
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
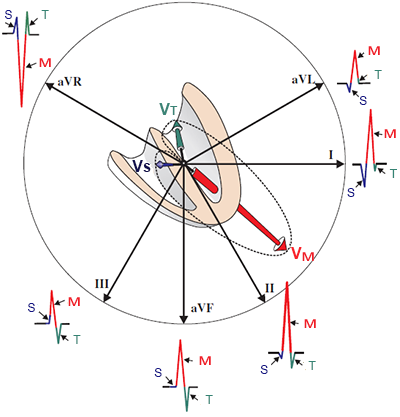
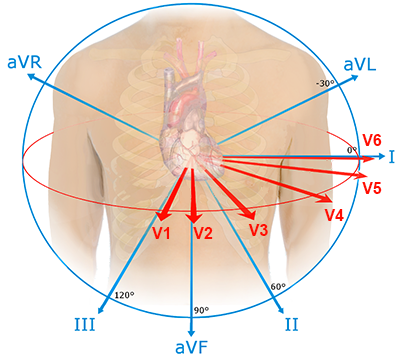
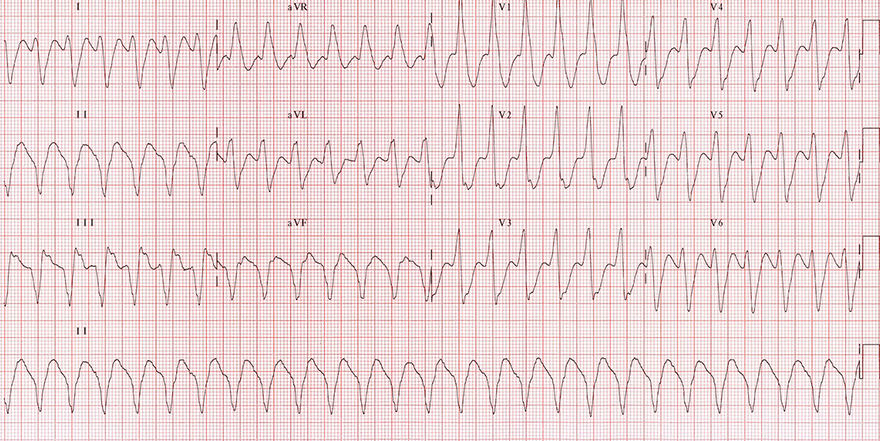
Ventricular Tachycardia
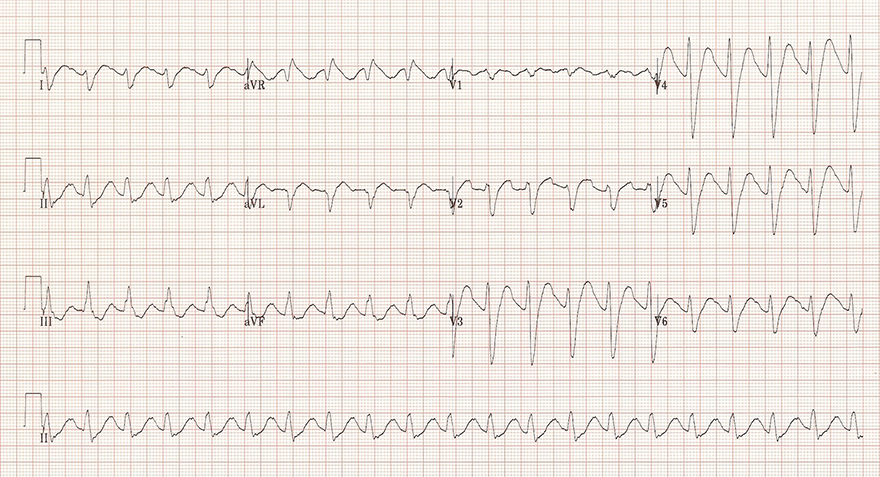
Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

Dextrocardia
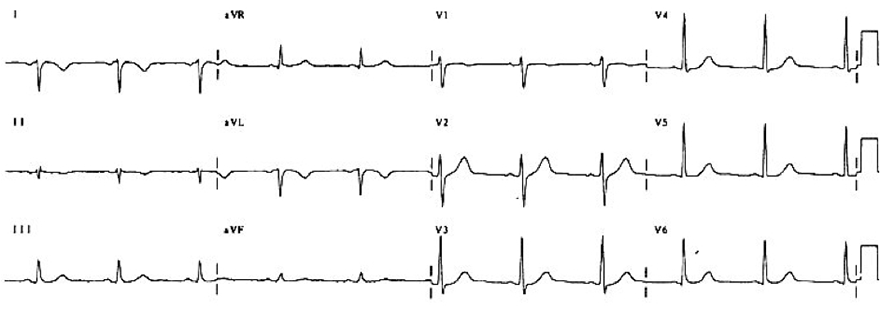
Swapped ECG Leads (Left and Right Arm)
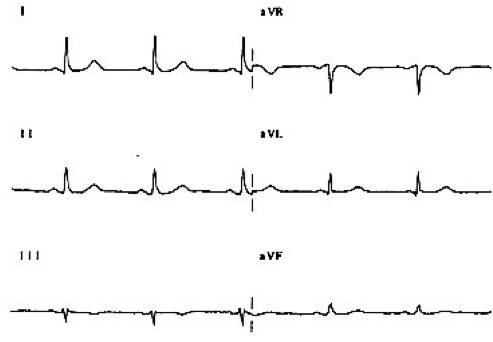
Correctly Placed Limb ECG Leads
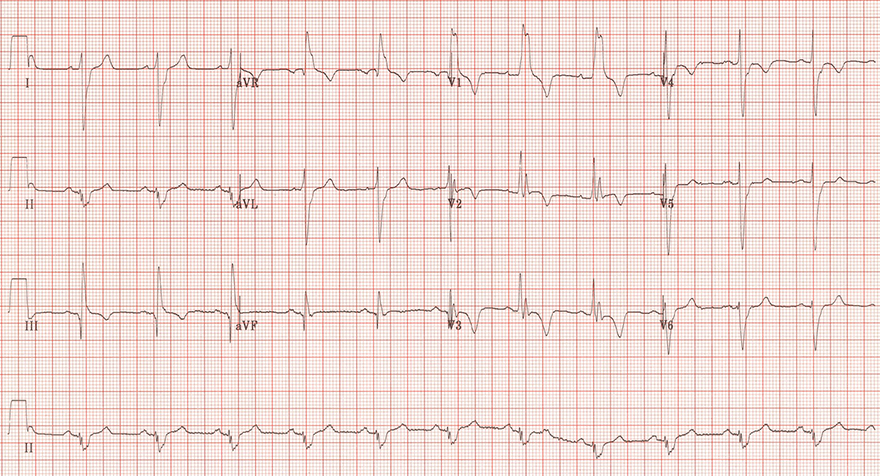
Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Sources
Limb Leads and R Wave
|
 |
Pathological R Wave
|
 |
ECG and Dominant R Wave in aVR
|
 Ventricular Tachycardia |

Ventricular Tachycardia

Tricyclic Antidepressants (Intoxication)

Dextrocardia

Swapped ECG Leads (Left and Right Arm)

Correctly Placed Limb ECG Leads

Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Sources