
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |


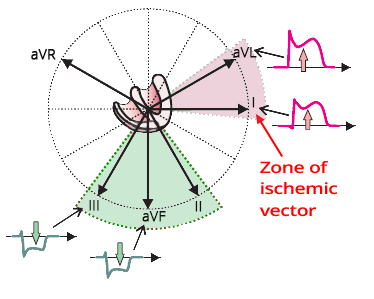




Acute Posterior-Lateral STEMI

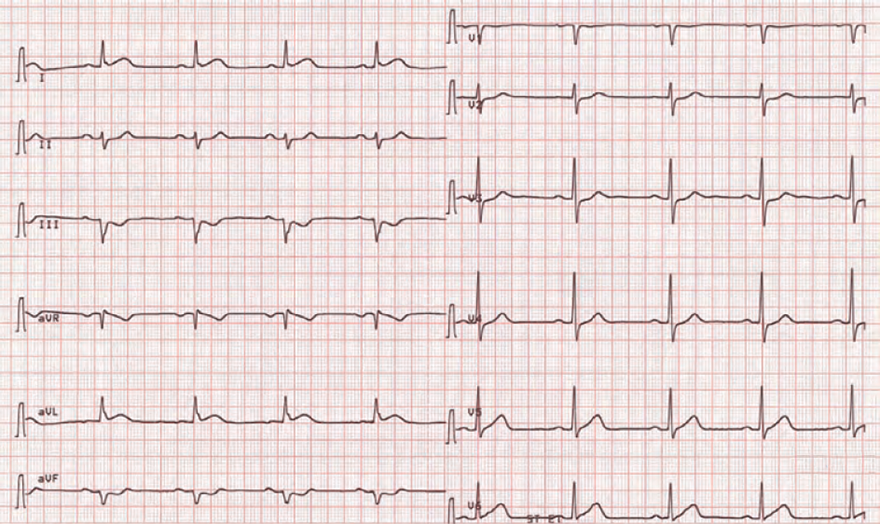
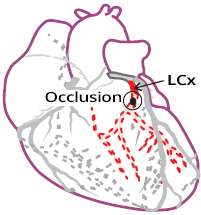
Acute Lateral STEMI


Coronary Angiography


Acute Antero-lateral STEMI


Acute Antero-lateral STEMI
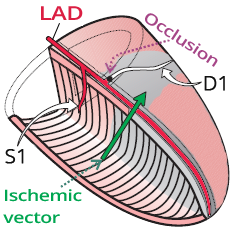
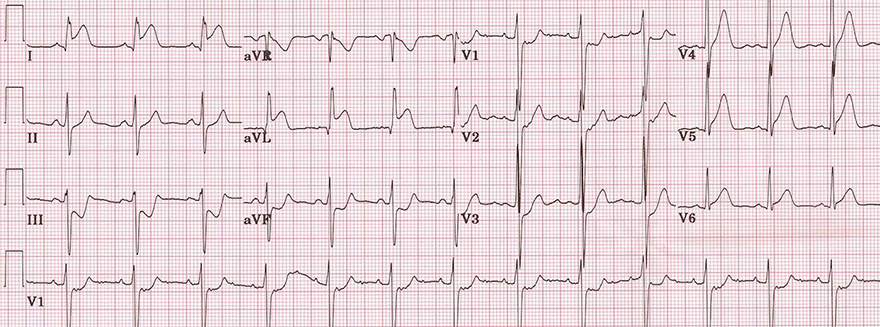
Acute Isolated High Lateral STEMI

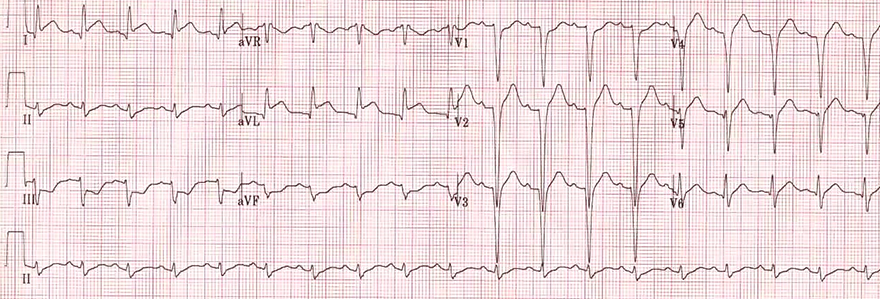
Acute Isolated High Lateral STEMI


Subacute Isolated High Lateral STEMI


Acute Inferior-Posterior-Lateral STEMI
Sources
|

|
Lateral Infarction
|

|
ECG and Lateral STEMI
|

|
|

|
Antero-lateral STEMI
|

|
Infero-posterior-lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Posterior-Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Lateral STEMI
|

|


Coronary Angiography

|
Acute Antero-lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Antero-lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Isolated High Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Isolated High Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Subacute Isolated High Lateral STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior-Posterior-Lateral STEMI
|

|
Sources