
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Myocardial infarction and ST elevation in aVR (forgotten lead)





Acute Proximal LAD Occlusion

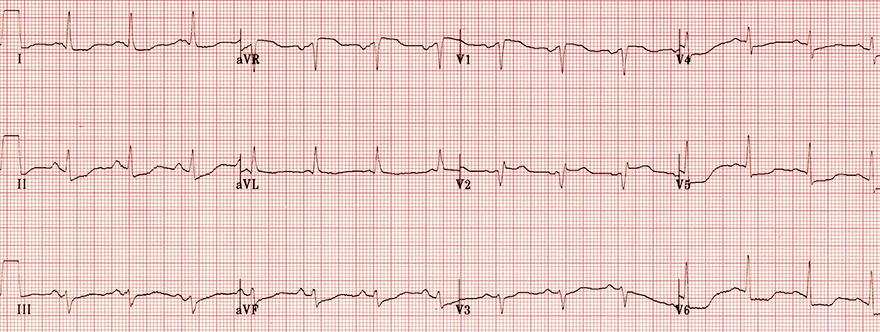
Acute Proximal LAD Occlusion

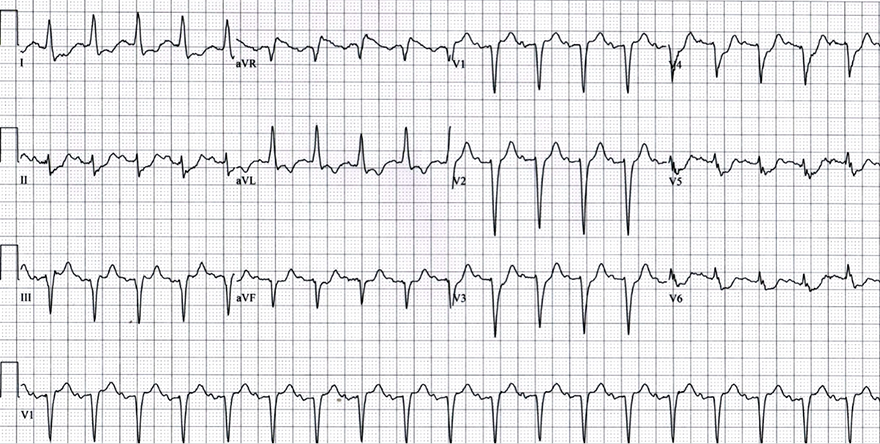
Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery

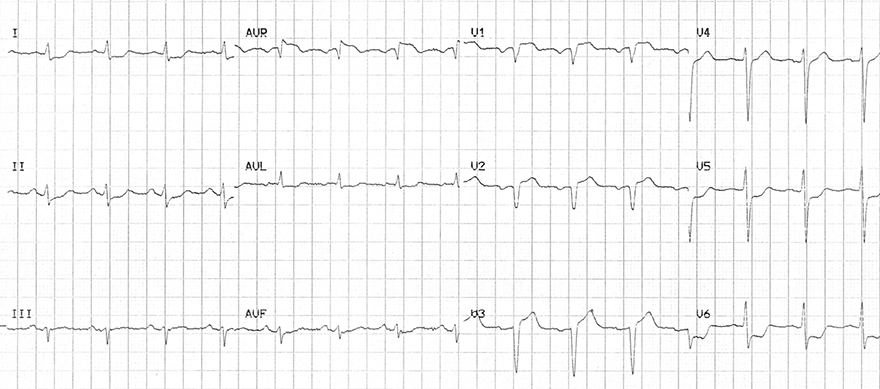
Triple Vessel Disease


Stenosis of the Left Main Coronary Artery

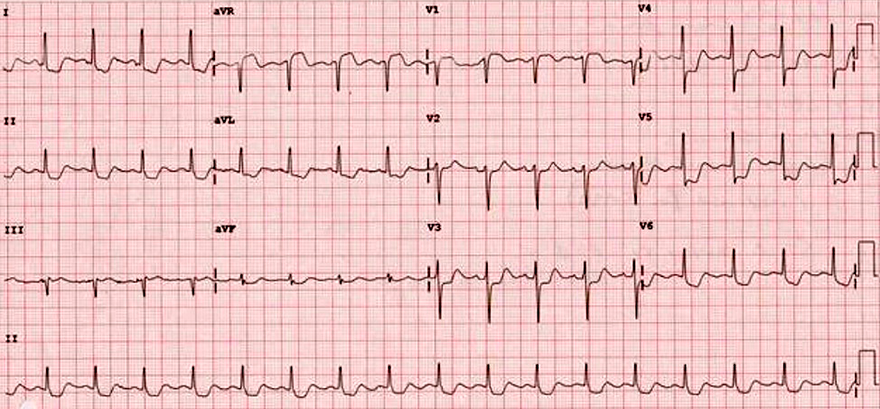
Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery


Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery
Sources
Home /
Myocardial infarction and ST elevation in aVR (forgotten lead)
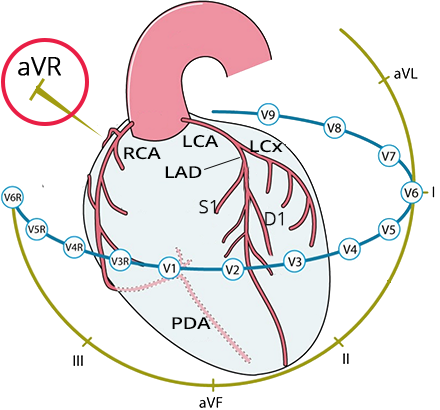
Lead aVR
|

|
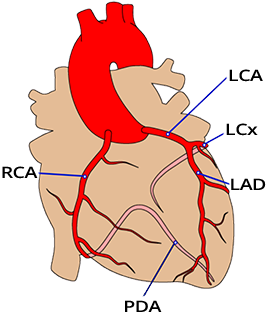
3 Major Arteries
|

|
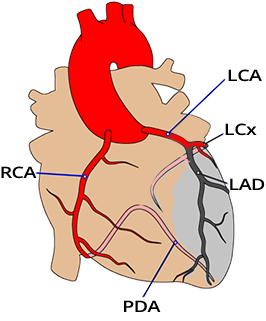
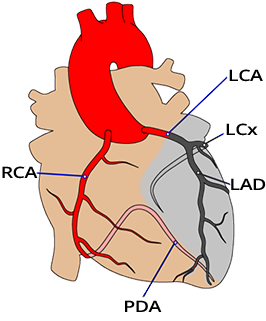
Proximal Occlusion of the LAD
|

|
Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|

|
Stenosis of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|
 |
Three-Vessel Disease
|
 |
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
|
 |

|
Acute Proximal LAD Occlusion
|

|

|
Acute Proximal LAD Occlusion
|

|

|
Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|

|

|
Triple Vessel Disease
|

|

|
Stenosis of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|

|

|
Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|

|

|
Acute Occlusion of the Left Main Coronary Artery
|

|
Sources