Home /
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) - ECG
Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT), Chaotic atrial tachycardia
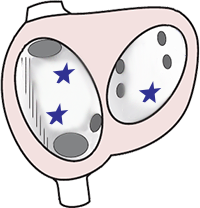
Ectopic Focus
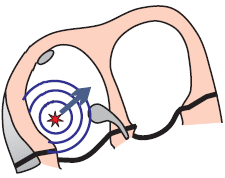
- Most commonly occurs in a structurally altered atrium
- Never located in the SA node
- Size is up to 5mm
- Generates impulses at a frequency of 130-250/min.
- The focus may start generating impulses through 3 mechanisms:
- Increased automaticity
- Trigger activity
- Micro-reentry
- Focal Atrial Tachycardia
- Has 1 focus in the atrium (mechanism is not reentry)
- Intra-Atrial Reentry Tachycardia
- Has 1 focus in the atrium (with a reentry mechanism)
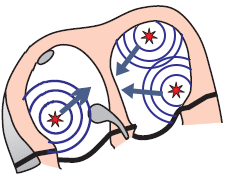
3 Foci and Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Physiological P Wave
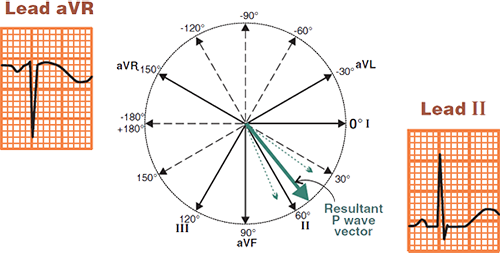
- The atrial vector originates in the SA node and directs
- Away from the aVR lead
- Towards the II lead
- The physiological P wave is
- Positive in lead II
- Negative in lead aVR
- In Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT), the P wave does not have a physiological shape
- Because the vector does not originate from the SA node

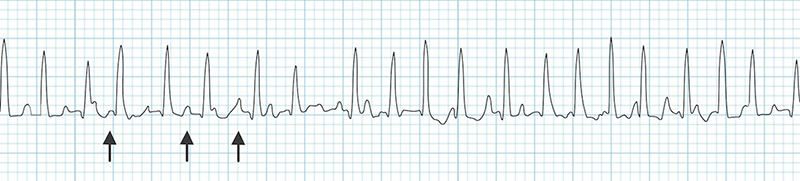
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
- The ECG shows 3 P waves of different shapes
- Because each ectopic focus creates its own vector
- Which has a different direction (a different P wave)
ECG and Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency 100-250/min.
- 3 foci generate impulses independently, the common frequency of impulses is 100-250/min.
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 0.12s)
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular
- 3 P waves of different shapes alternate
- Each ectopic focus creates a different P wave
- PQ interval varies
- Each ectopic focus is at a different distance from the AV node

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT)
- Frequency: 280/min.
- 3 P waves of different shapes alternate
- PQ interval varies
Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- The mechanism of origin is the same as in MAT, the only difference is in frequency

Multifocal Atrial Rhythm
- Frequency 40/min.
- If the frequency were > 100/min., it would be MAT
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular
- 3 different P waves
Heart Rate Calculation (6-Second Rule)
- If the heart rate is irregularly irregular:
- To calculate the heart rate, use the 6-second rule
- This is the average number of QRS complexes over 6 seconds (30 squares)
- Heart Rate = Number of QRS in 6s x 10
Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Rate 130/min.
- Atrial Fibrillation
- No P waves are present
- Heart rate is irregularly irregular
- The number of QRS complexes in 6s (30 squares) is 13
- 13 x 10 = 130/min.
Differential Diagnosis of Atrial Fibrillation
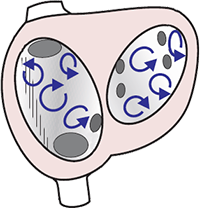
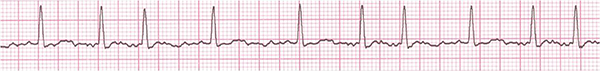
Atrial Fibrillation
- Atrial Fibrillation
- In the atria, there are many micro-reentry circuits
- These circuits generate impulses independently with a frequency of 350-600/min.
- Heart rhythm is irregularly irregular (RR intervals vary in length)
- Fibrillatory f waves (deformed baseline, P waves are absent)
- P waves cannot be differentiated

