
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
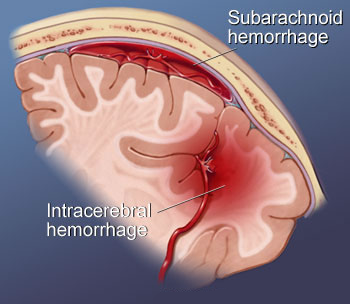

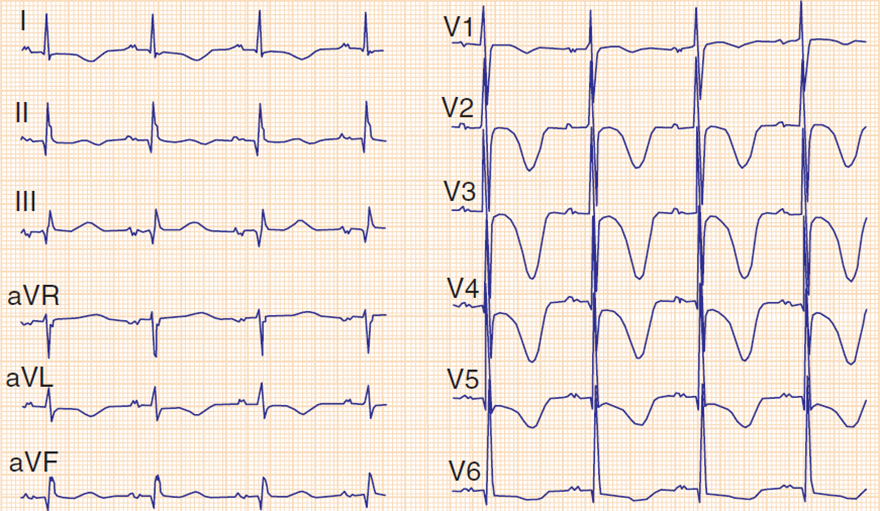
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
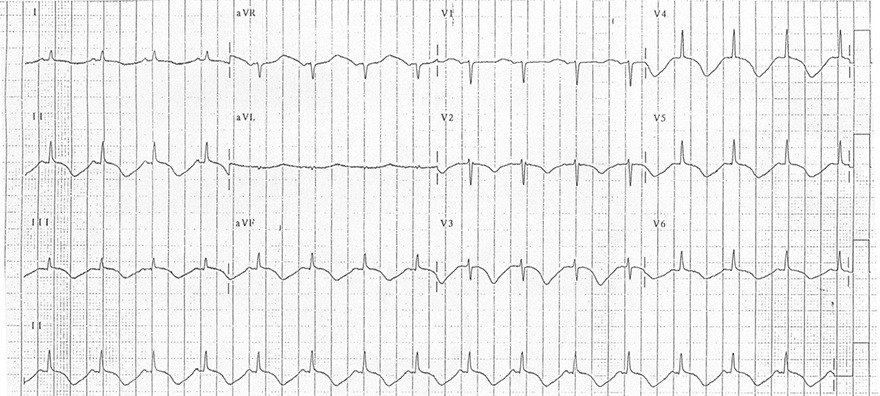
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
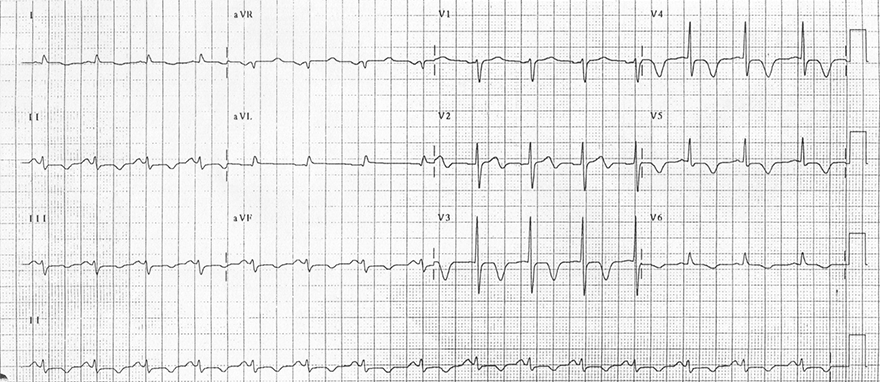
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
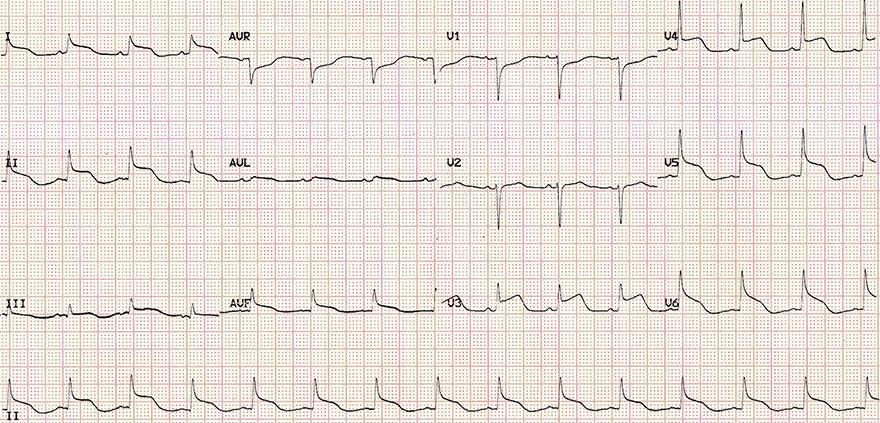
Head Trauma and Catecholamine Storm
Sources
Intracranial Hypertension
|

|
ECG and Intracranial Hypertension
|

|

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Subarachnoid Hemorrhage

Head Trauma and Catecholamine Storm
Sources