
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Cardiac memory, Memory induced T wave, Electrical remodeling, Chatterjee phenomenon (Post pacing T wave inversion)
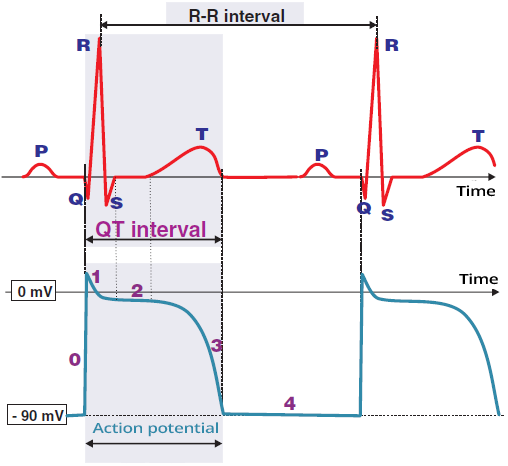
ECG (Lead V6) and Action Potential

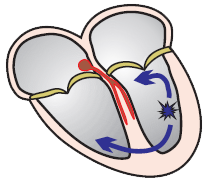
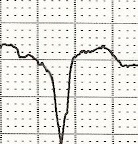
Wide QRS Complex
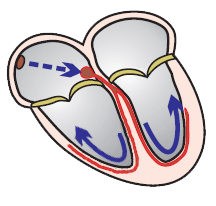
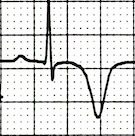
Sinus Rhythm and Memory T Waves
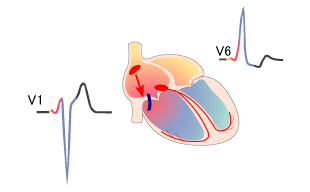
WPW Syndrome (Type B)
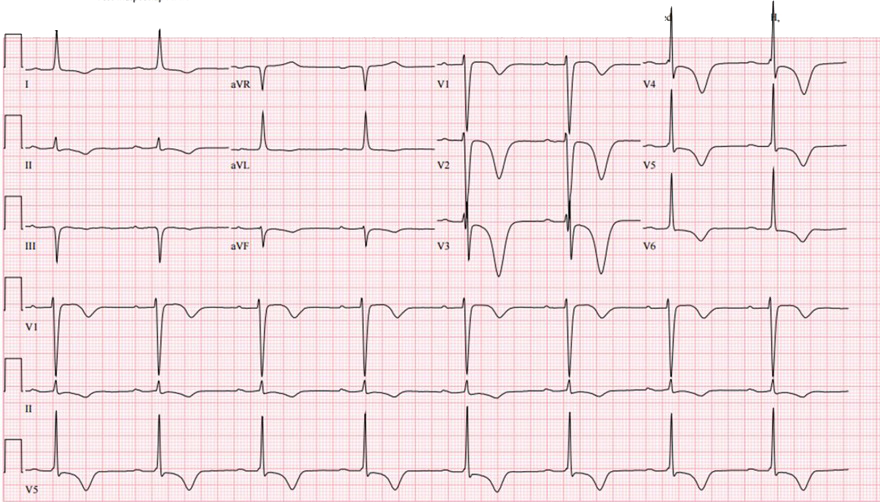
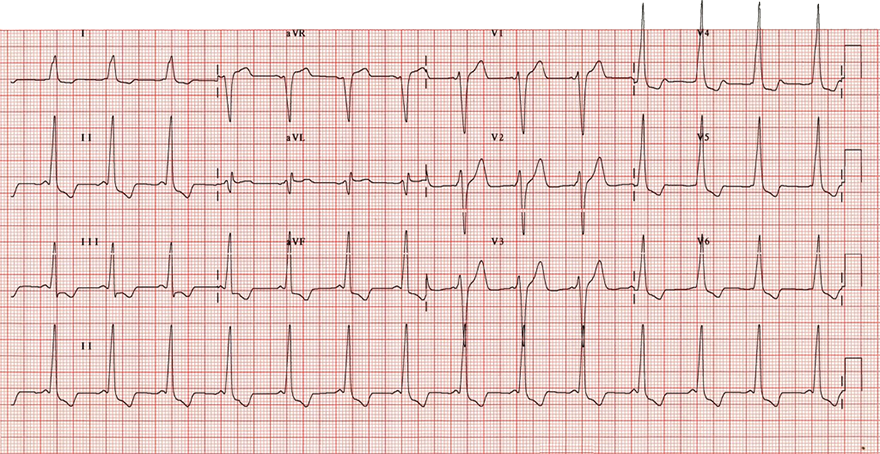
Memory T Waves
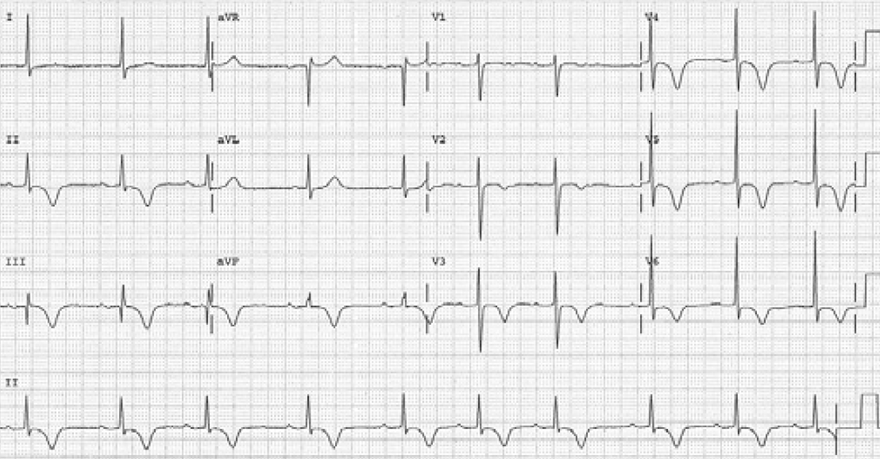
Memory T Waves
Sources
Home /
Cardiac memory, Memory induced T wave, Electrical remodeling, Chatterjee phenomenon (Post pacing T wave inversion)

ECG (Lead V6) and Action Potential
Cardiac Memory
|

|
 br br

Wide QRS Complex
|
 
Sinus Rhythm and Memory T Waves
|

|
WPW Syndrome (Type B)
|

|

Memory T Waves

Memory T Waves
Sources