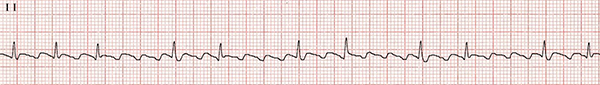
Atrial Flutter with Variable Conduction (2:1 and 4:1)
- Atrial Flutter
- There is one macro-reentry circuit throughout the entire right atrium
- The impulse circulates with a frequency of 300/min.
- Instead of P waves, the ECG shows Flutter (F) waves (sawtooth pattern) with a frequency of 300/min.
- The heart rhythm is regularly irregular
- One RR interval has a 2:1 conduction ratio
- The next RR interval has a 4:1 conduction ratio
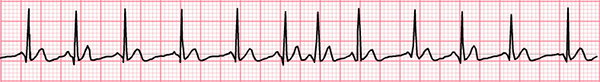
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- There are 3 ectopic foci in the atria generating impulses independently
- 3 different P waves are seen on the ECG
- The ECG shows 3 P waves of different shapes (each focus generates its own P wave)
- The heart rhythm is irregularly irregular (similar to atrial fibrillation)
- This is because the ectopic foci generate impulses (P waves) independently of each other
- However, each P wave is followed by a QRS complex

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 120/min.
- The heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- 3 different P waves (best seen in the continuous II lead)
- Right heart overload
- The patient had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Cor pulmonale refers to hypertrophic remodeling of the right heart due to pulmonary hypertension

Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
- Frequency: 110/min.
- The heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- 3 different P waves (best seen in the continuous II lead)
- Right heart overload
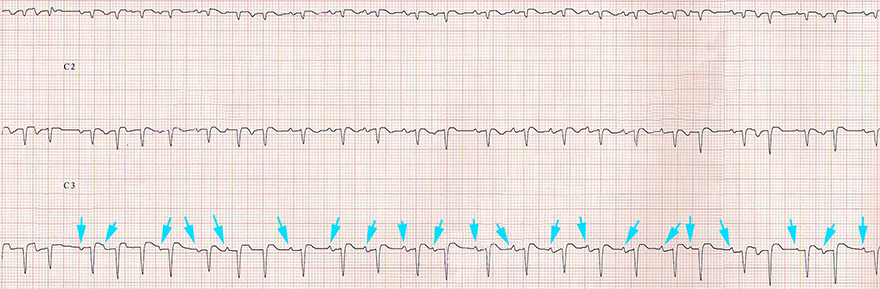
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
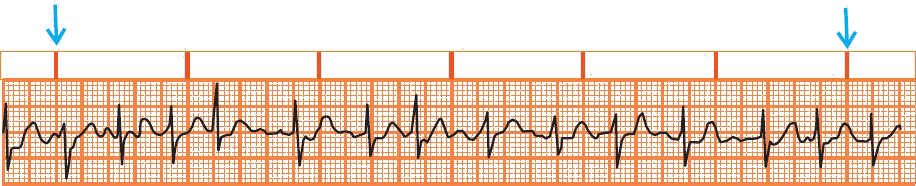
- This ECG shows only 3 leads V1-V3 (marked as C1-C3)
- Frequency: 140/min.
- The heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- 3 different P waves (blue arrows)
- The patient had chronic obstructive pulmonary disease

Atrial Fibrillation
- Frequency: 90/min.
- The heart rhythm is irregularly irregular
- P waves cannot be differentiated
- This is atrial fibrillation (which is often confused with MPT)
- Atrial fibrillation never has P waves
Sources
- ECG from Basics to Essentials Step by Step
- litfl.com
- ecgwaves.com
- metealpaslan.com
- medmastery.com
- uptodate.com
- ecgpedia.org
- wikipedia.org
- Strong Medicine
- Understanding Pacemakers



































