
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Left Anterior Hemiblock (LAHB), Left Anterior Fascicular Block

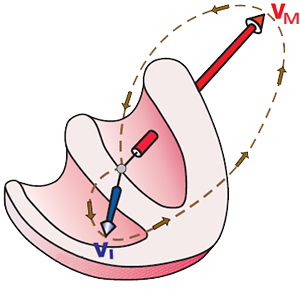
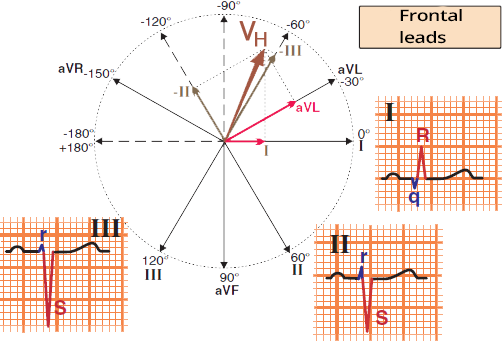
Left Anterior Fascicular Block (Quick Diagnosis)
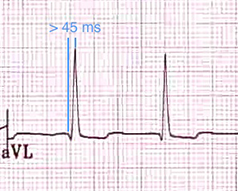
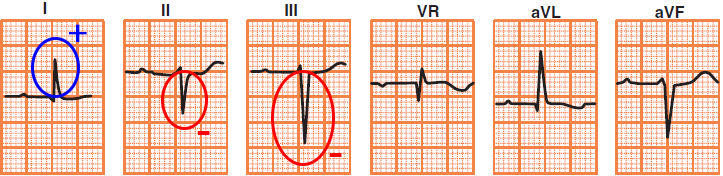



Differential Diagnosis Using V1-V2


Left Anterior Fascicular Block

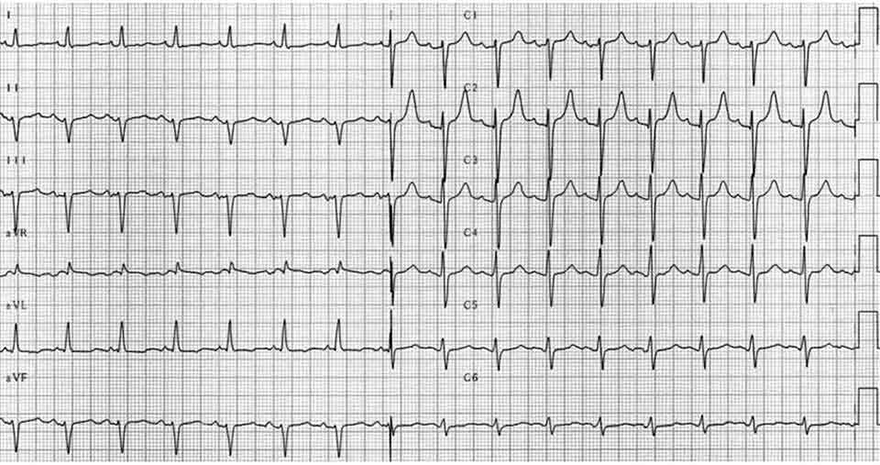
Left Anterior Fascicular Block

Trifascicular Block (Left Anterior Fascicular Block + AV Block of 1st Degree + RBBB)
Sources
Home /
Left Anterior Hemiblock (LAHB), Left Anterior Fascicular Block
Left Bundle Branch
|

|
Left Anterior Fascicular Block
|

|

Left Anterior Fascicular Block (Quick Diagnosis)
ECG and Left Anterior Fascicular Block
|

|

Differential Diagnosis
|

|

|
Differential Diagnosis Using V1-V2
|

|

|
Left Anterior Fascicular Block
|

|

|
Left Anterior Fascicular Block
|

|

Trifascicular Block (Left Anterior Fascicular Block + AV Block of 1st Degree + RBBB)
Sources