Home /
Multifocal Atrial Arrhythmia
Multifocal atrial arrhythmia, Wandering pacemaker, Wandering atrial pacemaker
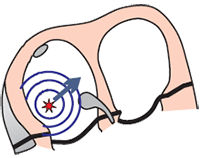
Sinus Rhythm
- Heart rhythm is always determined by the site (sites)
- We recognize 3 basic heart rhythms
- Sinus rhythm is the physiological heart rhythm
- Because the SA node generates impulses with the highest frequency
- The SA node is referred to as the primary pacemaker (pace setter)
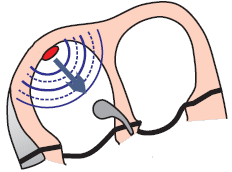
Automaticity of the Atria
- Every part of the conduction system and working myocardium
- Impulses are generated with the highest frequency by:
- Increased parasympathetic tone (vagus nerve) decreases the automaticity of the SA node
- Foci in the atria are activated and begin to generate impulses
- in place of the SA node (or together with the SA node)
- Increased parasympathetic tone is seen in
- Athletes
- Young individuals
Physiological P Wave
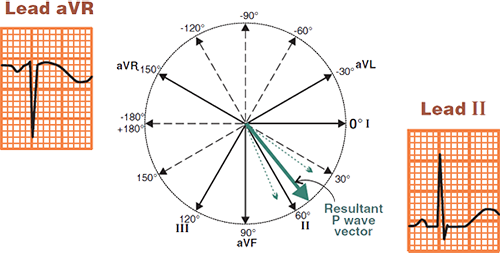
- Atrial vector originates in the SA node and directs
- AWAY from the aVR lead
- TOWARDS the II lead
- Physiological P wave is
- Positive in the II lead
- Negative in the aVR lead
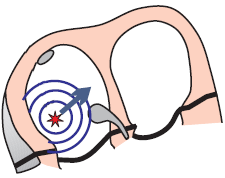
- In the case of wandering pacemaker
- P waves of varying shapes alternate
- Each P wave has a different vector (from a different focus)

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Heart rate: 70/min.
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular (varying RR intervals)
- The ECG shows 4 P waves of different shapes
- Because each ectopic focus generates a distinct vector, which has a different direction
- PQ interval varies
- Because each ectopic focus is at a different distance from the AV node
ECG and Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency < 100/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- 3 P waves of different shapes alternate (usually 3 waves, but sometimes 4)
- Each ectopic focus generates a different P wave
- PQ interval varies
- Each ectopic focus is at a different distance from the AV node

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency: 40/min.
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular (various RR intervals)
- The ECG shows 3 P waves of different shapes
- Because each ectopic focus generates a distinct vector, which has a different direction
- PQ interval varies
Frequency Calculation (6-Second Rule)
- If the heart rhythm is irregularly irregular:
- The frequency is calculated using the 6-second rule
- This is the average frequency of QRS complexes over 6 seconds (30 squares)
- Frequency = number of QRS complexes in 6s x 10

Wandering Pacemaker and Frequency 40/min.
- The number of QRS complexes in 6s (30 squares) is 4
- 4 x 10 = 40/min.
Wandering Pacemaker and Bigeminal Rhythm
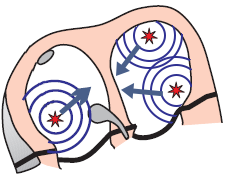

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm (Wandering Pacemaker)
- There are 3 ectopic foci in the atria (usually 3)
- They generate impulses independently of each other with f: < 100/min.
- The SA node may also alternately generate impulses
- The mechanism of the foci is automaticity
- 3 P waves of different shapes are present (each focus generates a different P wave)
- The heart rate is irregularly irregular (RR intervals of varying lengths)

Atrial Bigeminy Rhythm
- There is 1 ectopic focus in the atria
- which generates impulses alternately with the SA node
- The resulting frequency is < 100/min.
- The mechanism of the focus is increased automaticity
- 2 P waves of different shapes are present
- The heart rate is regularly irregular
- Atrial bigeminy rhythm is

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency: 80/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular (even though it may seem regular)

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency 100/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes (one P wave is hidden in the T wave - black arrow)
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular

