




Negative Hemisphere and Negative Deflection

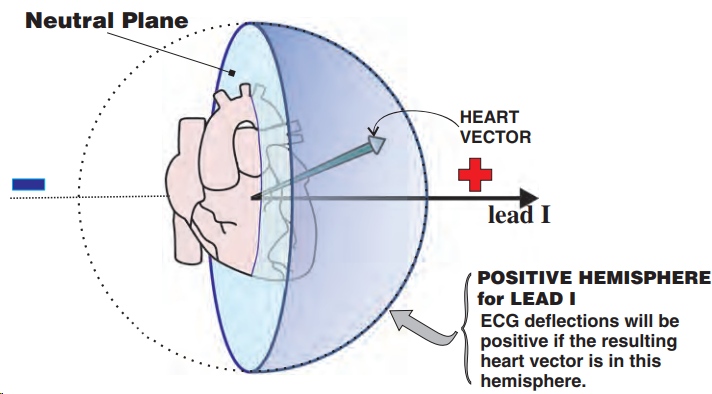
Positive Hemisphere and Positive Deflection

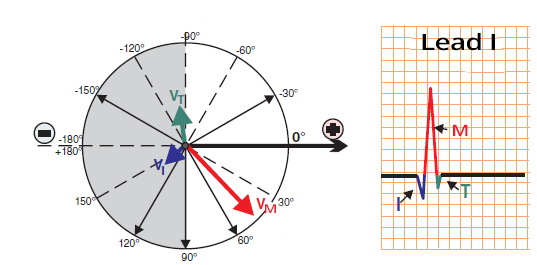
I Limb Lead
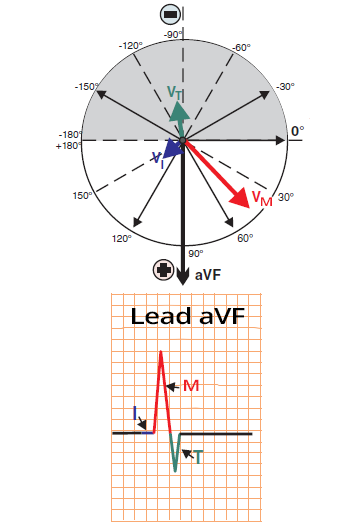
aVF Limb Lead
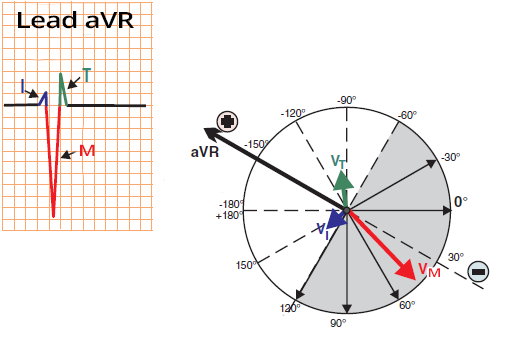
aVR Limb Lead

Limb Leads
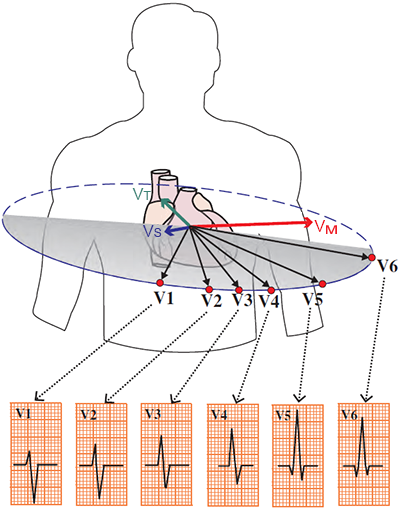
Chest Leads
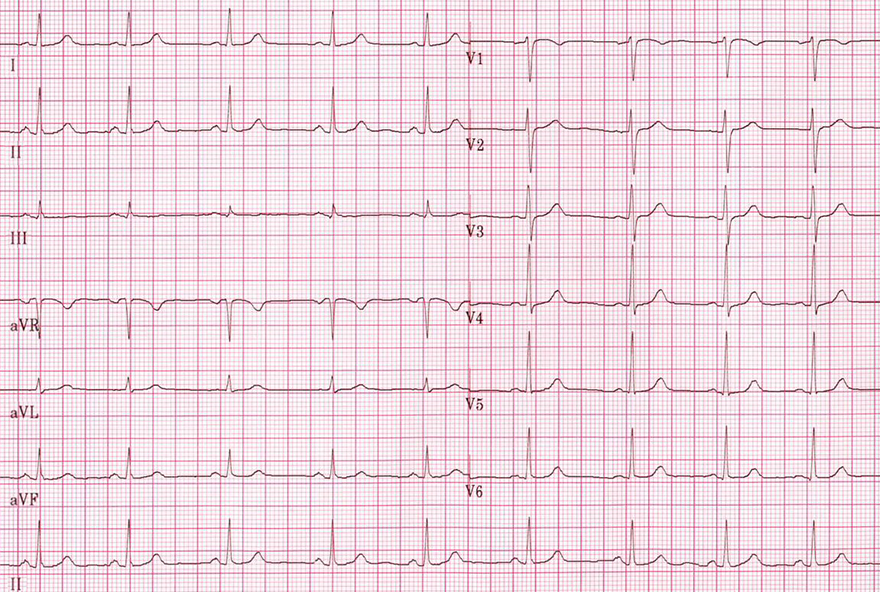
Sinus Rhythm
Sources
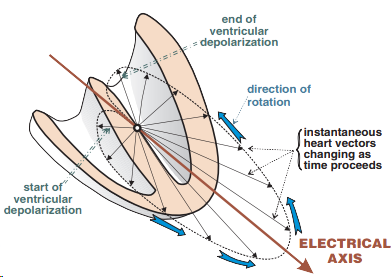
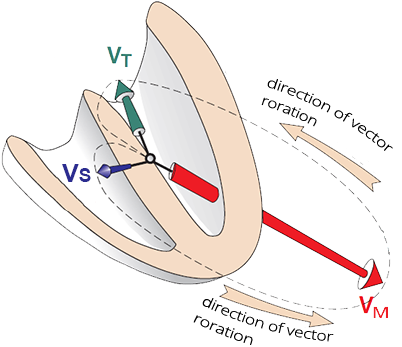
Ventricular Depolarization
|

|
Electrical Axis of the Heart
|

|
ECG Leads
|

|
Limb ECG Leads
|

|


|
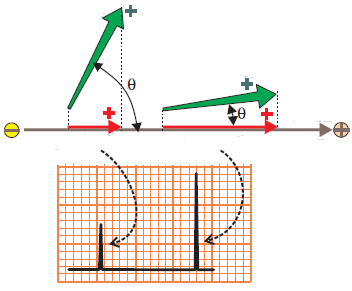
Positive and Negative ECG Deflections
|

|
Size of the ECG Deflection
|

|
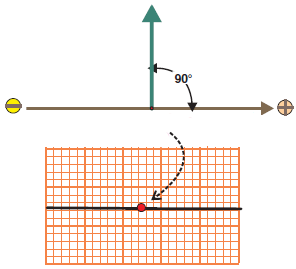
Isoelectric ECG Deflection
|

|
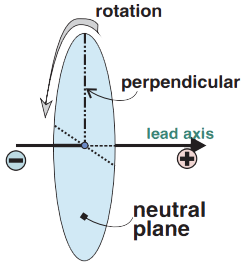
Neutral Plane
|

Neutral Plane of Lead I

Negative Hemisphere and Negative Deflection

Positive Hemisphere and Positive Deflection
|

|

I Limb Lead

|
aVF Limb Lead
|

aVR Limb Lead

|

|
|
Limb Leads
|
Chest Leads
|

Sinus Rhythm
Sources