Home /
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) - ECG
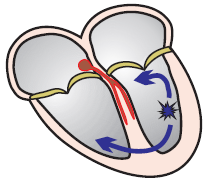
Monomorphic ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT) has a ventricular ectopic focus
- The focus generates impulses with a rate > 100/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (>0.12s) occur
- Rarely, QRS are narrow (VT from the area of the ventricular septum, Fascicular VT)
|
|
Basic Classification
- VT is at least 3 consecutive ventricular beats
- VT almost always occurs in a structurally damaged heart
- VT by duration
- Non-sustained VT: there are at least 3 ventricular QRS complexes and it lasts < 30s
- Sustained VT: it lasts > 30s
- VT by hemodynamics
- Hemodynamically stable: the patient is circulatorily stabilized
- Usually it is VT with a rate < 160/min.
- Hemodynamically unstable: the patient is circulatorily unstable
- Usually it is VT with a rate > 160/min.
- Not precisely defined what the patient's blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate should be...
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- It is the most common VT
- It occurs in a structurally damaged heart
- A reentry occurs in the scar
- And generates impulses with a rate > 100/min.
- All QRS complexes are monomorphic (identical)
- Therefore, it is referred to as monomorphic
|
|
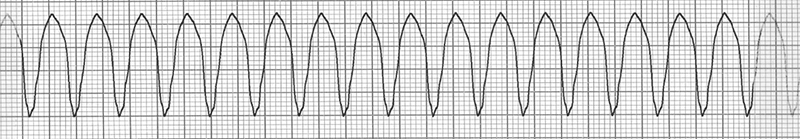
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- Frequency: 170/min.
- Wide QRS complexes (> 0.12s)
- All QRS complexes are identical
- P waves are not visible (hidden in wide QRS)
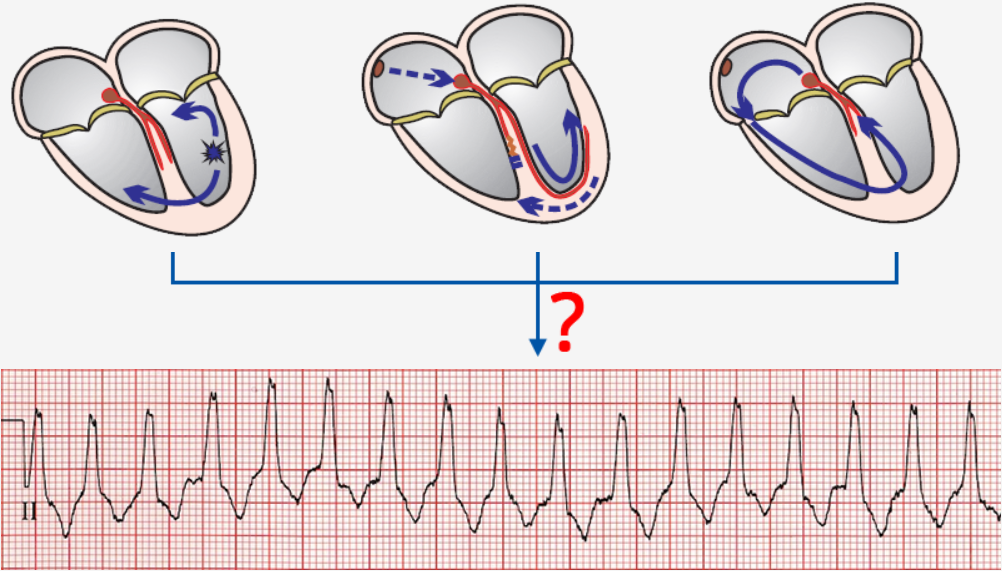
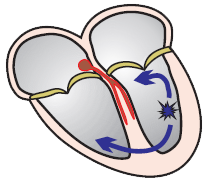
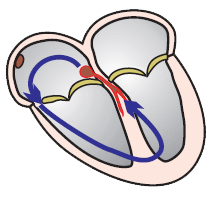
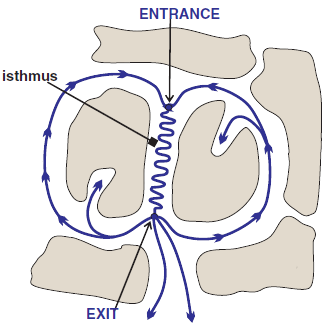
Re-entry and Ventricular Scar
- Monomorphic VT most commonly arises due to re-entry in a scar
- Re-entry in the scar most often has the shape of a figure-eight (8)
- The circling impulse is triggered by a timed
- Entrance
- It is the point of entry for VES into the re-entry
- VES must enter the Entrance outside
- VES then triggers the circling impulse
- Exit site
- It is the point of exit for the impulse from the re-entry
- From the exit site begins the ventricular vector
- which creates the wide QRS (> 0.12s)
- Isthmus is the area of slow conduction in the re-entry
|
|
ECG and Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- Monomorphic VT produces on ECG features of ventricular tachycardia
- VT never has all ECG features present
- Each feature has a certain sensitivity and specificity in the diagnosis of VT
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
- Every VT, including monomorphic VT, is a wide-complex tachycardia (WCT)
- Wide-complex tachycardia is defined as:
- Tachycardia (frequency > 100/min.)
