
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Sinus Tachycardia (2-Year-Old Child)

Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
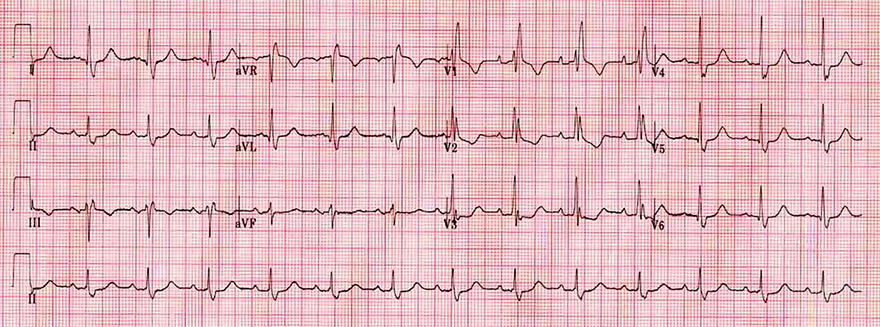
Right Tawar Bundle Branch Block
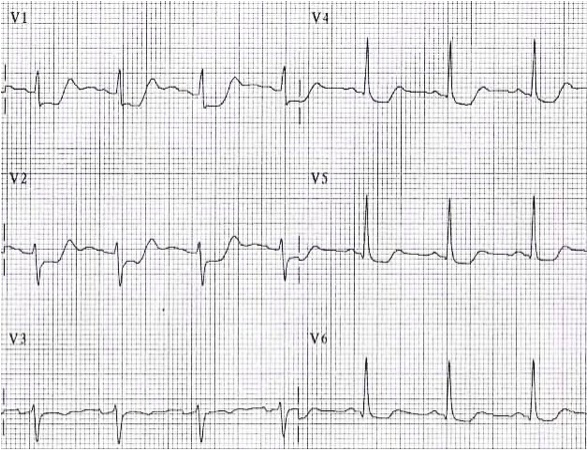
STEMI of the Posterior Wall
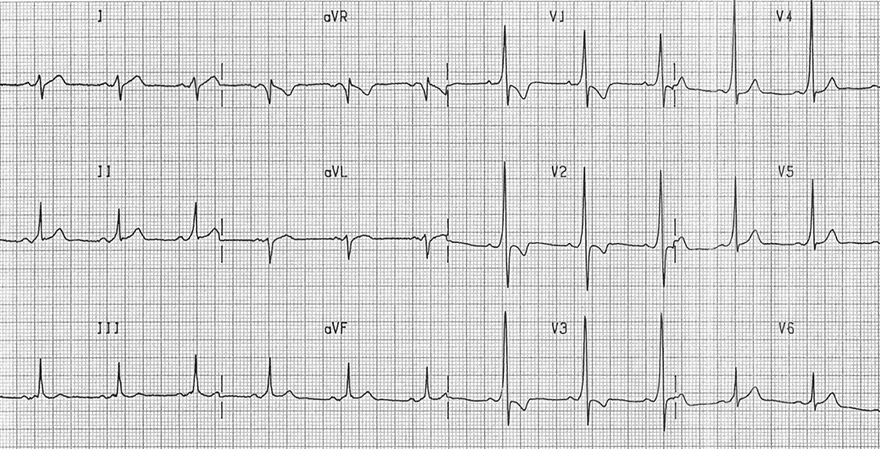
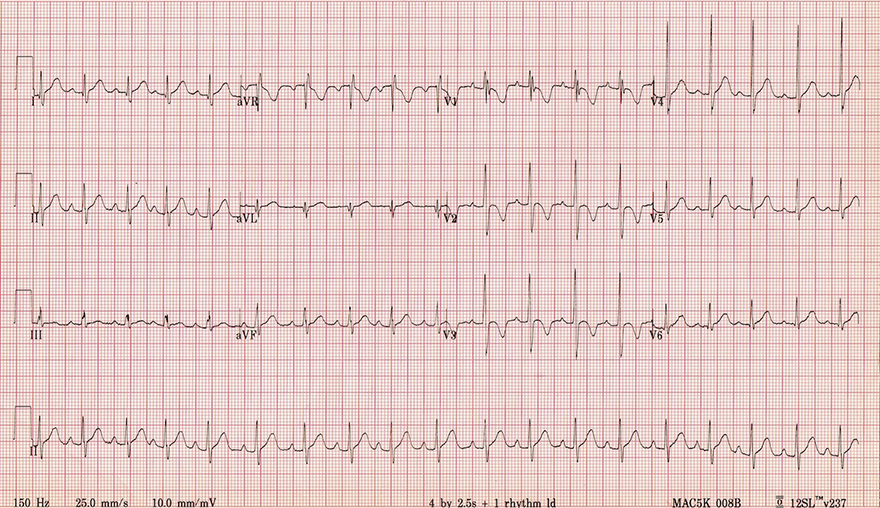
WPW Syndrome (Type A)

