
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Fascicular tachycardia, Belhassen-type VT, verapamil-sensitive VT, Infrafascicular tachycardia, Idiopathic fascicular left ventricular tachycardia
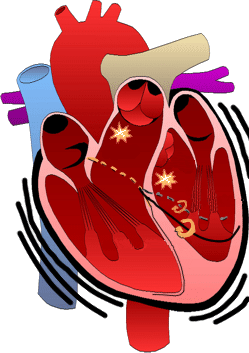




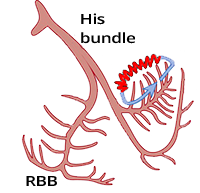


Posterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia
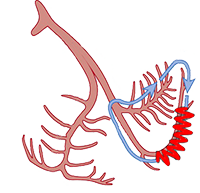
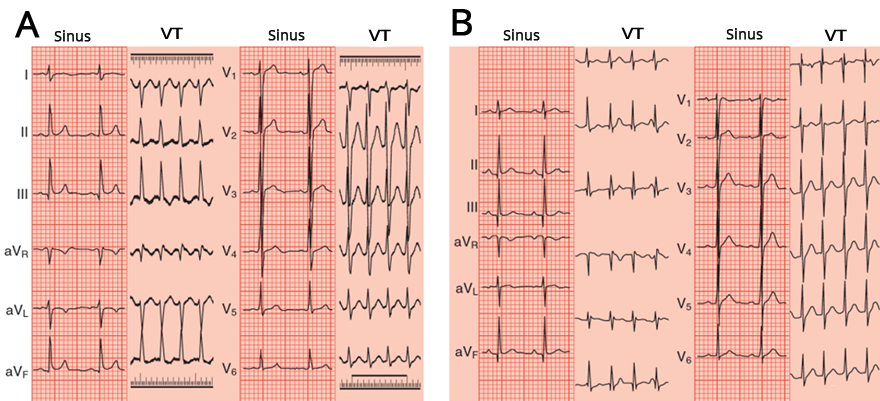
Posterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia

Anterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia
Septal Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia (Narrow Complex Ventricular Tachycardia)
Sources
Home /
Fascicular tachycardia, Belhassen-type VT, verapamil-sensitive VT, Infrafascicular tachycardia, Idiopathic fascicular left ventricular tachycardia
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|

|
Sinus Rhythm
|

|
Anterior and Posterior Fascicular Tachycardia
|

|
Upper Septal Fascicular Tachycardia
|

|
|

|
|
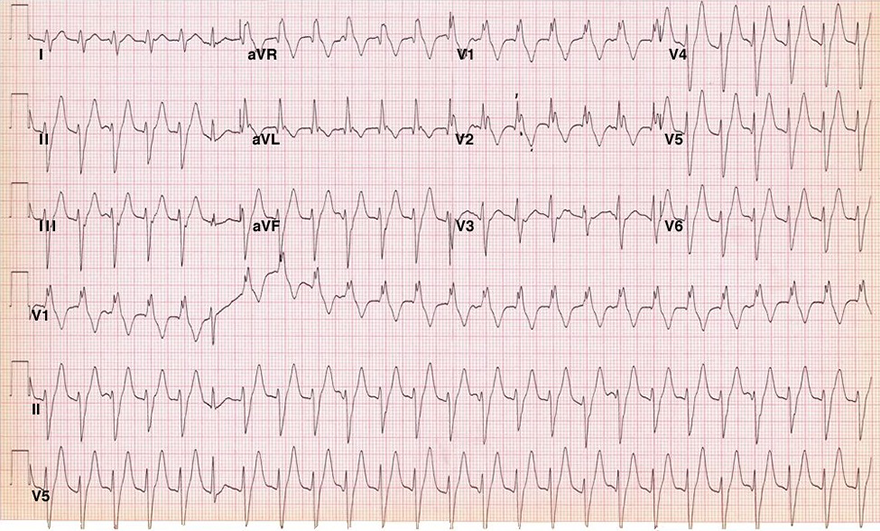
ECG and Fascicular Tachycardia
|

|

Posterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia

Posterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia

Anterior Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia

Septal Fascicular Ventricular Tachycardia (Narrow Complex Ventricular Tachycardia)
Sources