
- P wave is before the QRS complex (V1)
- Downsloping ST depressions (I, II, III, aVF, V5-V6)
- These are characteristic of digoxin use, the patient was not digoxin toxic
- Numerous ventricular extrasystoles
- which may indicate a borderline elevated level of digoxin
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers
Home /
Digoxin Toxicity - ECG
Digoxin toxicity, Digitalis toxicity
Therapeutic Window of Digoxin
- Digoxin is used for:
- Digoxin has a narrow therapeutic window
- The therapeutic plasma level is 0.5 - 1.5ng/ml
- A level of < 0.5ng/ml is ineffective
- A level of > 2ng/ml is toxic and poses a risk of cardiac arrhythmias
|

|
ECG and Digoxin
- ECG changes can occur even at therapeutic levels of digoxin
- The patient is not digoxin-intoxicated
- Changes are mainly in leads with high R waves (I, V5, V6)
- Digoxin affects repolarization (ST segment and T wave)
- Main ECG signs
|

|

Digoxin and Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Fibrillation
- The heart rate is irregularly irregular
- No P waves are visible
- Downsloping ST depression (II, III, aVF, V5, V6)
- The patient is not digoxin-intoxicated
- Flat to negative T waves (in all leads)
Digoxin Toxicity
- In digoxin toxicity (> 2ng/ml), changes occur in the conduction system:
- Most commonly,
- Digoxin toxicity is worsened by:
ECG and Digoxin Toxicity
- Digoxin toxicity does not have a single characteristic ECG pattern
- Most common arrhythmias in digoxin toxicity:

Digoxin Toxicity and Ventricular Bigeminy

Digoxin Toxicity, Focal Atrial Tachycardia, and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)

Digoxin Toxicity and Controlled Atrial Fibrillation
- Frequency of atria approximately 400/min.
- Regular QRS complex frequency 60/min.
- Atrial fibrillation almost always has an irregular ventricular response
- Third-degree AV block
- Atria and ventricles are electrically isolated from each other
- An escape junctional rhythm with a frequency of 60/min. is activated
- The patient was digoxin toxic

Digoxin Toxicity and Controlled Atrial Fibrillation
- Frequency of atria approximately 400/min.
- Regular QRS complex frequency 75/min.
- Atrial fibrillation almost always has an irregular ventricular response
- Third-degree AV block
- Atria and ventricles are electrically isolated from each other
- An escape junctional rhythm with a frequency of 75/min. is activated
- The patient was digoxin toxic

Digoxin Toxicity, Focal Atrial Tachycardia, AV Block, Bigeminy

Digoxin Toxicity and Atrial Flutter
- Frequency of F waves: 300/min.
- F waves have the characteristic "sawtooth" appearance
- Atrial flutter always has an F wave frequency of approximately 300/min.
- Conduction to the ventricles: 5:1, indicating slow conduction to the ventricles
- Every 5th F wave is followed by a QRS complex
- The patient was digoxin toxic

Digoxin Toxicity and Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia

Digoxin Toxicity and Bidirectional Ventricular Tachycardia

Digoxin and Sinus Rhythm
- Sinus Rhythm
- P wave is before the QRS complex (V1)
- Downsloping ST depressions (I, II, III, aVF, V5-V6)
- These are characteristic of digoxin use, the patient was not digoxin toxic
- Numerous ventricular extrasystoles
- which may indicate a borderline elevated level of digoxin
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers























