
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
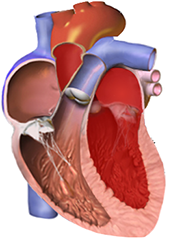
Physiological Myocardium

Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
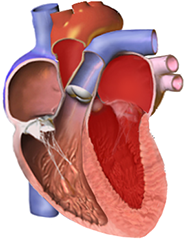
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
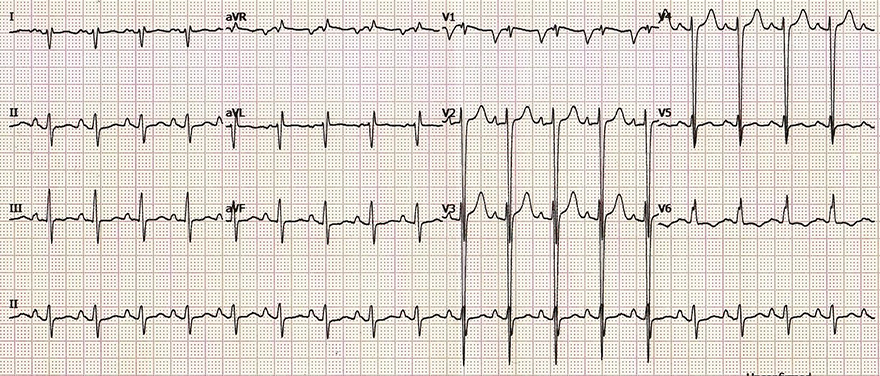
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
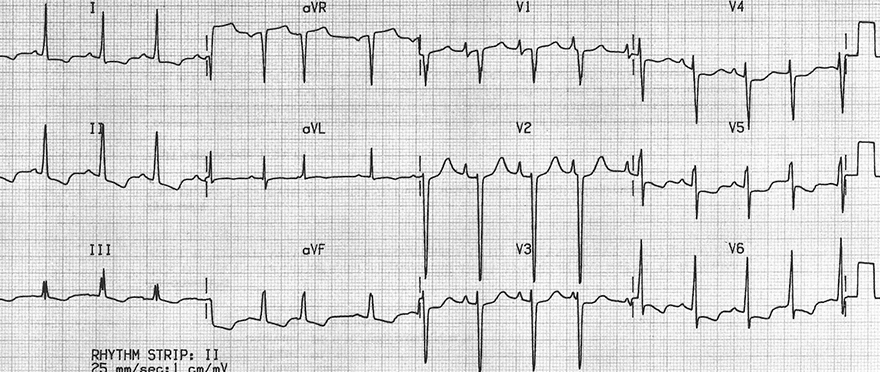
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
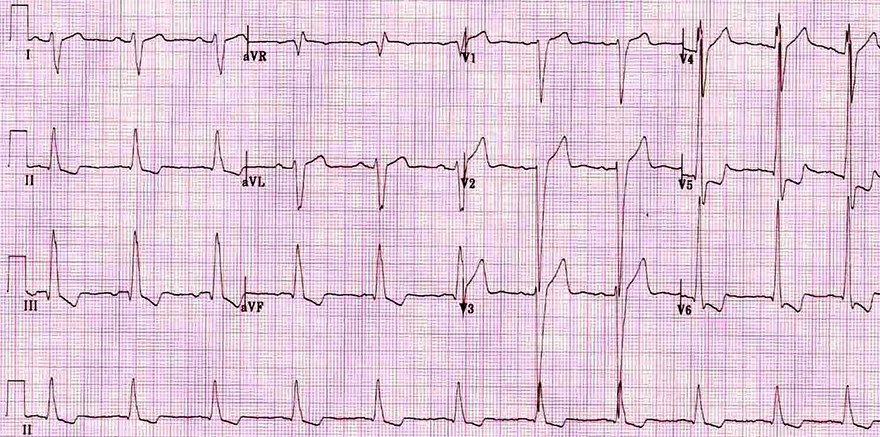
Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Sources

Physiological Myocardium
|

Dilated Cardiomyopathy
|

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
|

Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
|

Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Dilated Cardiomyopathy

Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Sources