
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

| Posi- tion | I | II | III | IV | V |
| Cham- ber(s) Paced |
Cham- ber(s) Sensed |
Response to Sensing |
Rate Modula- tion |
Multisite Pacing |
|
| O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | |
| A = Atrium | A = Atrium | T = Triggered | R = Rate Modula- tion |
A = Atrium | |
| V = Ventricle | V = Ventricle | I = Inhibited | V = Ventricle | ||
| D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (T+I) | D = Dual (A+V) |

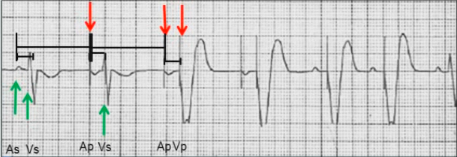
DDD pacing

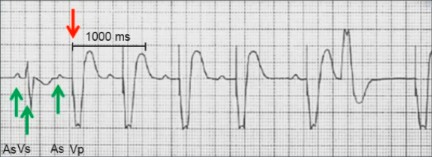
DDD Mode (AsVs)

DDD Mode (AsVp)

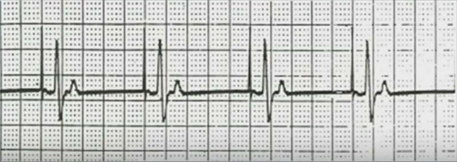
DDD Mode (ApVs)

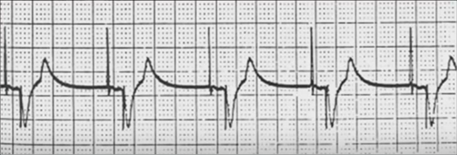
DDD Mode (ApVp)

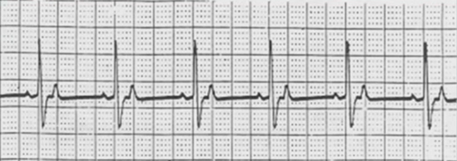
VDD Pacing

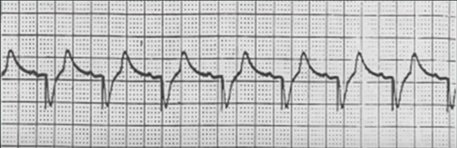
DDI Pacing

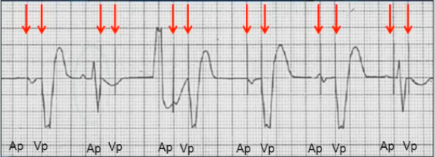
DOO Pacing

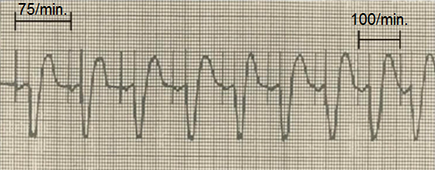
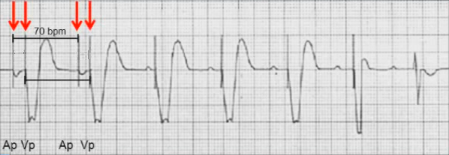
DDDR Pacing (ApVp)
Sources
Pacemaker
|

|
| Position | I | II | III | IV | V |
| Chamber(s) Paced |
Chamber(s) Sensed |
Response to Sensing |
Rate Modulation |
Multisite Pacing |
|
| O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | O = Off | |
| A = Atrium | A = Atrium | T = Triggered | R = Rate Modulation |
A = Atrium | |
| V = Ventricle | V = Ventricle | I = Inhibited | V = Ventricle | ||
| D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (A+V) | D = Dual (T+I) | D = Dual (A+V) |
Dual-Chamber Pacemaker Modes
|

|

|

|
DDD pacing

|

|
DDD Mode (AsVs)

|

|
DDD Mode (AsVp)

|

|
DDD Mode (ApVs)

|

|
DDD Mode (ApVp)

|

|
VDD Pacing

|

|
DDI Pacing

|

|
DOO Pacing
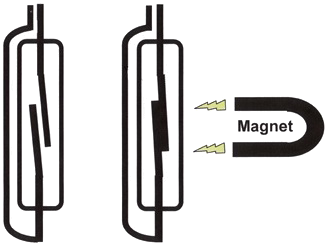
Magnet a Pacemaker
|

|

|

|
DDDR Pacing (ApVp)
Sources