
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Left Posterior Hemiblock (LPHB), Left Posterior Fascicular Block

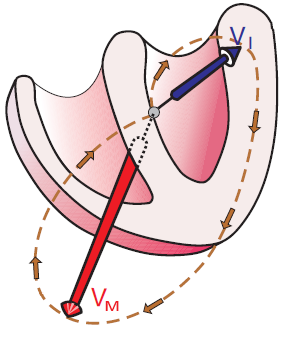
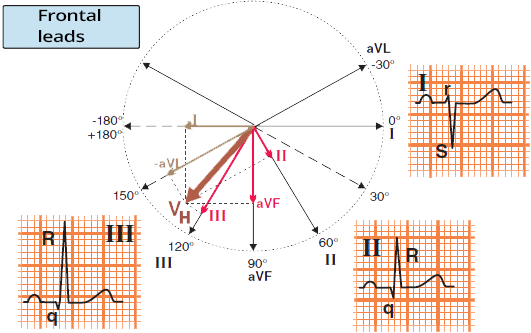
Left Anterior Fascicular Block (Quick Diagnosis)
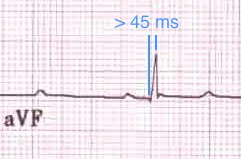
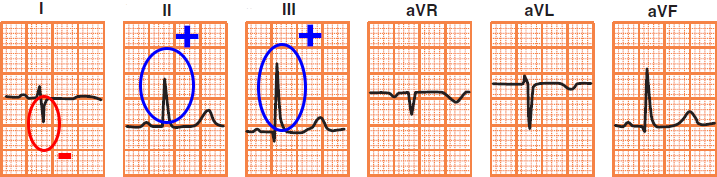


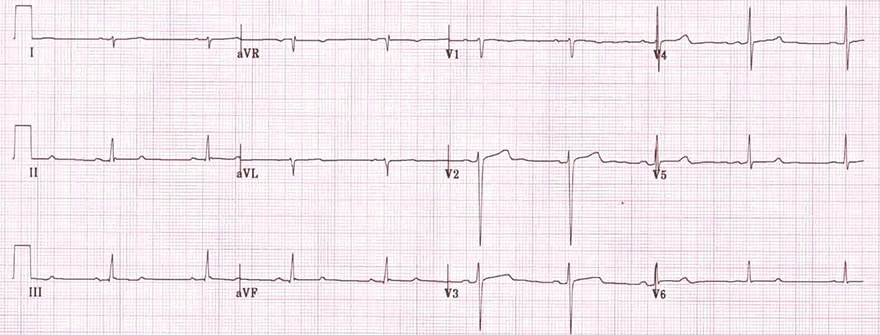
Left Posterior Fascicular Block

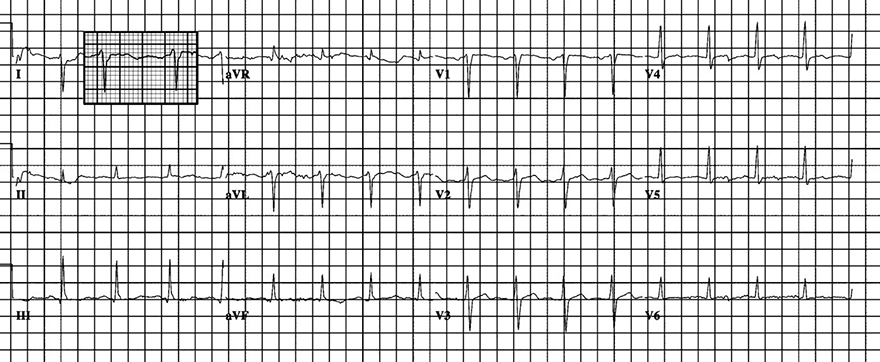
Left Posterior Fascicular Block

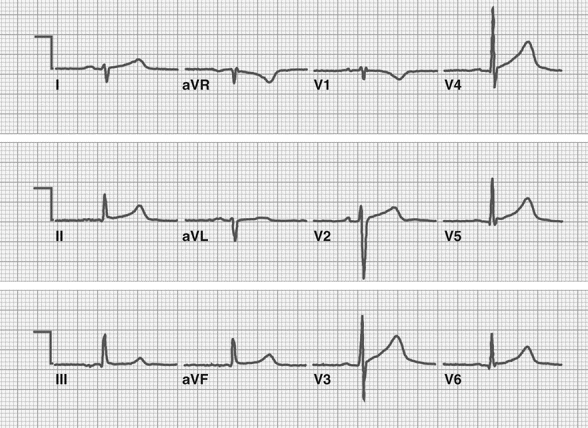
Left Posterior Fascicular Block


Left Posterior Fascicular Block

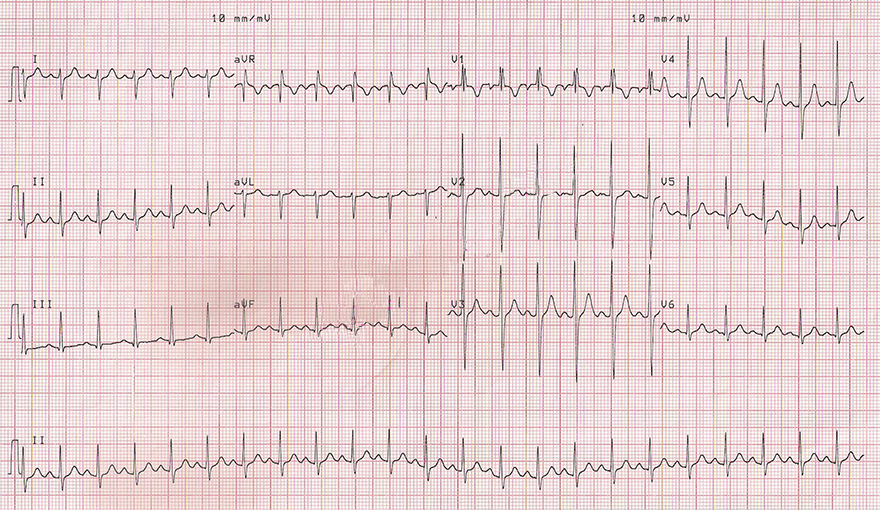
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + iRBBB)
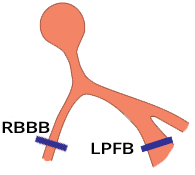
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + RBBB)
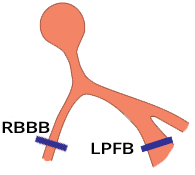

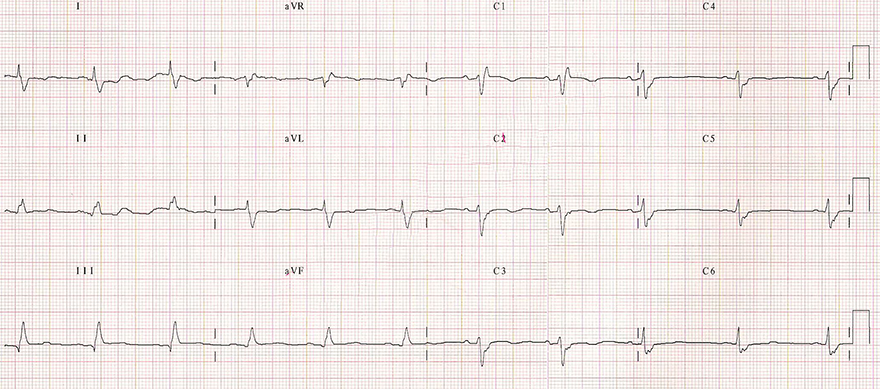
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + RBBB)
Sources
Home /
Left Posterior Hemiblock (LPFB), Left Posterior Fascicular Block
Left Bundle Branch
|

|
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
|

|

Left Anterior Fascicular Block (Quick Diagnosis)
|

|

Differential Diagnosis
|

|

|
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
|

|

|
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
|

|

|
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
|

|

|
Left Posterior Fascicular Block
|

|

|
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + iRBBB)
|

|

|
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + RBBB)
|
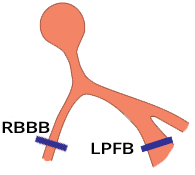
|

|
Bifascicular Block (LPFB + RBBB)
|
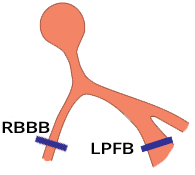
|
Sources