- With wide QRS complexes (≥ 0.12s)
Wide-Complex Tachycardia
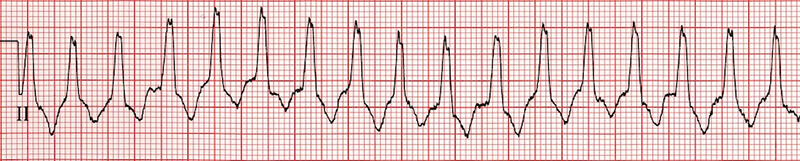
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Wide QRS complexes 0.2s
- Extreme right axis deviation (180° to -90°)
- Brugada sign
- Josephson's sign
- Notch on the descending part of the S wave (II, III, aVF)
- R (Q) wave interval in lead II > 50ms
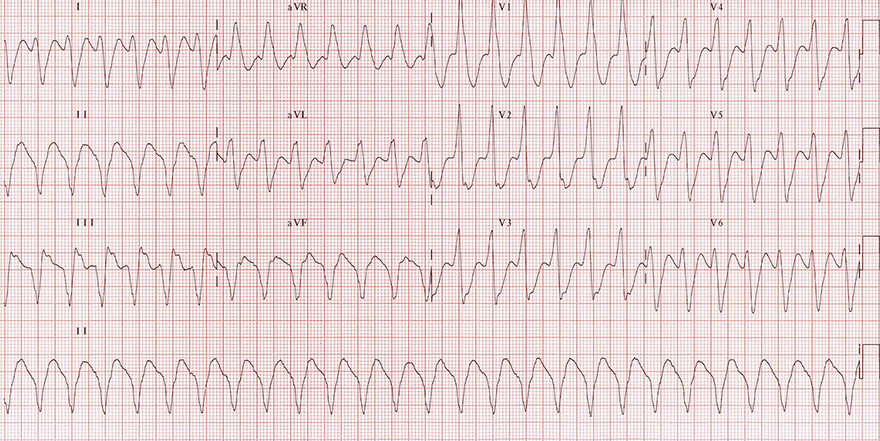
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Wide QRS complexes 0.2s
- Positive precordial concordance (V1-V6)
- Brugada sign
- RS interval > 100ms (aVR, aVL)
- In the second half of the EKG, there is ventricular bigeminy
- R (Q) wave interval in lead II > 50ms
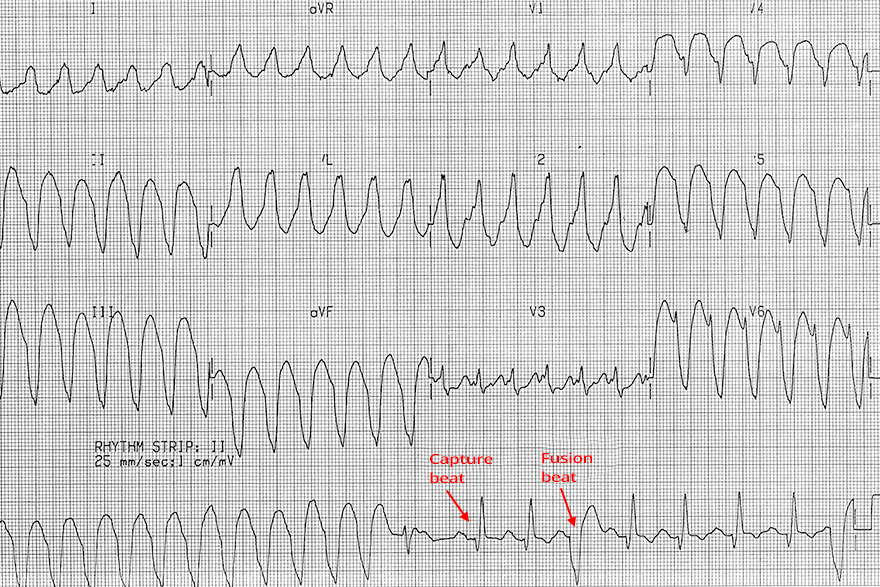
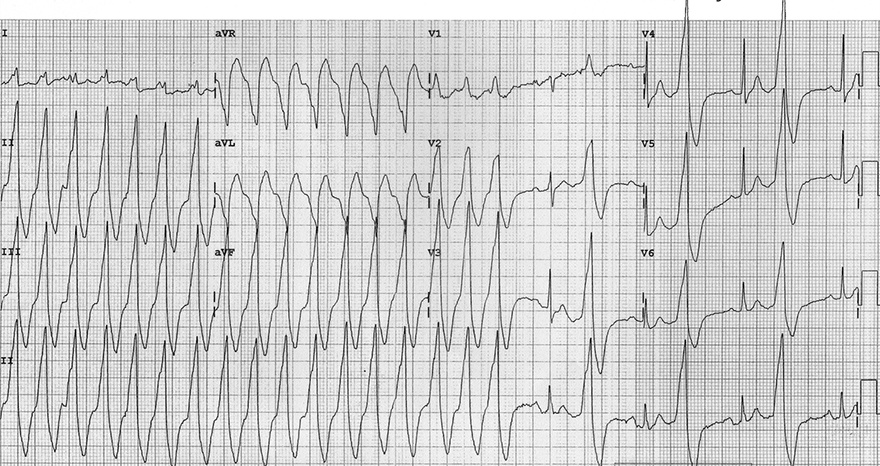
