
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
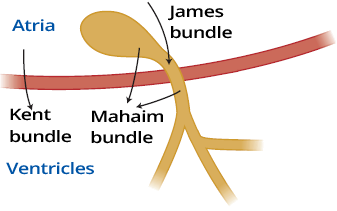
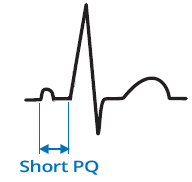
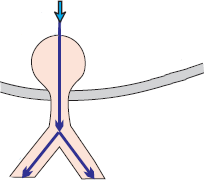
Lown Ganong Levine (LGL) syndrome, Short PQ syndrome, Clerc Levy Cristesco (CLC) syndrome





LGL Syndrome


LGL Syndrome


LGL Syndrome
Sources
Home /
Lown Ganong Levine (LGL) syndrome, Short PQ syndrome, Clerc Levy Cristesco (CLC) syndrome
|

|
Lown-Ganong-Levine (LGL) Syndrome
|

|
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|
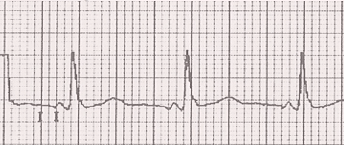
ECG and LGL Syndrome
|

|

|
LGL Syndrome
|

|

|
LGL Syndrome
|

|

|
LGL Syndrome
|

|
Sources