Home /
ECG patterns of depolarization during ventricular pacing


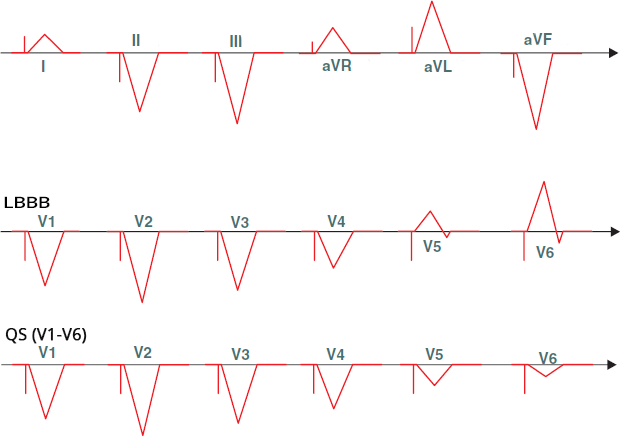
Ventricular Pacing from the Right Ventricular Apex

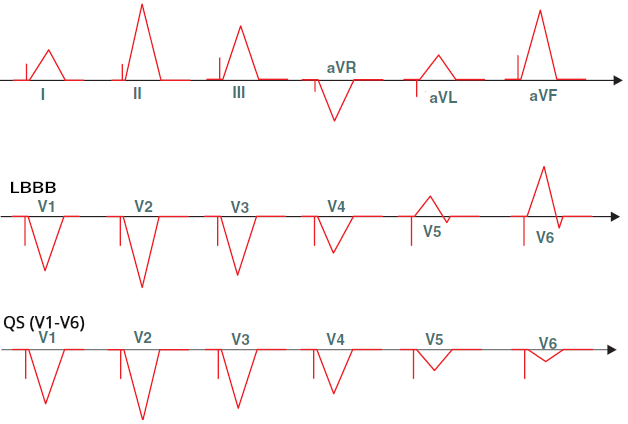
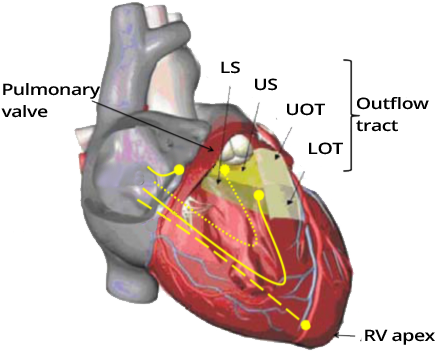
Ventricular Pacing from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract


Ventricular Pacing from the Left Ventricle

Biventricular Ventricular Pacing
Sources
Home /
ECG patterns of depolarization during ventricular pacing
Ventricular Electrode
|

|
|

|
|

|

Ventricular Pacing from the Right Ventricular Apex
|

|

Ventricular Pacing from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
|

|

Ventricular Pacing from the Left Ventricle

Biventricular Ventricular Pacing
Sources