
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
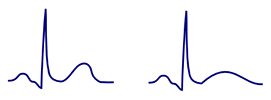
Concordant T Wave

Disconcordant T Wave
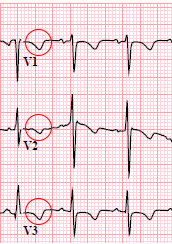
Persistent Juvenile T Waves
Persistent Juvenile T Waves

Persistent Juvenile T Waves
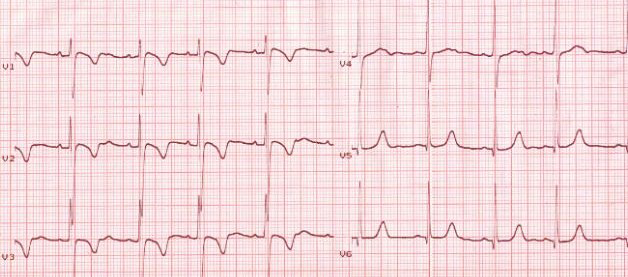
Persistent Juvenile T Waves
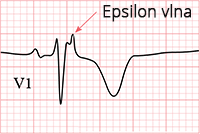
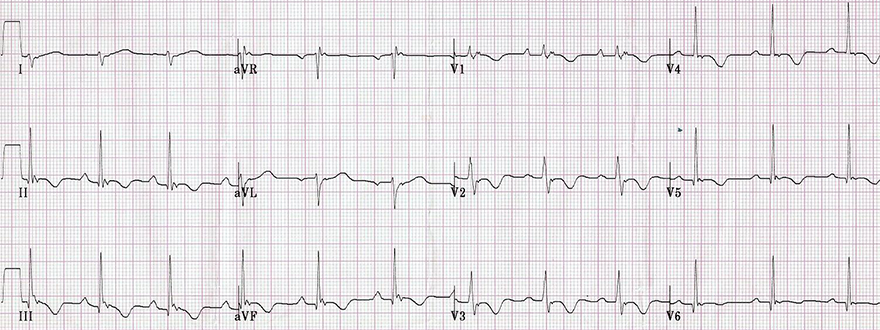
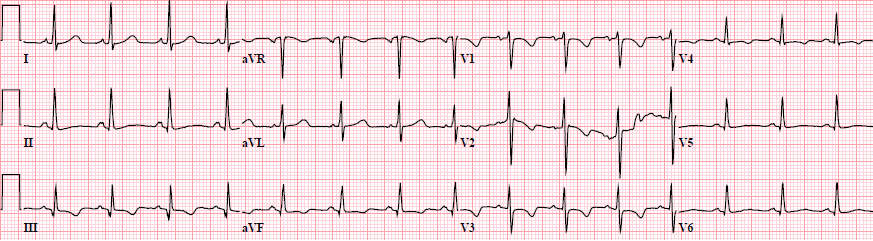
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia

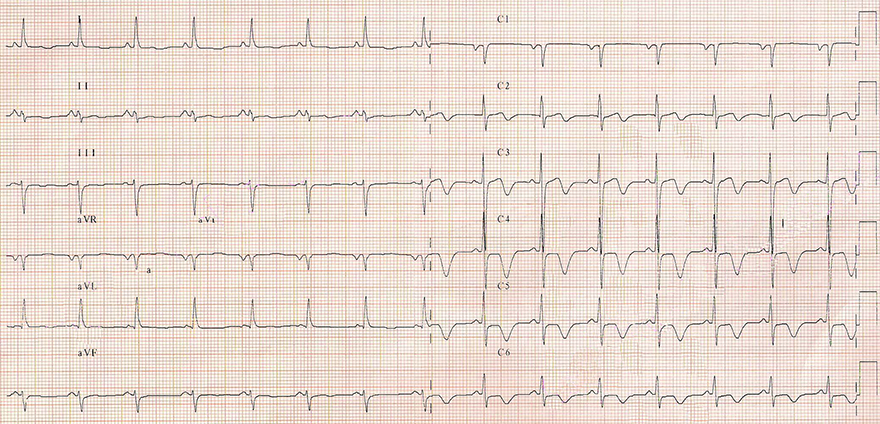
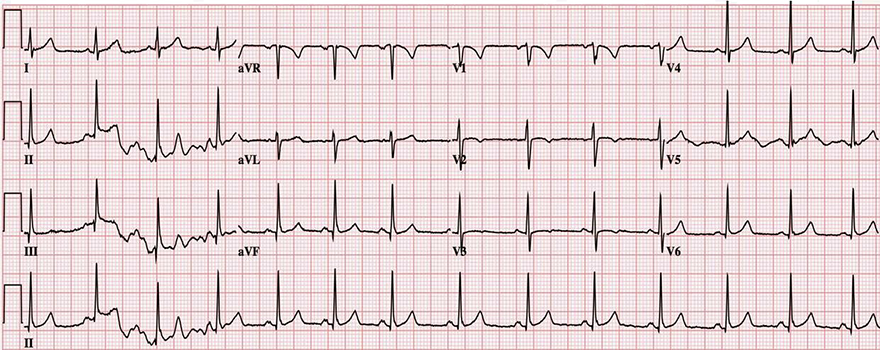
Inverted Ischemic T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris
Sources
Normal T Wave
|

Concordant T Wave 
Disconcordant T Wave |
ECG and Persistent Juvenile T Waves
|

|

Persistent Juvenile T Waves

Persistent Juvenile T Waves

Persistent Juvenile T Waves

Persistent Juvenile T Waves

|
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia
|

|

|
Inverted Ischemic T Waves and Unstable Angina Pectoris
|

|
Sources