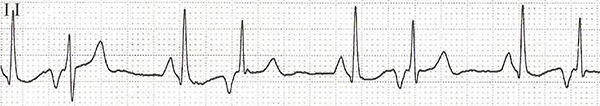
Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency 80/min.
- 3 P waves of different shapes
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
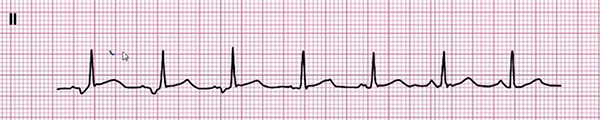
Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency: 90/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
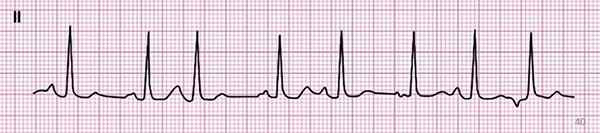
Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency: 80/min.
- 3 P waves of different shapes (the 3rd P wave is hidden in the T wave)
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
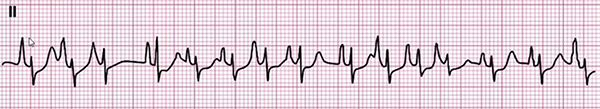
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 125/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
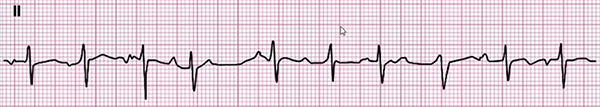
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 130/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
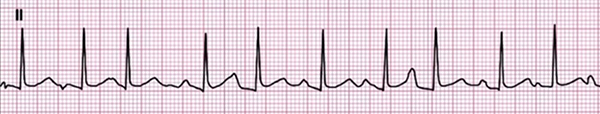
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 115/min.
- 4 P waves of different shapes (some P waves are hidden in the T wave)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
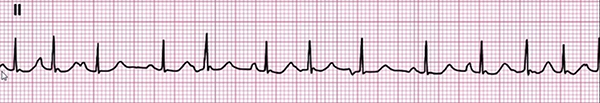
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 140/min.
- 3 P waves of different shapes (some P waves are hidden in the T wave)
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
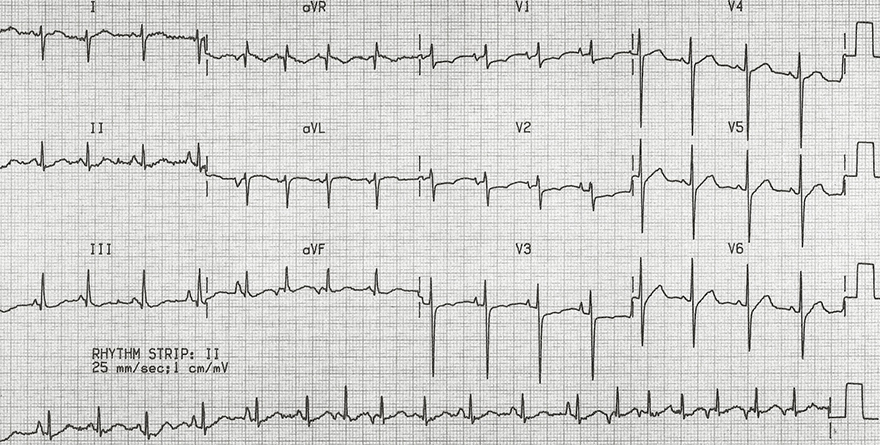
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 120/min.
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- 3 different P waves (most visible in continuous lead II)
- Right heart overload
- The patient had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
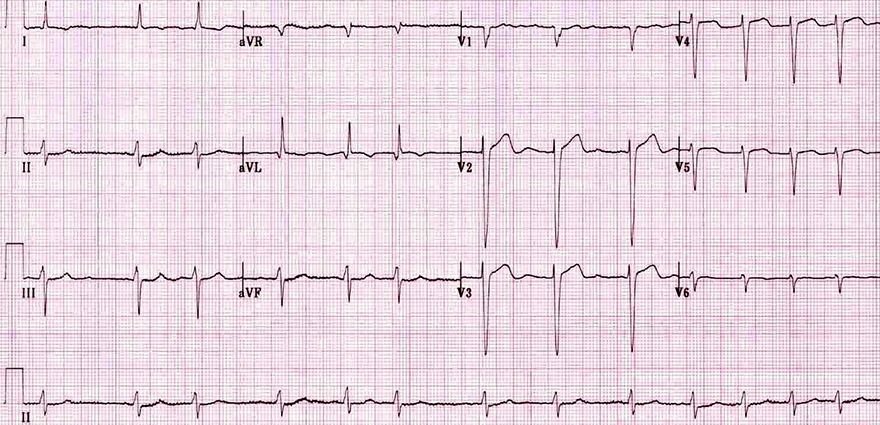
Atrial Fibrillation
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers