Home /
Intra-atrial reentry/reentrant tachycardia (IART)

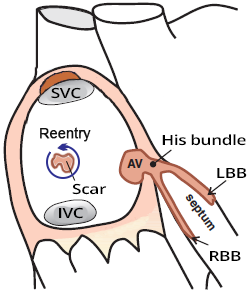
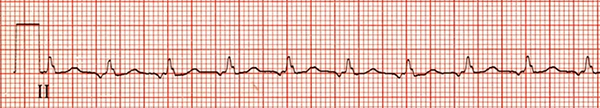
Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
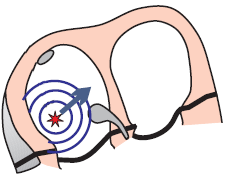
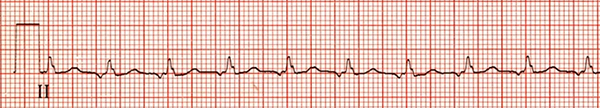
Focal Atrial Tachycardia
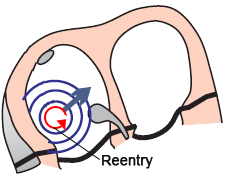

Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
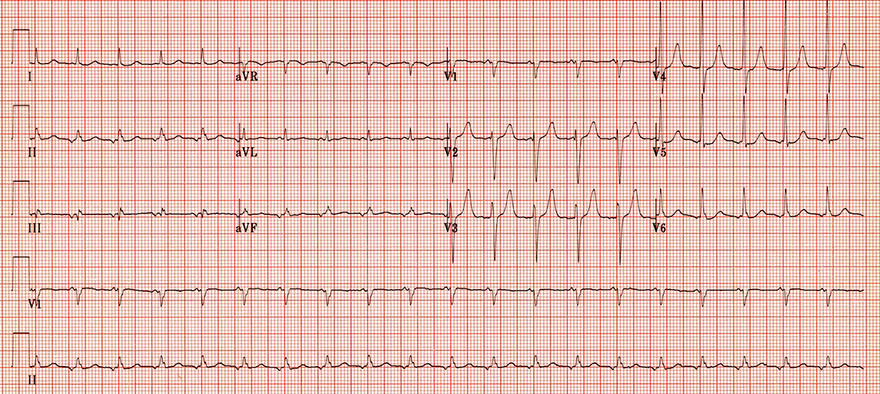
Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia (IART)
Sources
Home /
Intra-atrial reentry/reentrant tachycardia (IART)
|

|
Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
|

|

Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia


|
Focal Atrial Tachycardia
|


|
Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
|

Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia (IART)
Sources