
|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |

|
ECGbook.com Making Medical Education Free for All |
Upload ECG for Interpretation |
Home /
P sinistrocardiale, Left atrial enlargement, Left atrial abnormality, Delay of left atrial activation, Left atrial dilatation, Left atrial distention, Left atrial overload


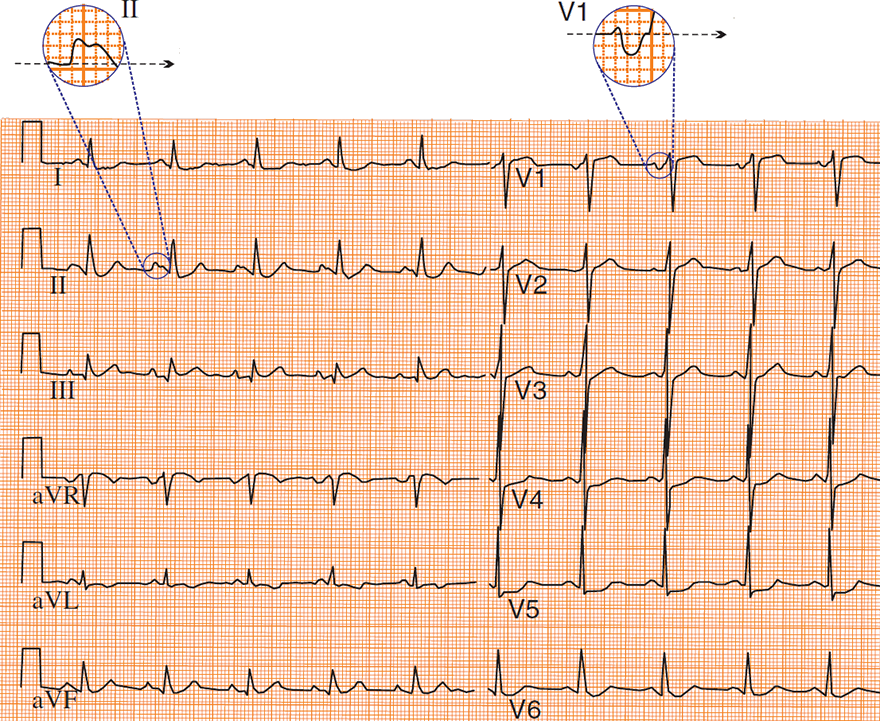
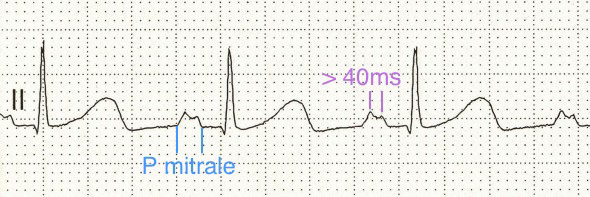
P Mitrale and Lead II
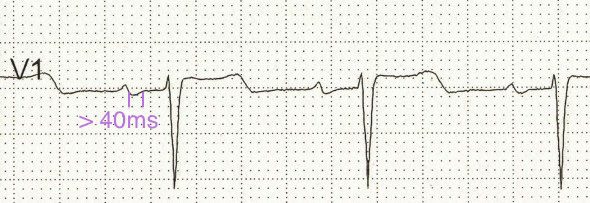
P Mitrale and Lead V1
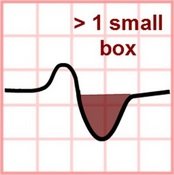
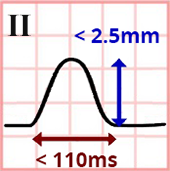

Normal P Wave


P Mitrale
P Mitrale
P Mitrale
P Mitrale
P Mitrale
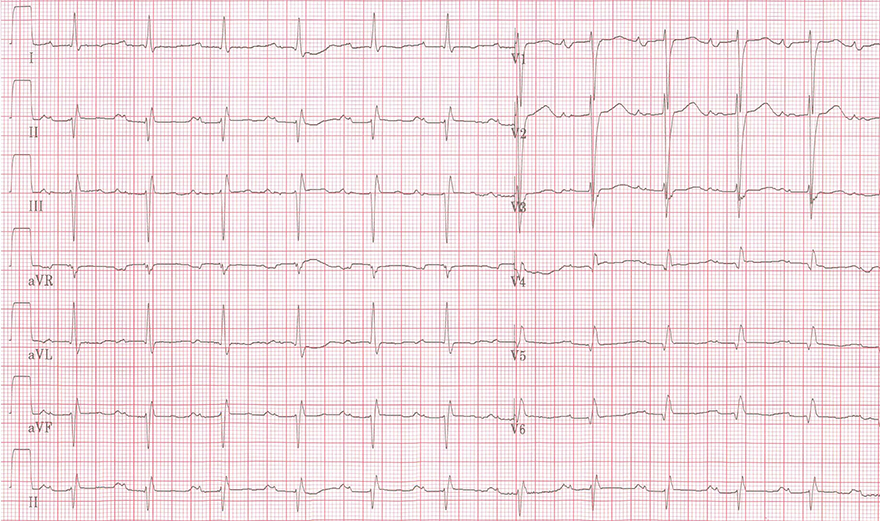
P Mitrale
Sources
Home /
P sinistrocardiale, Left atrial enlargement, Left atrial abnormality, Delay of left atrial activation, Left atrial dilatation, Left atrial distention, Left atrial overload
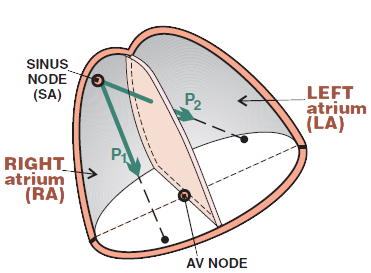
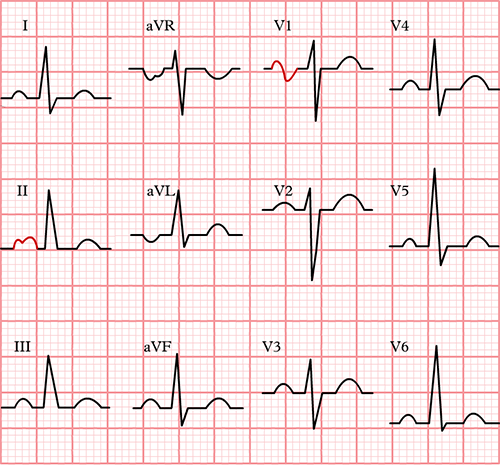
Physiological P Wave
|

|
|

|
P Mitrale and Atrial Vector
|

|

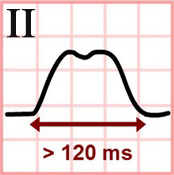
P Mitrale and Lead II

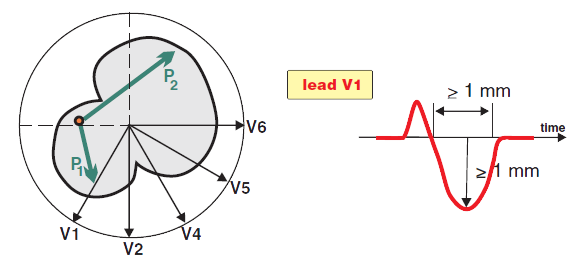
P Mitrale and Lead V1
ECG and P Mitrale
|


|

|

|

|
Normal P Wave

|

|

|
P Mitrale

P Mitrale

P Mitrale

P Mitrale

P Mitrale

P Mitrale
Sources