
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, NSTEMI Heart attack, Unstable angina pectoris
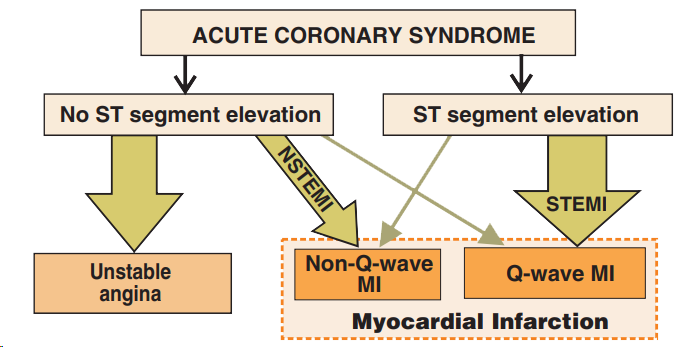
Acute Coronary Syndrome
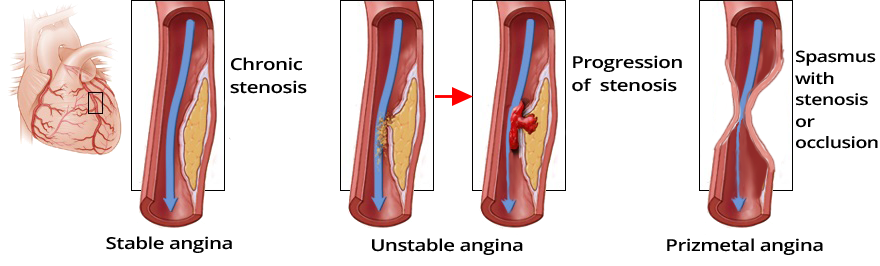
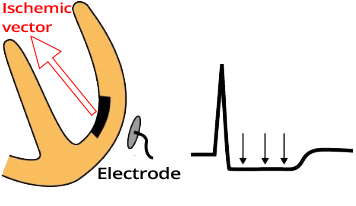
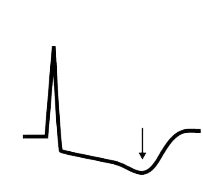

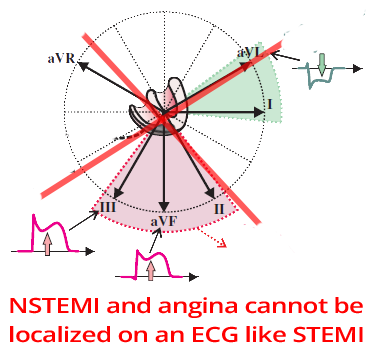
Acute Coronary Syndrome Without ST Elevation
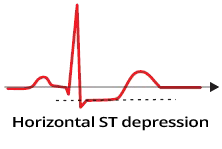

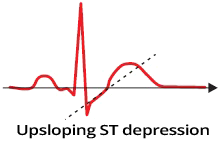
ST Depression and Ischemia
Flat Ascending ST Depression

Steep Ascending ST Depression


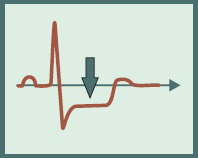
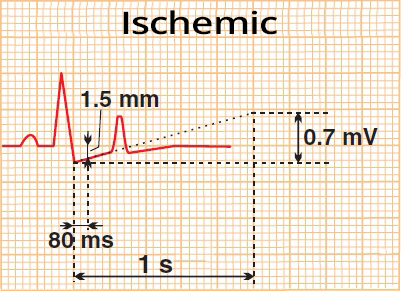
ST Depression

