
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |






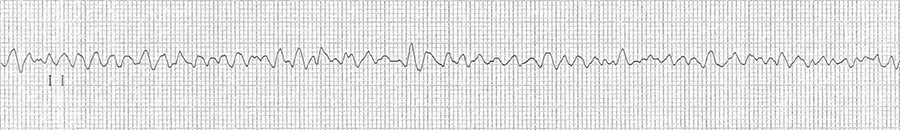
Ventricular Fibrillation and Hyperkalemia
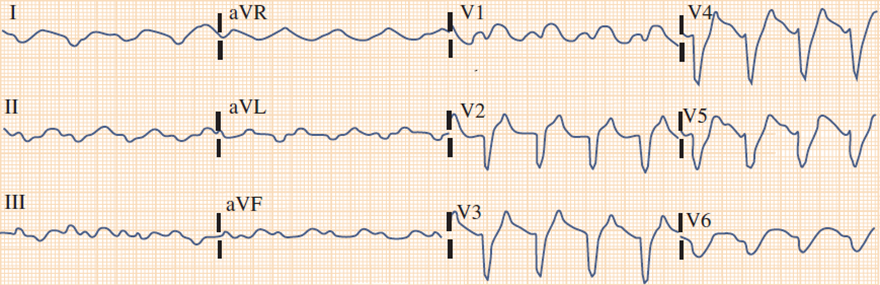
Hyperkalemia (7.1mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (6.5 mmol/l)
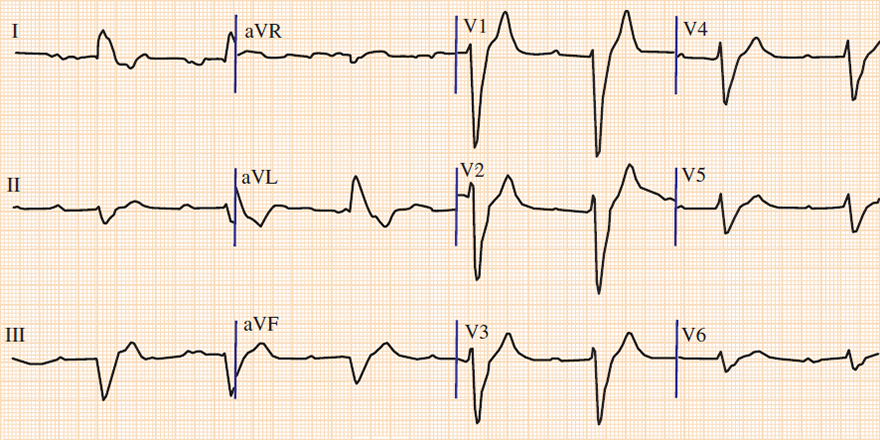
Hyperkalemia (7.3 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (7 mmol/l)
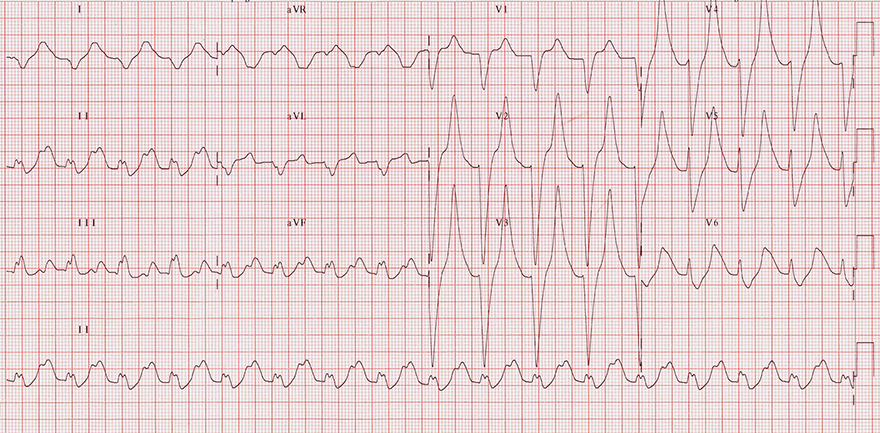
Hyperkalemia (9.2 mmol/l)
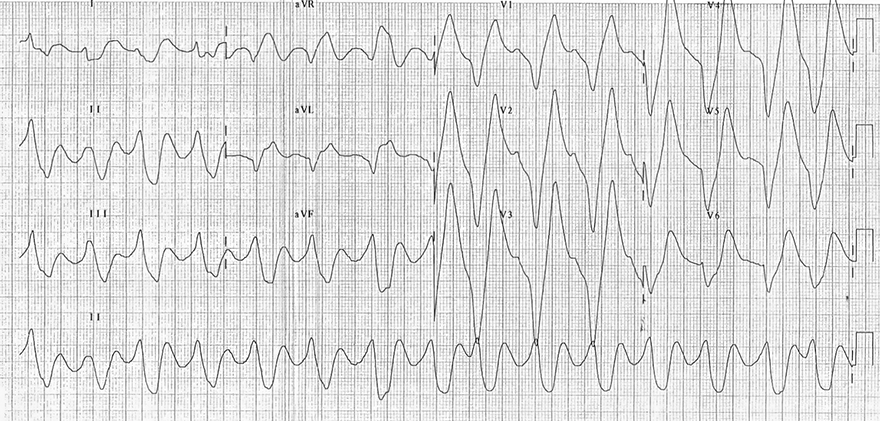
Hyperkalemia (9 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (9.9 mmol/l)
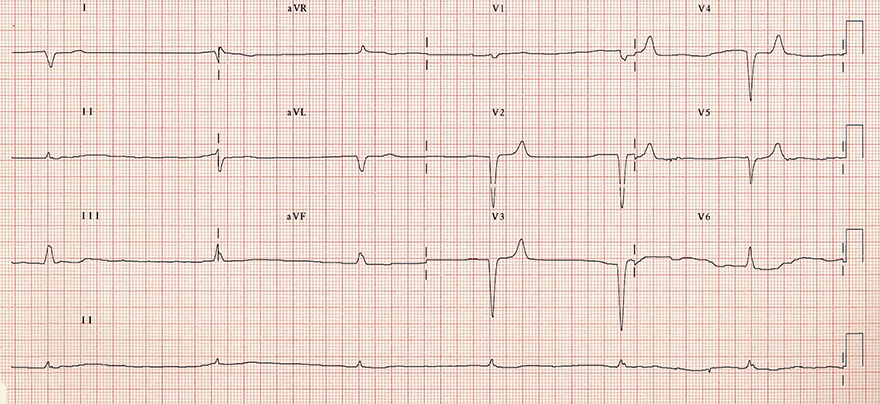
Hyperkalemia (7 mmol/l)
Sources
Potassium (K+)
|

|
ECG and Hyperkalemia
|

|
K+ > 5.6 mmol/l
|

|

|
K+ > 6.5 mmol/l
|

|
K+ > 7 mmol/l
|

|
K+ > 9 mmol/l
|

|

Ventricular Fibrillation and Hyperkalemia
|

|
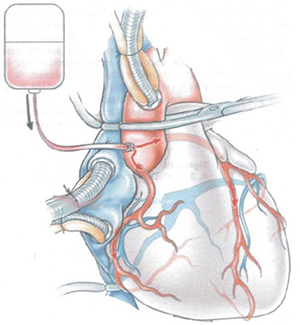
Cardioplegia
|

|

Hyperkalemia (7.1mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (6.5 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (7.3 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (7 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (9.2 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (9 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (9.9 mmol/l)

Hyperkalemia (7 mmol/l)
Sources