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Wide QRS complexes: 0.2s
- In the second half of the continuous lead (rhythm strip), capture beats and fusion beats are recorded
- The continuous lead was recorded after the 12-lead EKG
- Therefore, the beats are not shown in the precordial and chest leads
- Brugada sign
- R (Q) wave interval in lead II > 50ms
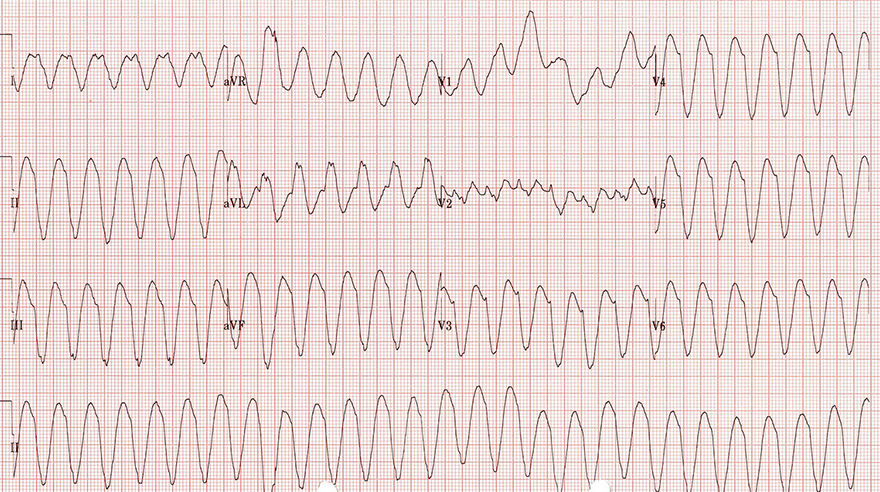
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Frequency 150/min.
- Wide QRS complexes 0.2s
- Josephson's sign
- Notch on the descending part of the S wave (III)
- Extreme right axis deviation (180° to -90°)
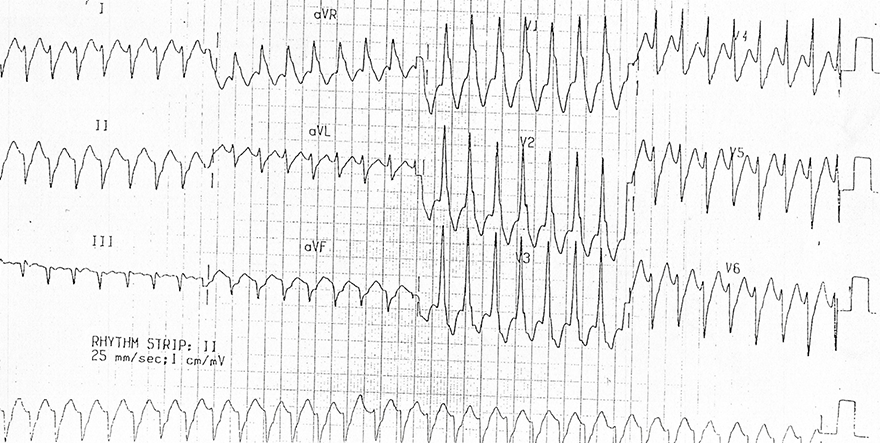
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Frequency 180/min.
