
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
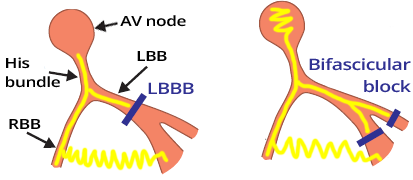
Wide QRS Complex (≥0.12s)
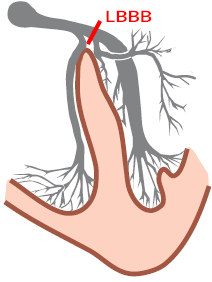
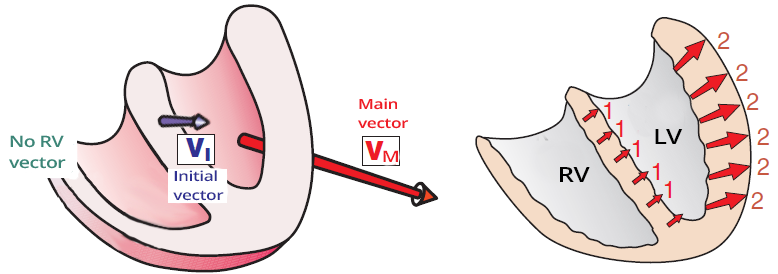
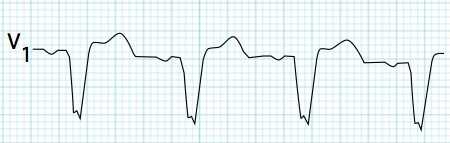
Ventricular Activation in Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

Leads (V1, V6) and Left Bundle Branch Block


Ventricular Septal Infarction and Left Bundle Branch Block

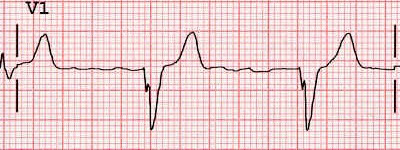
Left Bundle Branch Block
Lead V1 (V2)
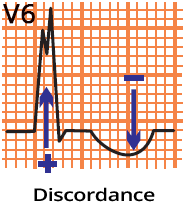
qrS "W" Configuration (V1)

rS Configuration (V1)

Q (QS) Configuration (V1)
Lateral Leads (V5-V6, I, aVL)
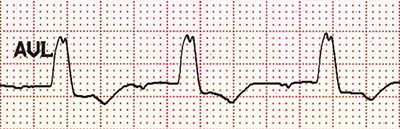
RsR "M" Configuration (aVL)
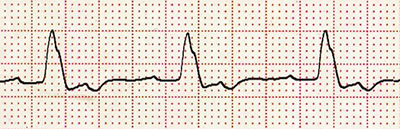
R Configuration (with notch) (V6)

R Configuration (monophasic R) (V6)
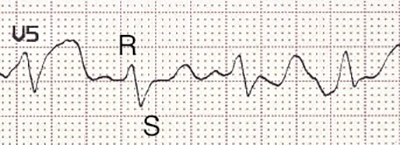
RS Configuration (V5)

Incomplete LBBB (V6)

Complete LBBB (V6)

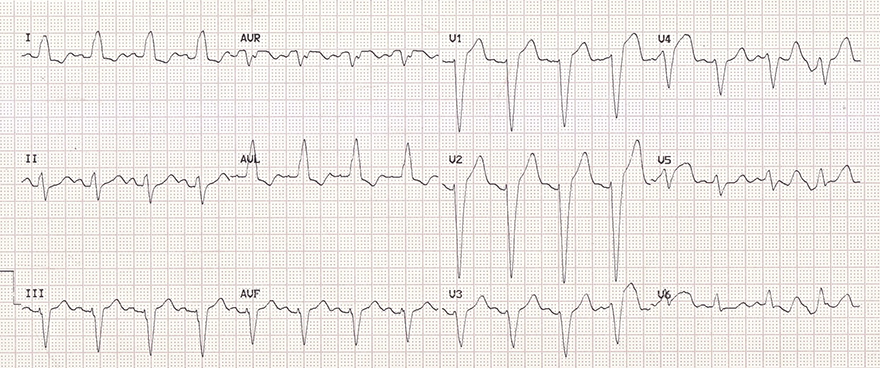
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

