
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
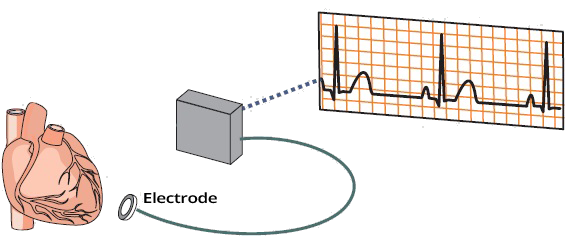
Millivolts and the ECG Curve


Calibration Mark and ECG Paper

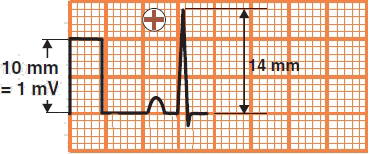


Calibration 10mm
Calibration 5mm

Calibration 20mm
Paper speed 25mm/s
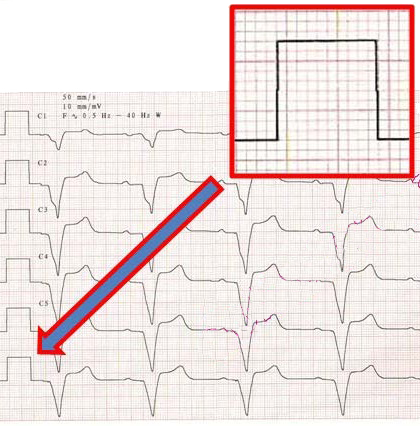
Paper speed 50mm/s
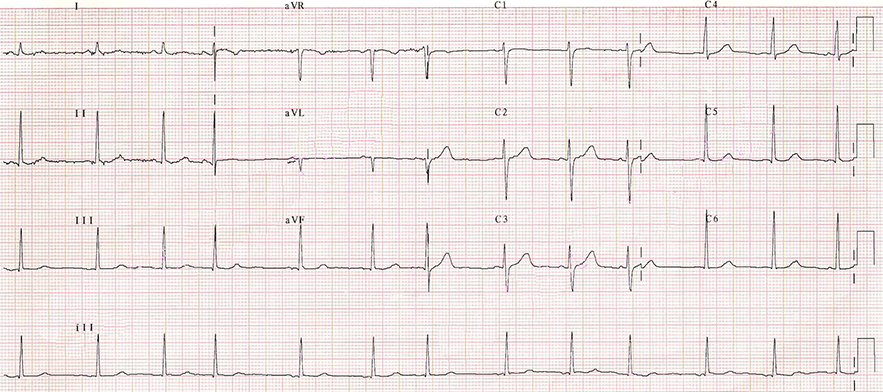
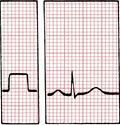
Standard Calibration 10mm
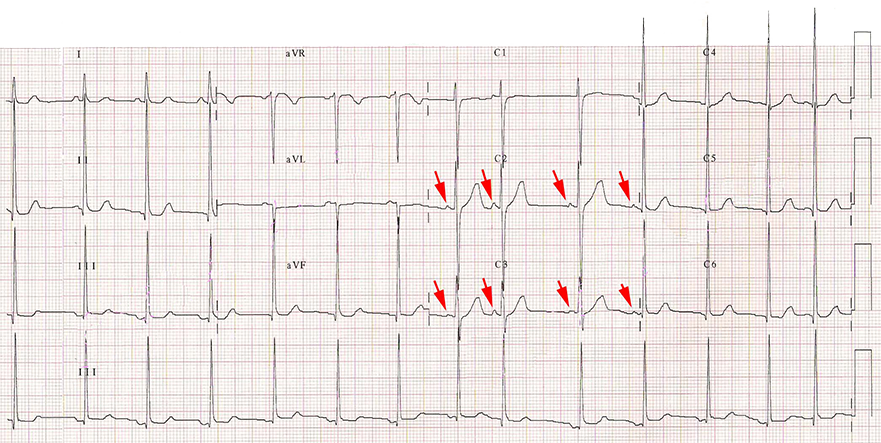
Calibration 20mm
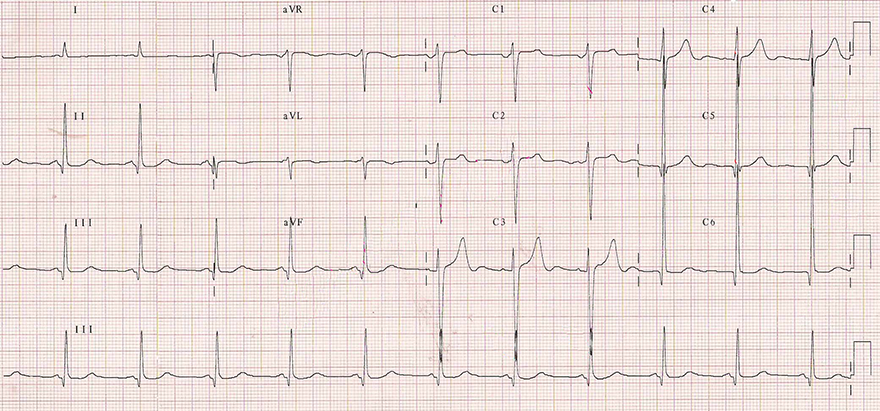
Calibration 10mm
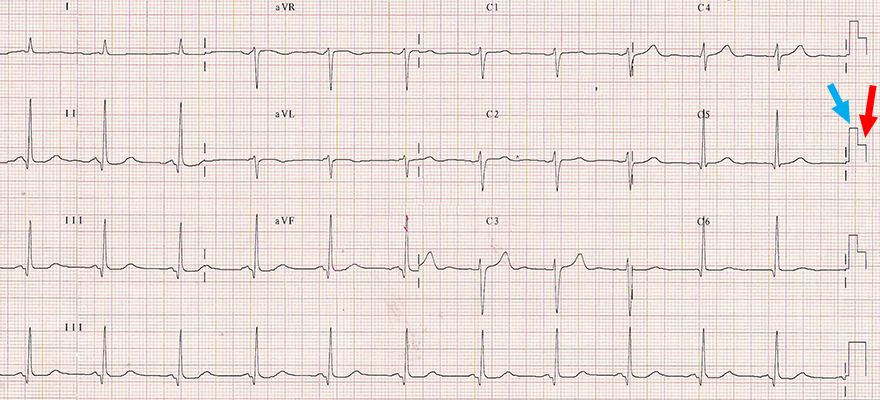
Dual Calibration 10/5mm