Negative T Waves
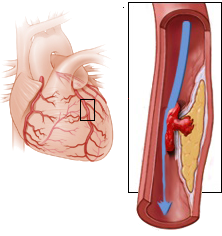

Unstable Angina Pectoris


Unstable Angina Pectoris
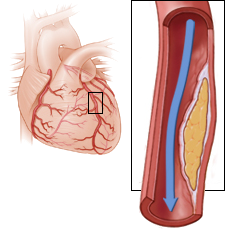

Ischemia Post-Ergometry

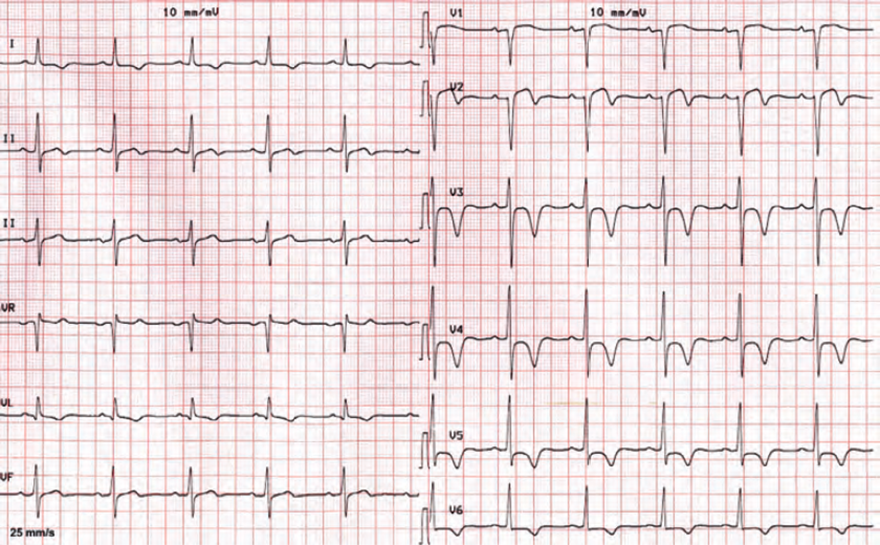
Unstable Angina Pectoris


Unstable Angina Pectoris

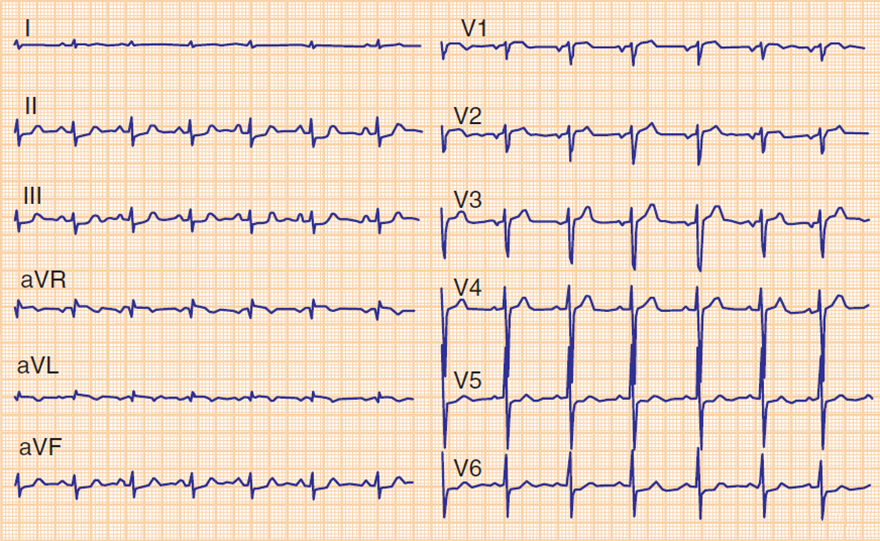
Pseudonormalization - Hyperacute STEMI
Sources
Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, NSTEMI Heart attack, Unstable angina pectoris

Acute Coronary Syndrome


|

|

|
Acute Coronary Syndrome Without ST Elevation

|

|

|
ST Depression and Ischemia

Flat Ascending ST Depression
|

Steep Ascending ST Depression
|
Negative T Waves and ACS Without ST Elevation
|
 
|
|

|

|
ST Depression
|

|
Negative T Waves
|

|
Unstable Angina Pectoris
|

|

|
Unstable Angina Pectoris
|

|

|
Ischemia Post-Ergometry
|

|

|
Unstable Angina Pectoris
|

|

|
Unstable Angina Pectoris
|

|

|
Pseudonormalization - Hyperacute STEMI
|

|
Sources