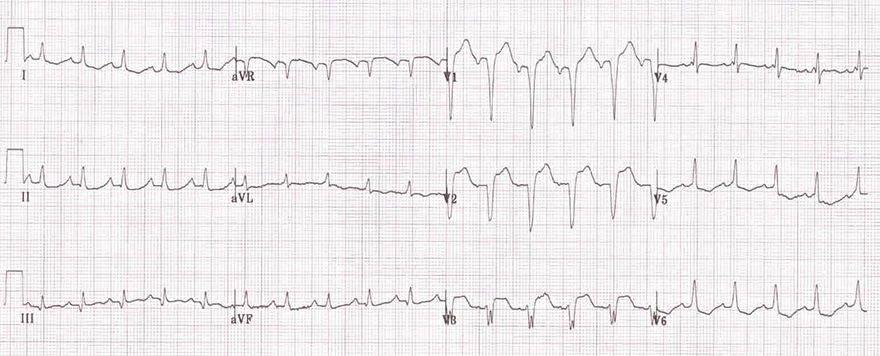
Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block (iLBBB)

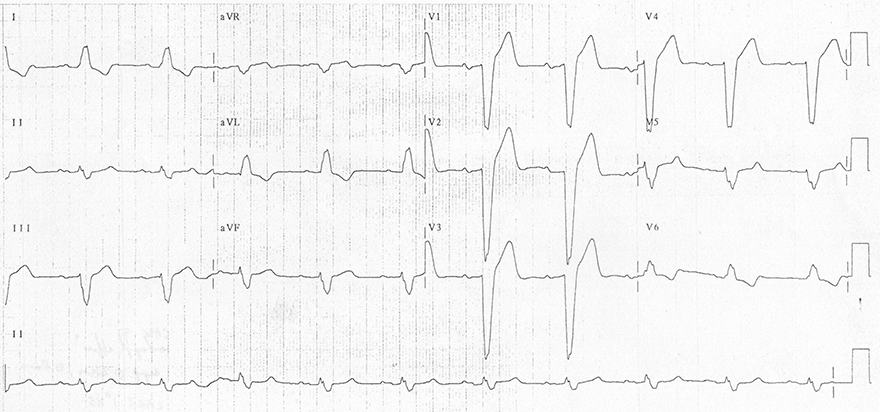
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

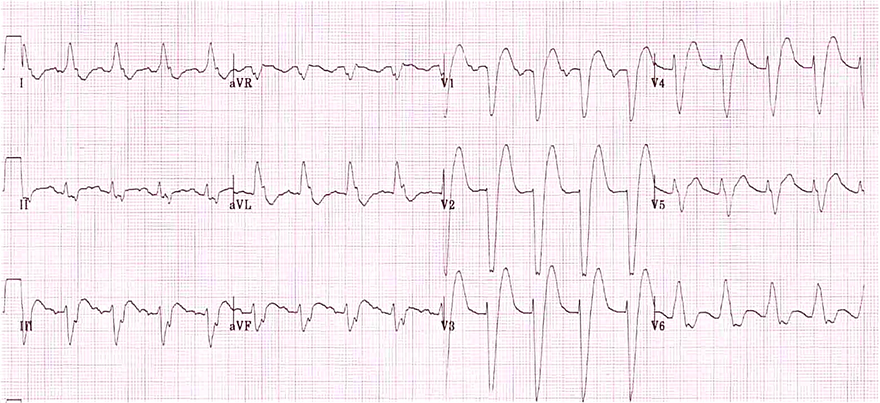
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

