
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
P cardiale, P biatriale, Biatrial enlargement (hypertrophy)
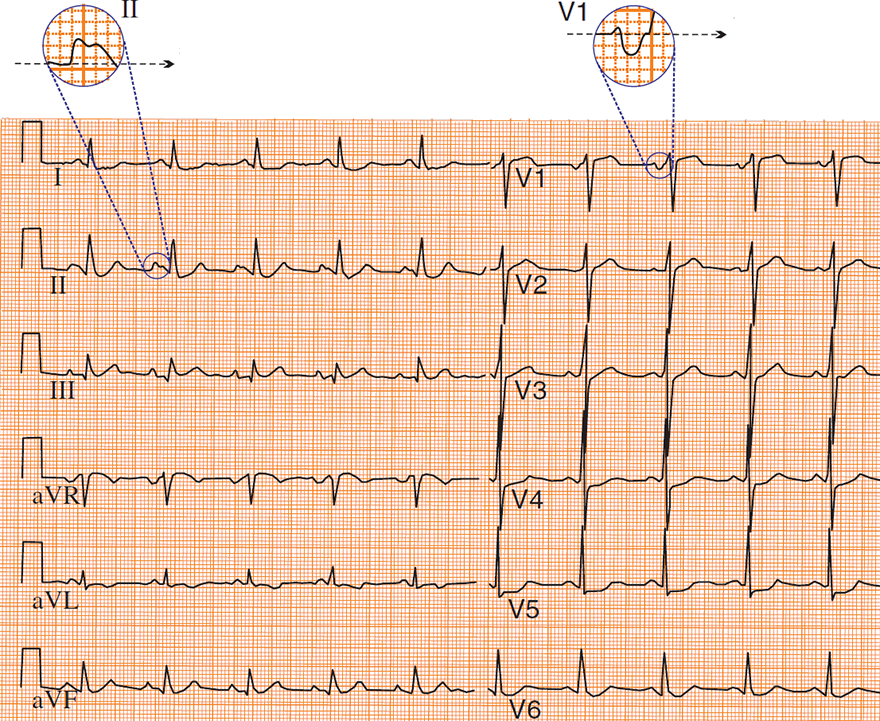
P Mitrale
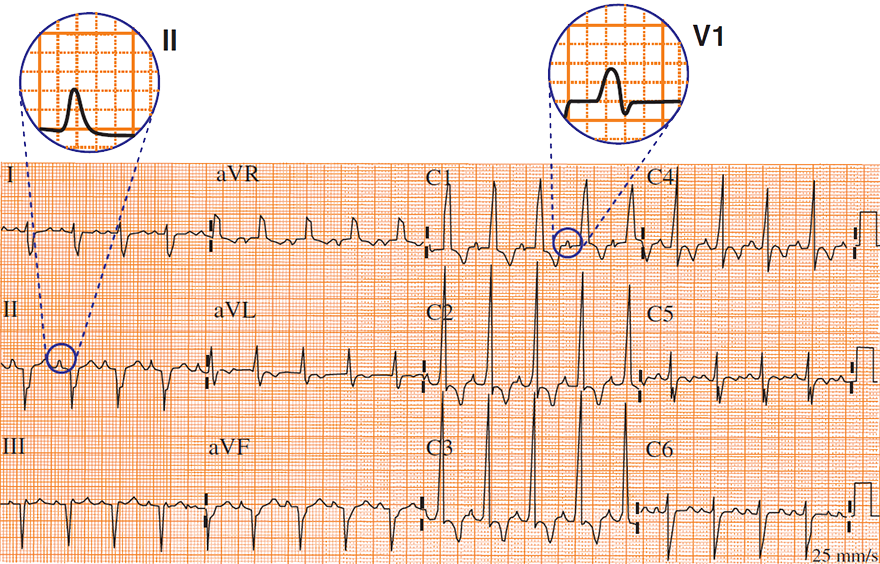
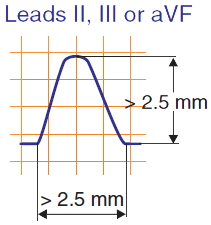
P Pulmonale
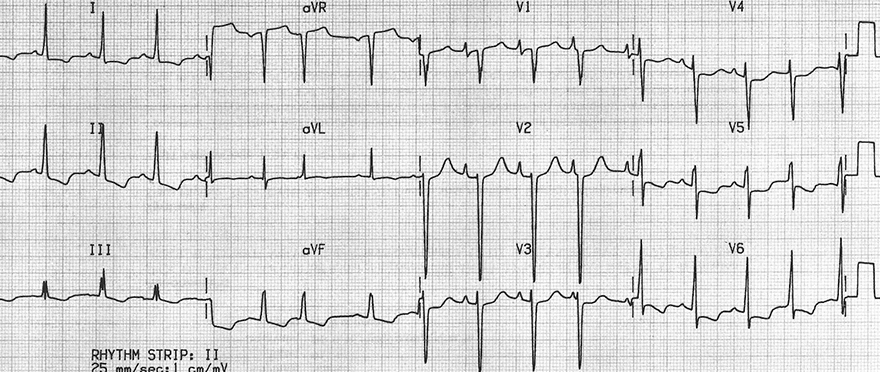
Biatrial Hypertrophy
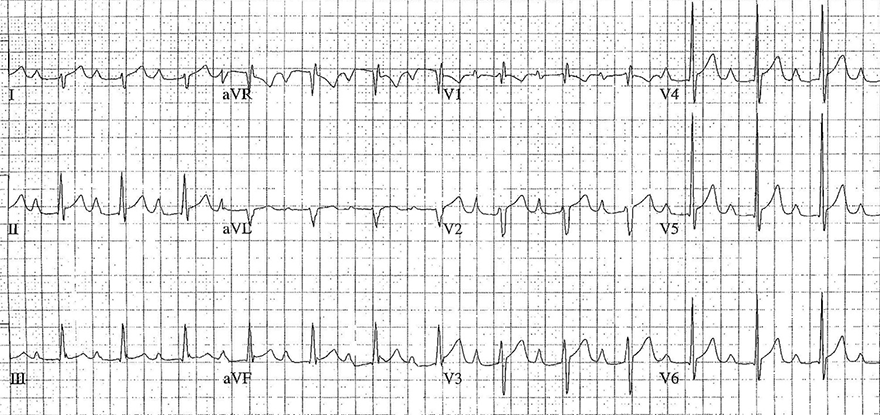
Biatrial Hypertrophy
Sources
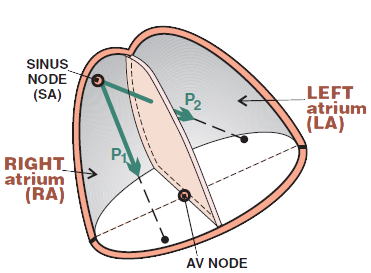
Physiological P Wave
|

|
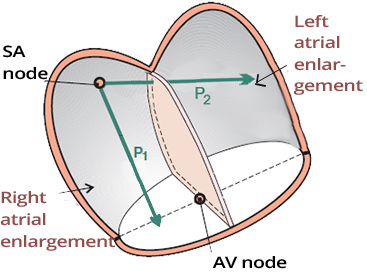
Biatrial Hypertrophy
|

|
ECG and Biatrial Hypertrophy
|


|

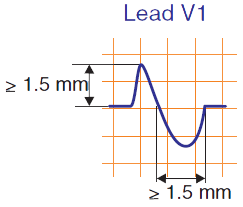
P Mitrale

P Pulmonale

Biatrial Hypertrophy

Biatrial Hypertrophy
Sources