Calibration 10mm
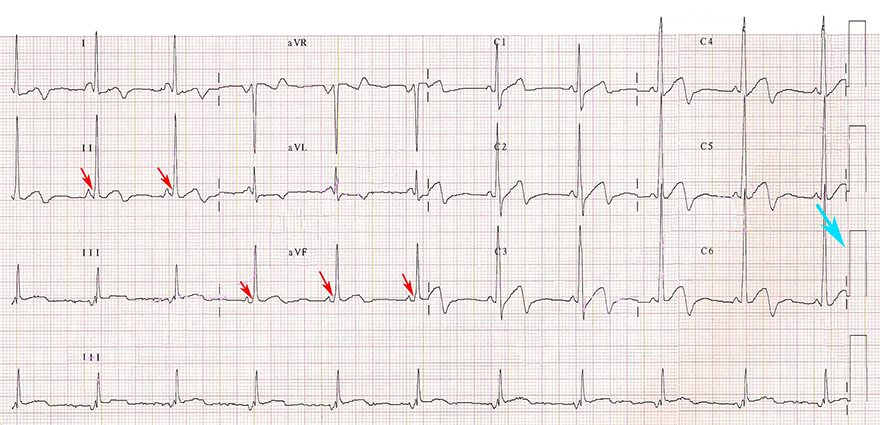
Calibration 20mm
Sources

Millivolts and the ECG Curve
|

|

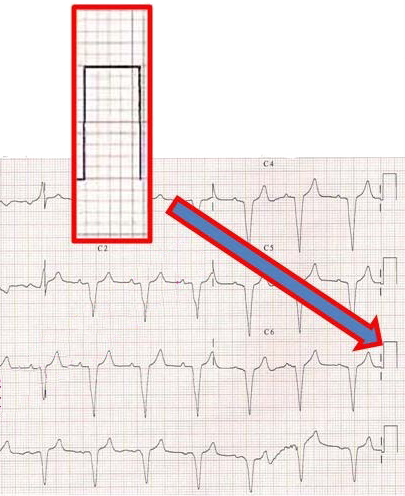
Calibration Mark and ECG Paper
Calibration Mark
|

|
ECG Amplitude
|
 
|

Calibration 10mm
|

Calibration 5mm
|

Calibration 20mm
|

|

|
|
Paper speed 25mm/s
|
Paper speed 50mm/s
|

Standard Calibration 10mm

Calibration 20mm

Calibration 10mm

Dual Calibration 10/5mm

Calibration 10mm

Calibration 20mm
Sources