


Sources
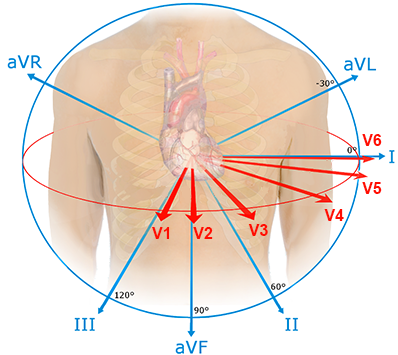
Standard 12-lead ECG
|

|
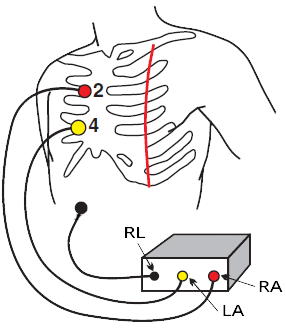
Modified Chest Lead
|

|
5-Electrode System
|

|
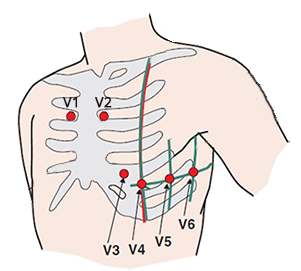
Leads V1 and V2 in the 6th Intercostal Space
|

|
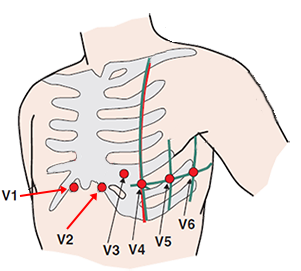
Leads V1 and V2 in the 2nd Intercostal Space
|

|
Lewis Lead
|

|
Esophageal ECG
|

|
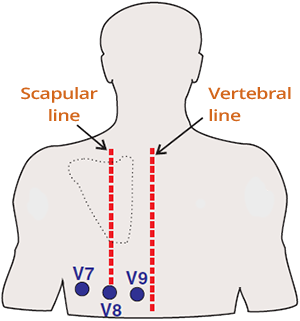
Posterior Leads (V7-V9)
|

|
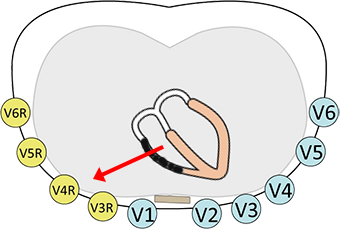
Right-Sided Leads (V4R-V6R)
|

|
Sources