Swapped Leads V1 and V3

Dextrocardia
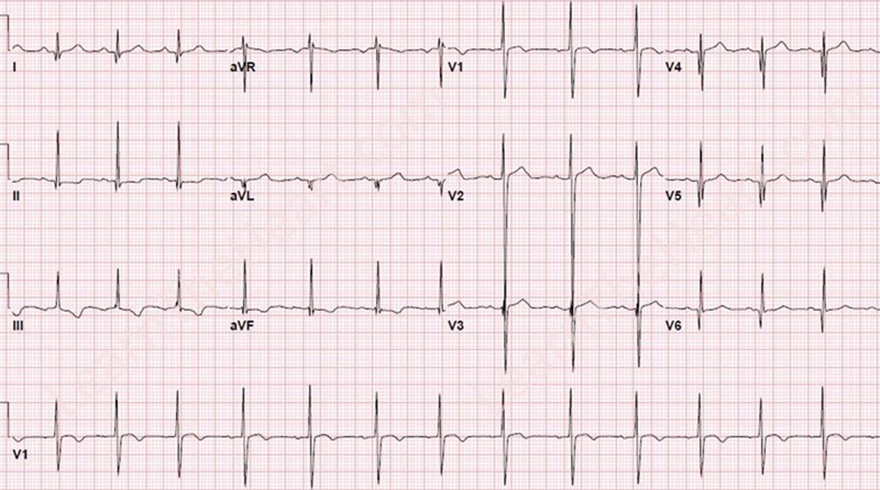
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
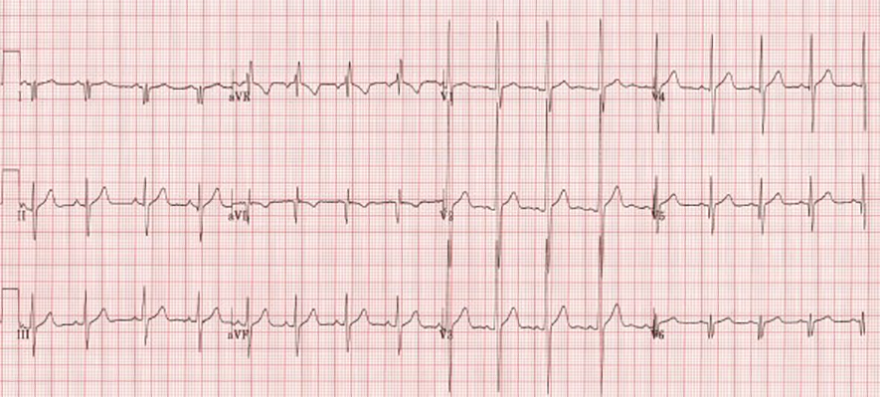
Muscular Dystrophy
Sources
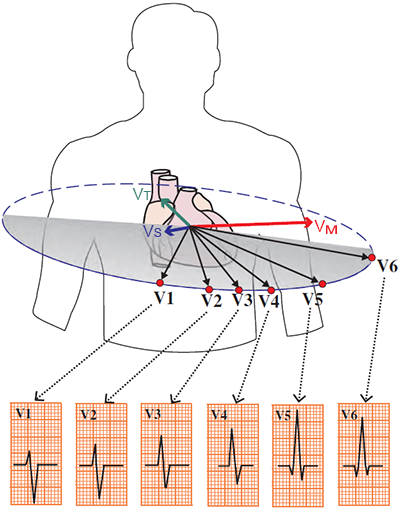
Precordial Leads and R Wave
|
 |
Pathological R Wave
|
 |
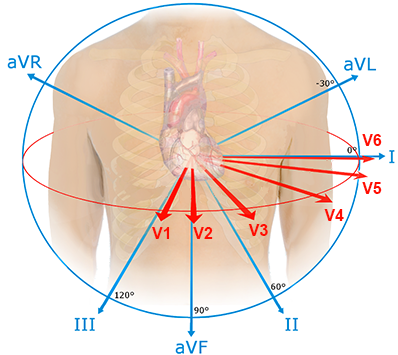
ECG and Dominant R Wave in V1
|
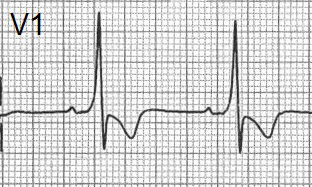 WPW Syndrome (Type A) |

Sinus Tachycardia (2-Year-Old Child)

Right Ventricular Hypertrophy

Right Tawar Bundle Branch Block

STEMI of the Posterior Wall

WPW Syndrome (Type A)

Swapped Leads V1 and V3

Dextrocardia

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy

Muscular Dystrophy
Sources