
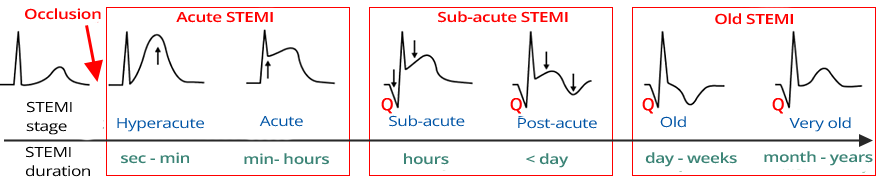
STEMI Stages by Phase




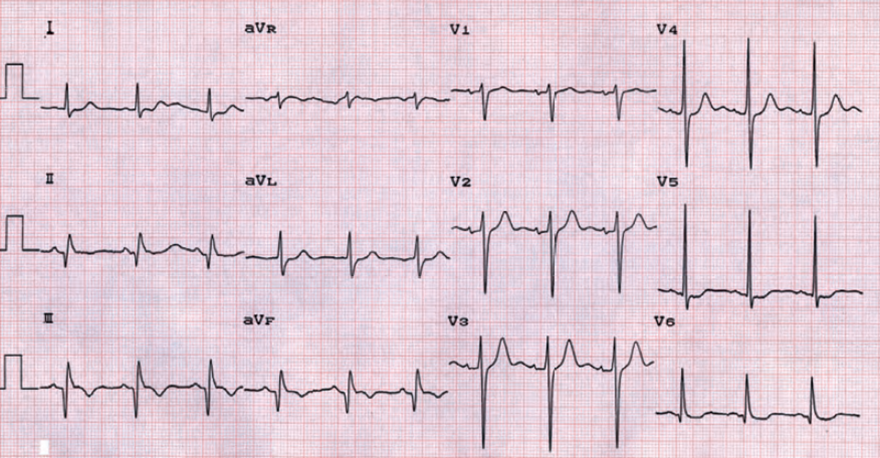
Subacute Inferior STEMI

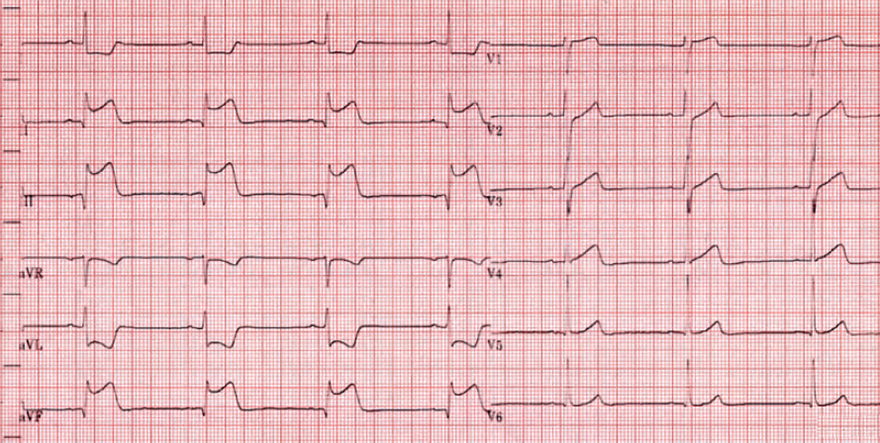
Old Inferior STEMI

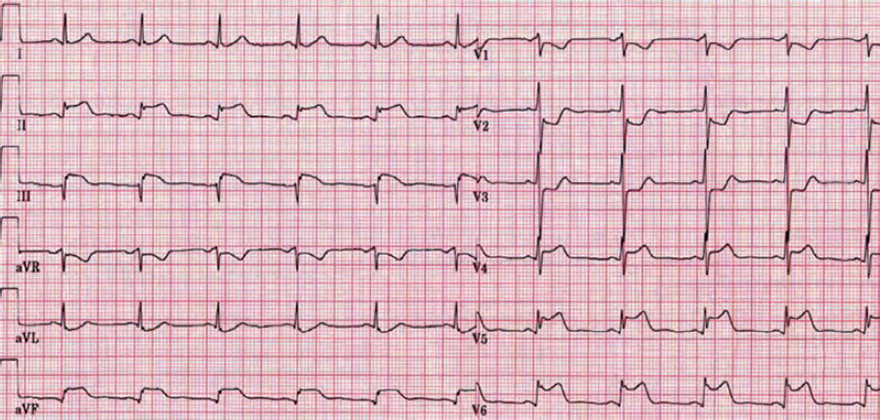
Acute Inferior STEMI and Right Ventricular STEMI

Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI

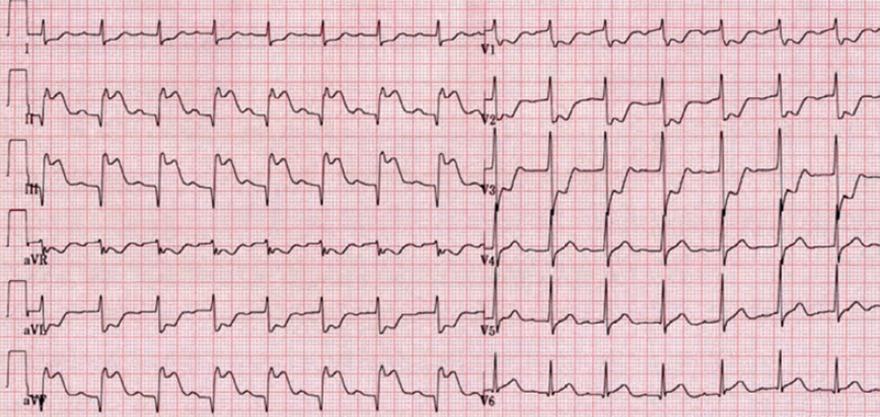
Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI


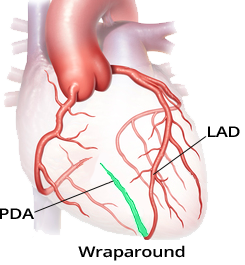
Acute Anterior and Inferior STEMI (Wraparound)

Coronary Angiography

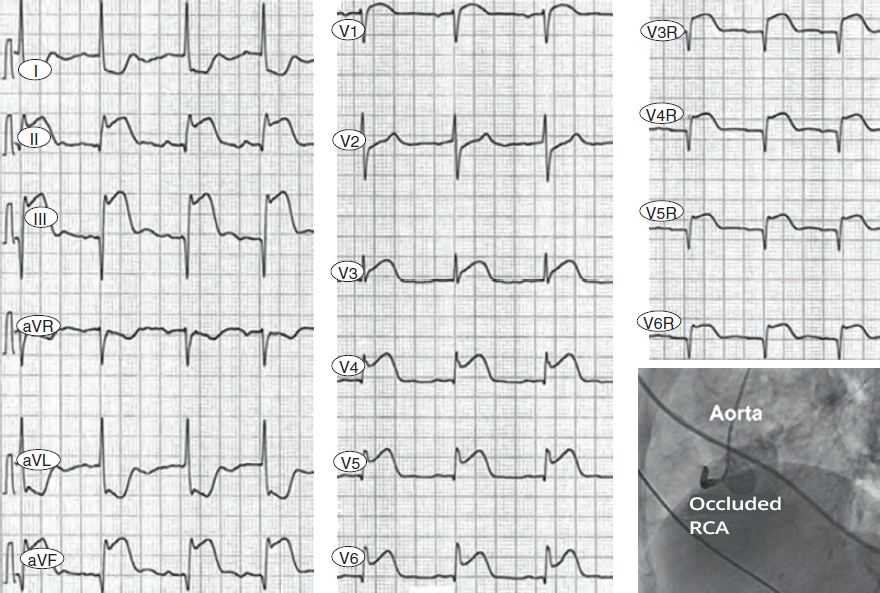
Acute Inferior STEMI and Right Ventricular STEMI
Sources
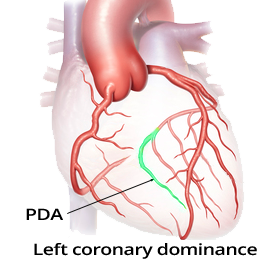
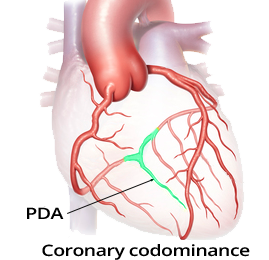
Coronary Artery Dominance
|

|

|

|

|
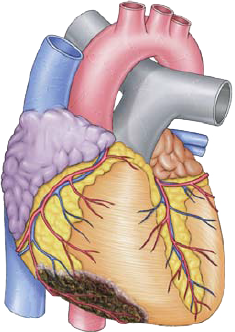
Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction
|

|
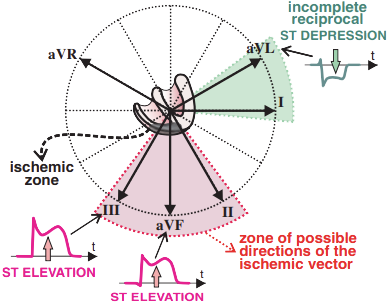
ECG and Inferior Wall STEMI
|

|

STEMI Stages by Phase
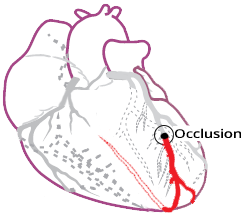
Occlusion of the Right Coronary Artery
|

|
ECG and Occlusion of the Dominant RCA
|

|
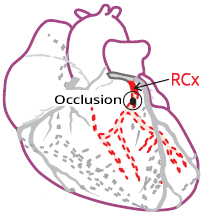
Occlusion of the Left Coronary Artery (LCx)
|

|
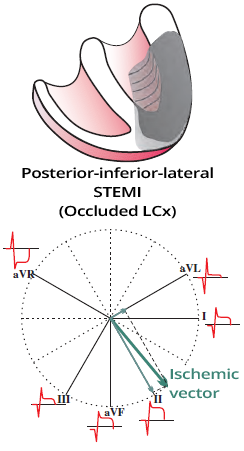
ECG and Occlusion of the Dominant LCx (Left Circumflex Artery)
|

|
Occlusion of the RIA in "Wraparound"
|
 |

|
Subacute Inferior STEMI
|

|

|
Old Inferior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior STEMI and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior and Posterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Anterior and Inferior STEMI (Wraparound)
|

|

|
Coronary Angiography
|

|
Acute Inferior STEMI and Right Ventricular STEMI
|

|
Sources