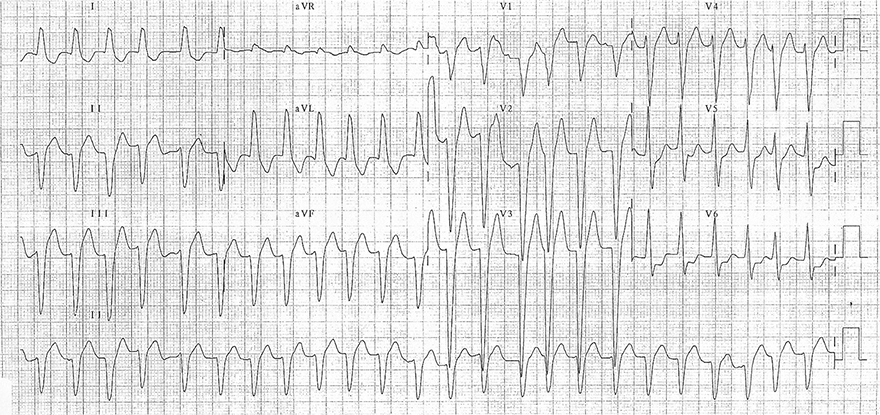
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) and Atrial Fibrillation
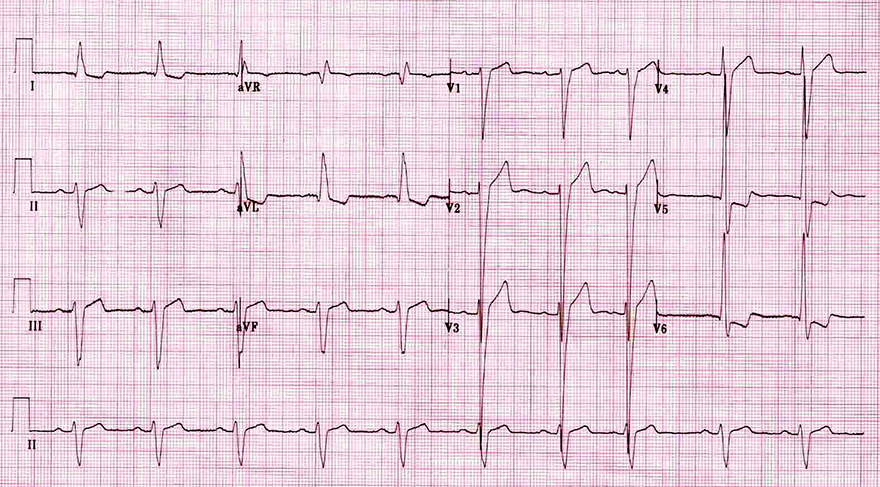
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Sources
Wide QRS Complex
|
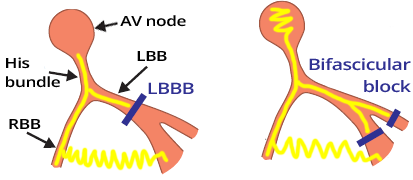
|
Wide QRS Complex (≥0.12s)
Causes of LBBB
|

|

Ventricular Activation in Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)

Leads (V1, V6) and Left Bundle Branch Block


Ventricular Septal Infarction and Left Bundle Branch Block
|

|

Left Bundle Branch Block
|
Lead V1 (V2)
|
Lateral Leads (V5-V6, I, aVL)
|

qrS "W" Configuration (V1) |

RsR "M" Configuration (aVL) |

rS Configuration (V1) |

R Configuration (with notch) (V6) |

Q (QS) Configuration (V1) |

R Configuration (monophasic R) (V6) |

RS Configuration (V5) |

Incomplete LBBB (V6)
|

Complete LBBB (V6)
|

|
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
|

|

|
Incomplete Left Bundle Branch Block (iLBBB)
|

|

|
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
|

|

|
Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB)
|

|

Left Bundle Branch Block (LBBB) and Atrial Fibrillation
|

|

|
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
|

|
Sources