
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT) Tachycardia, Adenosine Sensitive VT


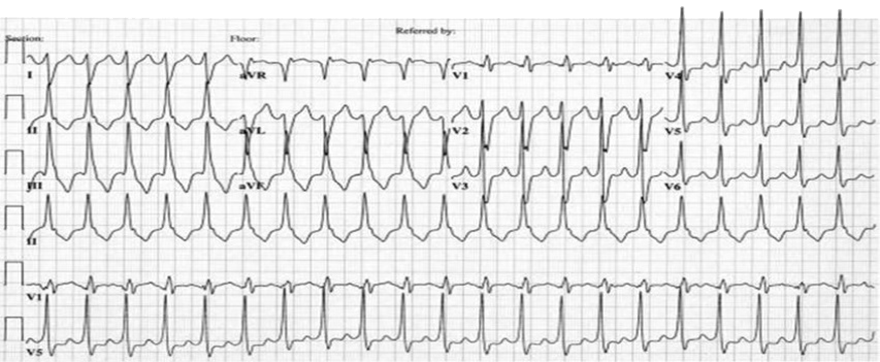
Ventricular Tachycardia from the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract

Ventricular Extrasystole from the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract
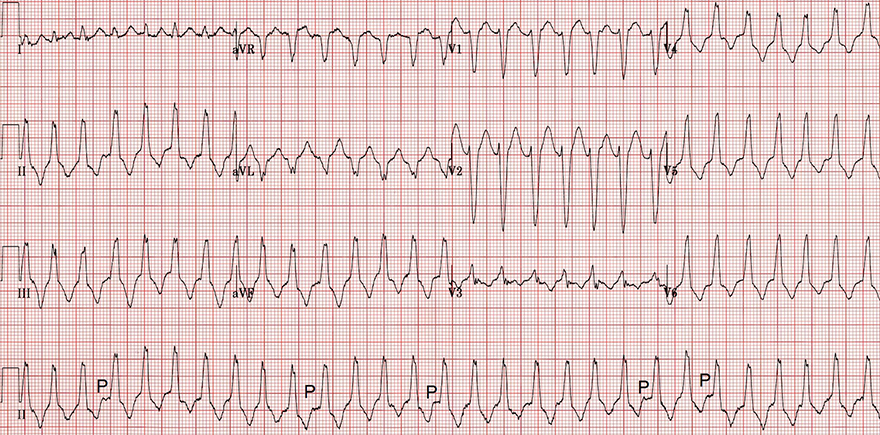
Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
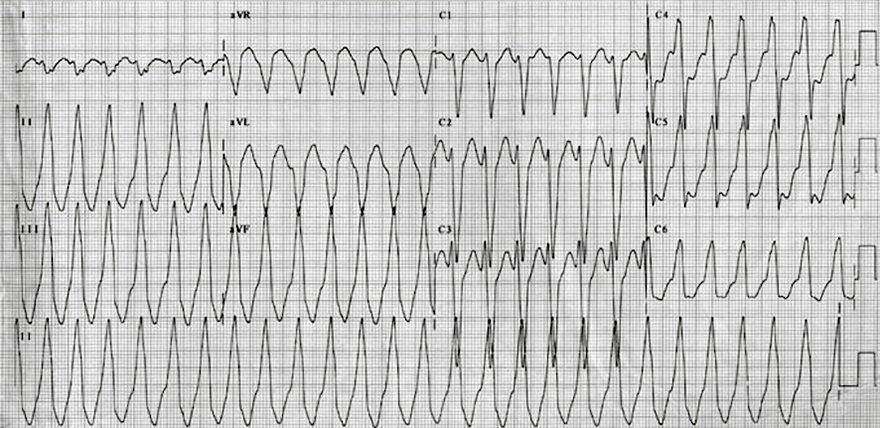
Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
Sources
Home /
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT) Tachycardia, Adenosine Sensitive VT
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia
|

|
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Tachycardia
|

|

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract

Ventricular Extrasystole from the Left Ventricular Outflow Tract

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract

Ventricular Tachycardia from the Right Ventricular Outflow Tract
Sources