
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

| SA Node | 60-100/min. |
| Internodal Pathways | 55-60/min. |
| AV Node | 45-50/min. |
| His Bundle | 40-45/min. |
| Tawara Branches | 40-45/min. |
| Purkinje Fibers | 35-40/min. |
| Myocardium | 30-35/min. |
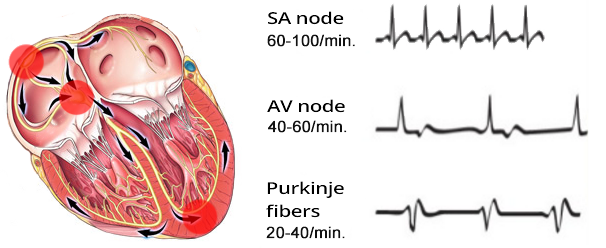
3 Main Pacemakers

Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the SA Node)
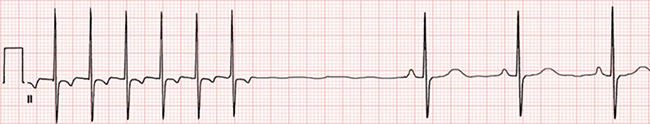
Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the SA Node)
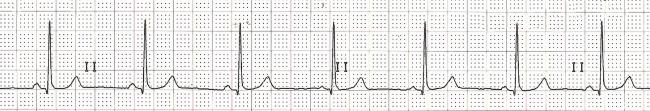
Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the AV Node)

Ventricular Rhythm
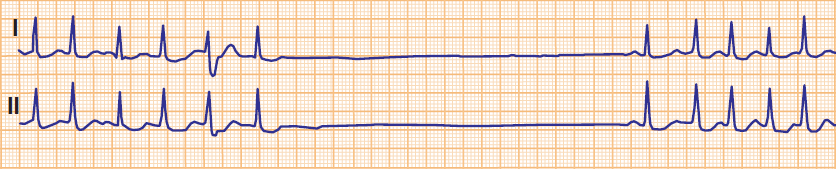
Sick Sinus Syndrome and Overdrive Suppression
Sources
Pacemaker
|

|
| SA Node | 60-100/min. |
| Internodal Pathways | 55-60/min. |
| AV Node | 45-50/min. |
| His Bundle | 40-45/min. |
| Tawara Branches | 40-45/min. |
| Purkinje Fibers | 35-40/min. |
| Myocardium | 30-35/min. |

3 Main Pacemakers

Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the SA Node)

Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the SA Node)

Overdrive Suppression (Suppression of the AV Node)

Ventricular Rhythm

Sick Sinus Syndrome and Overdrive Suppression
Sources