
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |


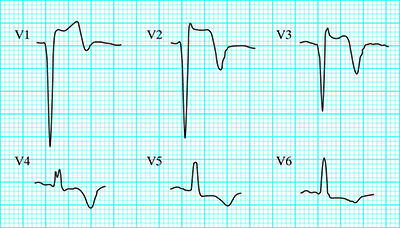

Classification of STEMI by Stage


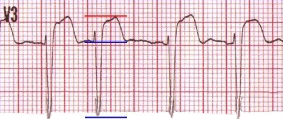

Acute STEMI Infarction

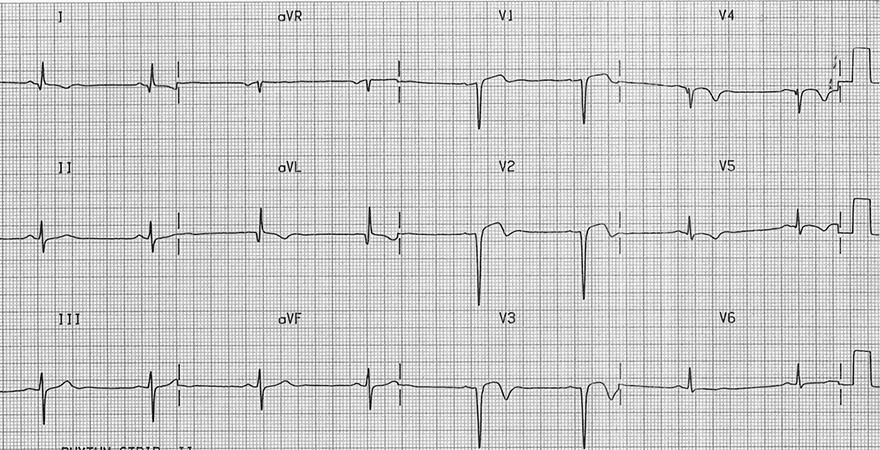
Anterior Wall Aneurysm

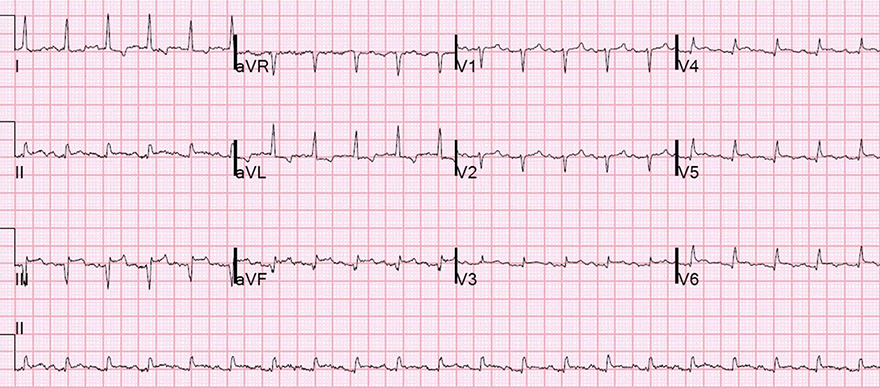
Inferior Wall Aneurysm

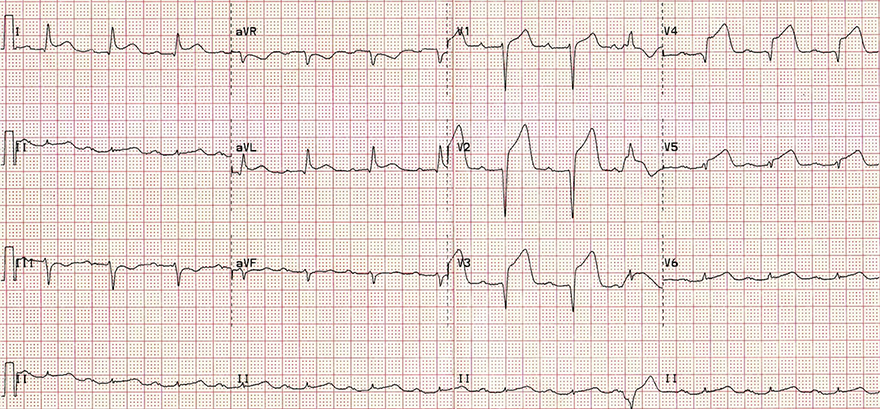
Acute Anterior STEMI

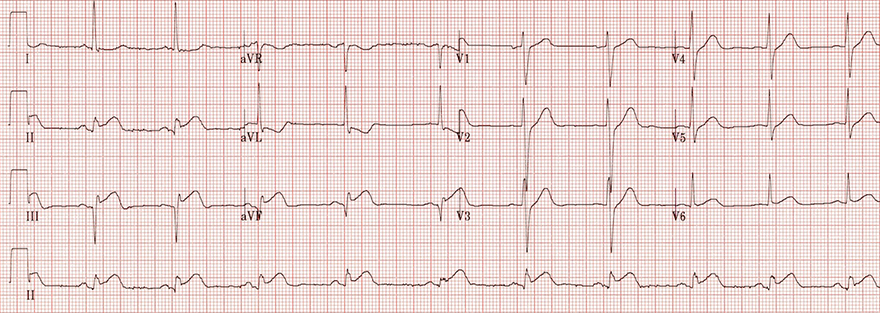
Acute Inferior STEMI


Anterior Wall Aneurysm

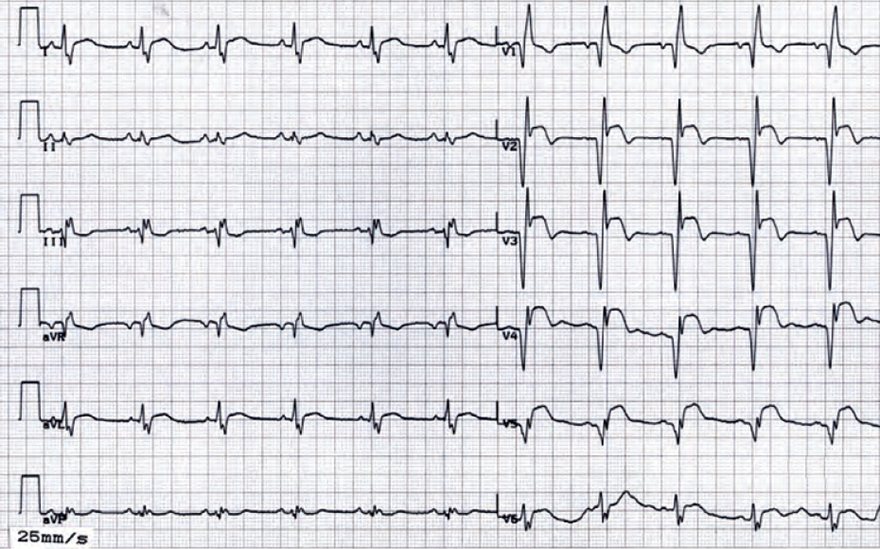
Anterior Wall Aneurysm


Anterior Wall Aneurysm
Sources
STEMI and the Left Ventricle
|

|
Aneurysm of the Left Ventricle
|

|
|

|

Classification of STEMI by Stage
 T=1, QRS=11, T/QRS = 0.09  T=1.5, QRS=13, T/QRS = 0.11 |
 T=6, QRS=18, T/QRS = 0.33  T=5, QRS=13, T/QRS = 0.38 |
Acute STEMI Infarction

|
Anterior Wall Aneurysm
|

|

|
Inferior Wall Aneurysm
|

|

|
Acute Anterior STEMI
|

|

|
Acute Inferior STEMI
|

|

|
Anterior Wall Aneurysm
|

|

|
Anterior Wall Aneurysm
|

|

|
Anterior Wall Aneurysm
|

|
Sources