- Wide QRS complexes 0.18s
- Extreme right axis deviation (180° to -90°)
- In V1 there is a monophasic R wave
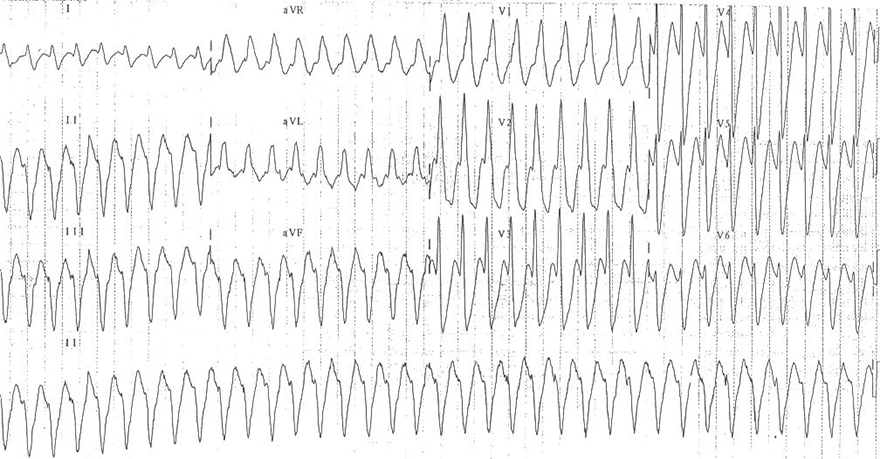
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Frequency 180/min.
- Wide QRS complexes 0.18s
- Extreme right axis deviation (180° to -90°)
- In V1, there is a monophasic R wave
- In V6, there is an rS configuration
- Small r wave and large S wave
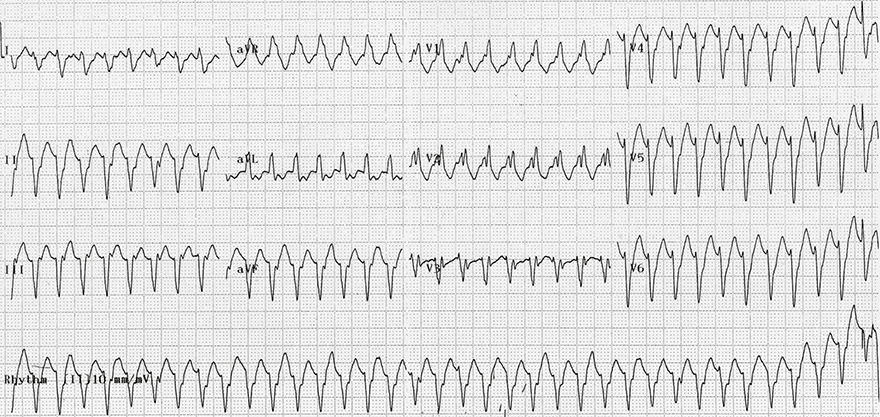
Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia
- All QRS complexes are wide and uniform (with deformed P waves)
- Signs of ventricular tachycardia:
- Frequency 180/min.
- Wide QRS complexes 0.14s
- Extreme right axis deviation (180° to -90°)
- In V1, there is an rsR configuration (right bunny ear is larger), which is a typical image of right bundle branch block (RBBB)
- However, RBBB does not have extreme right axis deviation
- In V1, there is a monophasic R wave
- In V6, there is an rS configuration
- Small r wave and large S wave
- AV dissociation
- Is a key sign of ventricular tachycardia
- P waves deform QRS complexes in the inferior II lead and V1 lead
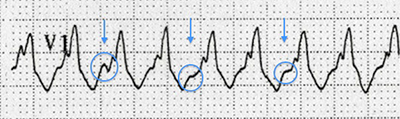
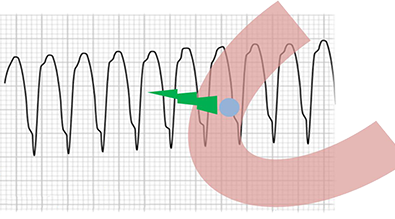
AV Dissociation
- Lead V1 from the previous ECG
- P waves deform QRS complexes
- P waves (blue arrows) and QRS complexes are independent from each other
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers