
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Focal atrial tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT), Unifocal atrial tachycardia, Ectopic atrial tachycardia

Focal Atrial Tachycardia
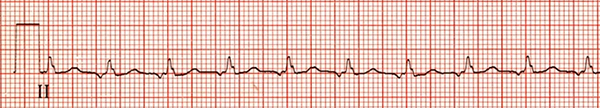
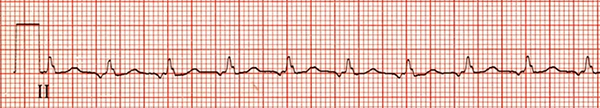
Focal Atrial Tachycardia
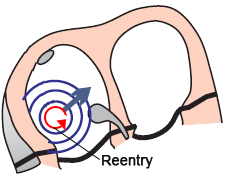
Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
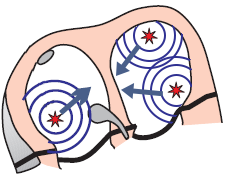
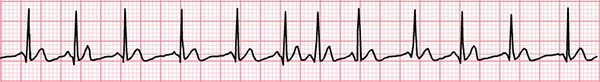
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia

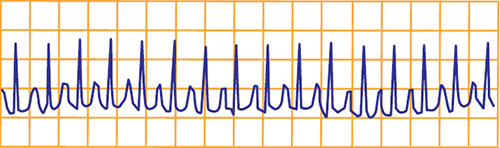
Supraventricular Tachycardia


Carotid Sinus Massage
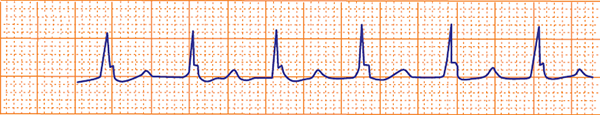
Supraventricular Tachycardia

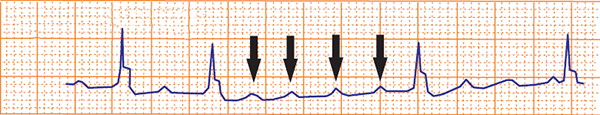
Carotid Sinus Massage
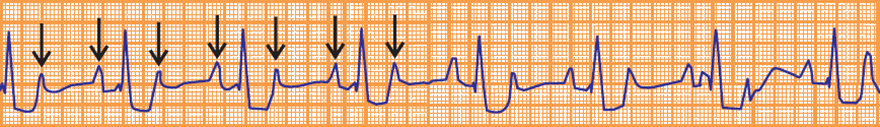
Focal Atrial Tachycardia and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)
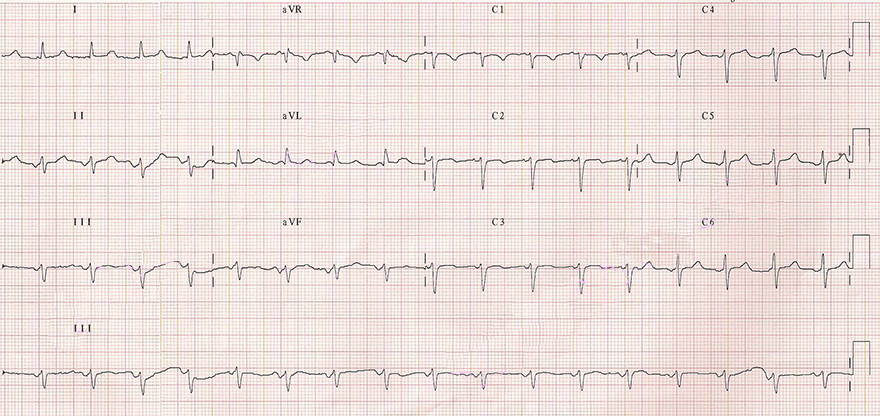
Focal Atrial Tachycardia
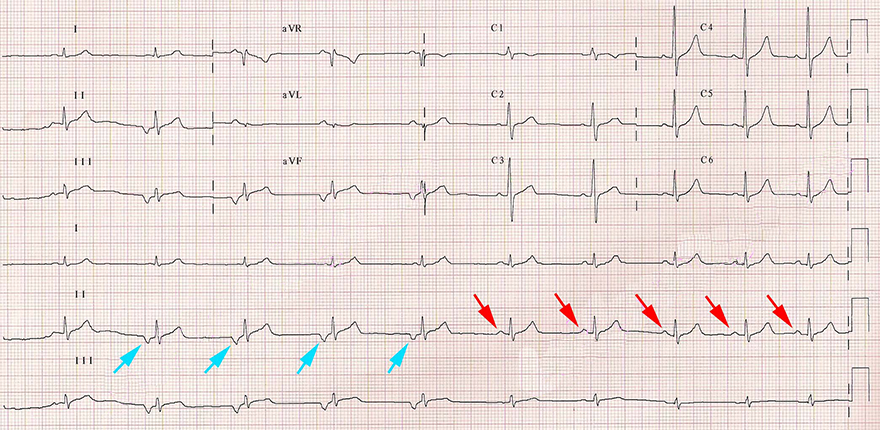
Focal Atrial Rhythm and Sinus Rhythm
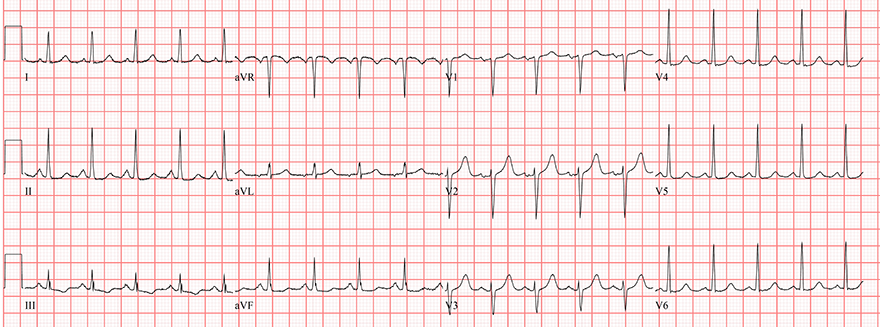
Sinus Tachycardia
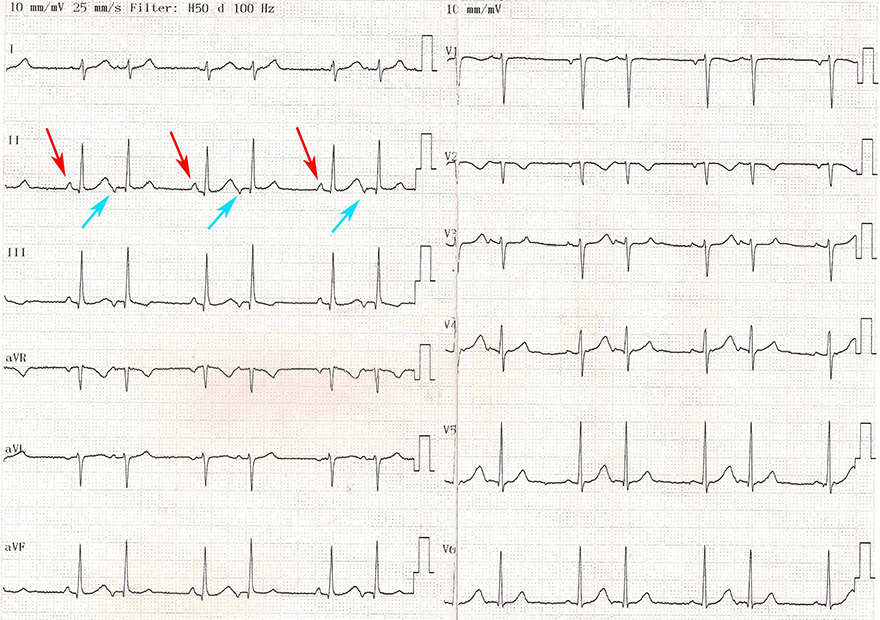
Atrial Bigeminy Rhythm
Sources
Home /
Focal atrial tachycardia, Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT), Unifocal atrial tachycardia, Ectopic atrial tachycardia
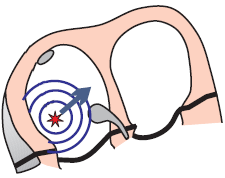
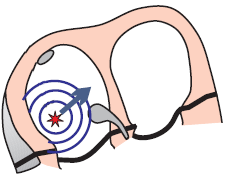
Ectopic Focus
|

|
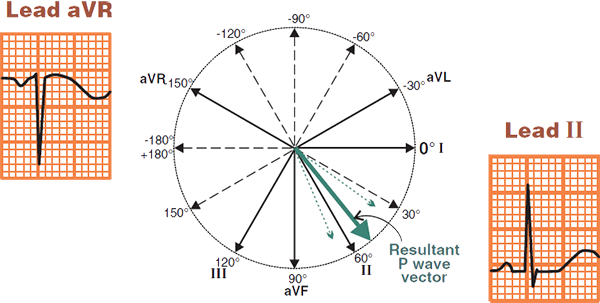
Focus Localization
|

|
Physiological P Wave
|

|

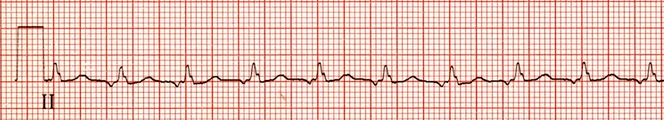
Focal Atrial Tachycardia

|
 Focal Atrial Tachycardia
|

|
 Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
|

|

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
|
AV Conduction
|

|

Supraventricular Tachycardia

Carotid Sinus Massage
|

|

Supraventricular Tachycardia

Carotid Sinus Massage
|

|

Focal Atrial Tachycardia and Second-Degree AV Block (2:1)

Focal Atrial Tachycardia

Focal Atrial Rhythm and Sinus Rhythm

Sinus Tachycardia

Atrial Bigeminy Rhythm
Sources